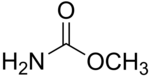
Methyl carbamate
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methyl carbamate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.037 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H5NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 75 g/mol |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.136 (56 °C) |
| Melting point | 52 °C (126 °F; 325 K) |
| Boiling point | 177 °C (351 °F; 450 K) |
| 20 g/L[1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Methyl carbamate (also called methylurethane, or urethylane) is an organic compound and the simplest ester of carbamic acid (H2NCO2H). It is a colourless solid.[2]
Methyl carbamate is prepared by the reaction of methanol and urea:
- CO(NH2)2 + CH3OH → CH3OC(O)NH2 + NH3
It also forms in the reaction of ammonia with methyl chloroformate or dimethyl carbonate.
Safety and occurrence
[edit]Unlike its close relative ethyl carbamate it is not mutagenic in Salmonella (it tested negative in the Ames test), but it is mutagenic in Drosophila.[3] Experimental evidence does show that it is a carcinogen in rats, and not carcinogenic in mice. The compound is "known to the state of California to cause cancer" per Proposition 65.[4]
Production, use, and exposure
[edit]The compound was detected in wines preserved with dimethyl dicarbonate.[5]
Methyl carbamate is used primarily in the textile and polymer industries as a reactive intermediate. In the textile industry, it is used in the manufacture of dimethylol methyl carbamate-based resins that are applied on polyester cotton blend fabrics as durable-press finishes. The treated fabrics have good crease-angle retention, resist acid souring in commercial laundries, do not retain chlorine, and have flame-retardant properties. Methyl carbamate also is used in the manufacture of pharmaceuticals, insecticides, and urethane.[6]
N-Methyl carbamates are widely used as insecticides.[7] They have anticholinesterase activity without a cumulative effect.
See also
[edit]- Carbamate
- Ethyl carbamate (urethane)
References
[edit]- ^ "Alfa Aesar Methyl carbamate". Alfa Aesar. Alfa Aesar. Retrieved 4 October 2021.
- ^ Jäger, Peter; Rentzea, Costin N.; Kieczka, Heinz (2012). "Carbamates and Carbamoyl Chlorides". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a05_051. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Foureman P, Mason JM, Valencia R, Zimmering S (1994). "Chemical mutagenesis testing in Drosophila. IX. Results of 50 coded compounds tested for the National Toxicology Program". Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 23 (1): 51–63. PMID 8125083.
- ^ OEHHA Archived 2006-05-12 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Inchem.org
- ^ National Toxocology Program
- ^ National Pesticide Information Center at Oregon State University
