Markhor
| Markhor | |
|---|---|

| |
| Male markhor in captivity at the Augsburg Zoo | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Family: | Bovidae |
| Subfamily: | Caprinae |
| Tribe: | Caprini |
| Genus: | Capra |
| Species: | C. falconeri[1]
|
| Binomial name | |
| Capra falconeri[1] (Wagner, 1839)
| |
| Subspecies | |
|
See text | |
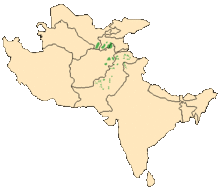
| |
| Distribution of the markhor | |
The markhor (Capra falconeri) /ˈmɑːrkɔːr/ is a large wild Capra (goat) species native to South Asia and Central Asia, mainly within Pakistan, the Karakoram range, parts of Afghanistan, and the Himalayas. It is listed on the IUCN Red List as Near Threatened since 2015.[2]
The markhor is the national animal of Pakistan, where it is also known as the screw-horn or screw-horned goat.[3] The word mārkhor (مارخور), meaning "snake-eater", comes from both Pashto and classical Persian languages, referencing the ancient belief that the markhor would actively kill and consume snakes.[4] This regional myth is believed to stem from the "snake-like" form of the male markhor's horns, twisting and curling like a snake, possibly leading ancient peoples to associate them with snakes.
On 2 May 2024, the United Nations General Assembly declared 24 May as the International Day of the Markhor.[5][6]
Description
[edit]Markhor stand 65 to 115 centimetres (26 to 45 in) at the shoulder, are 132 to 186 centimetres (52 to 73 in) long and weigh from 32 to 110 kilograms (71 to 243 lb).[7] They have the highest maximum shoulder height among the species in the genus Capra, but is surpassed in length and weight by the Siberian ibex.[8] The coat is of a grizzled, light brown to black colour, and is smooth and short in summer, while growing longer and thicker in winter. The fur of the lower legs is black and white. Markhor are sexually dimorphic, with males having longer hair on the chin, throat, chest and shanks.[7] Females are redder in colour, with shorter hair, a short black beard, and are maneless.[9] Both sexes have tightly curled, corkscrew-like horns, which close together at the head, but spread upwards toward the tips. The horns of males can grow up to 160 cm (63 in) long, and up to 25 cm (10 in) in females.[7] The males have a pungent smell, which surpasses that of the domestic goat.[10]
Behaviour and ecology
[edit]
Markhor are adapted to mountainous terrain, and can be found between 600 and 3,600 m (2,000 and 11,800 ft) in elevation. They typically inhabit shrub forests made up primarily of oaks (Quercus ilex), pines (Pinus gerardiana), and junipers (Juniperus macropoda).[2] They are diurnal, and are mainly active in the early morning and late afternoon. Their diets shift seasonally: in the spring and summer periods they graze, but turn to browsing in winter, sometimes standing on their hind legs to reach high branches. The mating season is during winter, when the males fight each other by lunging, locking of horns, and attempting to push each other off balance. The gestation period lasts 135–170 days, and usually results in the birth of one or two kids, and occasionally three. Markhor live in herds, usually numbering nine animals, composed of adult females and their young. Adult males are largely solitary. Adult females and kids comprise most of the markhor population, with adult females making up 32% and kids making up 31%. Adult males comprise 19% of the population, while subadults (males aged 2–3 years) make up 12%, and yearlings (females aged 12–24 months) 9%.[11] Their alarm call closely resembles the bleating of domestic goats.[7] Early in the season the males and females may be found together on the open grassy patches and clear slopes among the forest. During the summer, the males remain in the forest, while the females generally climb to the highest rocky ridges above.[9] In the spring, the females stay closer to cliffs in areas with more rock coverage to provide protection for their offspring. The males stay in higher elevated areas with more access to vegetation for foraging so as to improve their body's condition.[12]
Predators
[edit]Eurasian lynx (Lynx lynx), snow leopard (Panthera uncia), Himalayan wolf (Canis lupus chanco) and brown bear (Ursus arctos) are the main predators of the markhor.[11][13] The golden eagle (Aquila chrysaetos) has been reported to prey upon young markhor. The markhor possess keen eyesight and a strong sense of smell to detect nearby predators. Markhor are very aware of their surroundings and on high alert; in exposed areas, they are quick to spot and flee from predators.[14]
Taxonomy
[edit]

Aegoceros (Capra) Falconeri was the scientific name proposed by Johann Andreas Wagner in 1839 based on a female specimen from the Indian Himalayas.[15]
Multiple subspecies have been recognized, often based on horn configuration, but it has been shown that this can vary greatly even within the same population confined to one mountain range.[16]
- Astor markhor or Astore markhor (C. f. falconeri)
- Bukharan markhor (C. f. heptneri)
- Kabul markhor (C. f. megaceros)
- Kashmir markhor (C. f. cashmiriensis)
- Sulaiman markhor (C. f. jerdoni)
Astor markhor
[edit]The Astor markhor has large, flat horns, branching widely and then going up nearly straight with only a half turn. It is synonymous with Capra falconeri cashmiriensis or Pir Panjal markhor, which has heavy, flat horns, twisted like a corkscrew.[17] The Astor markhor also has a tendency to sexually segregate outside the mating season because of multiple different mechanisms. The females are usually confined to cliffs with less forage coverage, while the males live in areas with a lot more forage coverage. [18]
Within Afghanistan, the Astor markhor is limited to the east in the high and mountainous monsoon forests of Laghman and Nuristan. In India, this subspecies is restricted to a portion of the Pir Panjal range in southwestern Jammu and Kashmir. Throughout this range, Astor markhor populations are scattered, starting east of the Banihal Pass (50 km from the Chenab River) on the Jammu–Srinagar highway westward to the disputed border with Pakistan. Recent surveys indicate it still occurs in catchments of the Limber and Lachipora Rivers in the Jhelum Valley Forest Division, and around Shupiyan to the south of Srinagar. In Pakistan, the Astor markhor there is restricted to the Indus and its tributaries, as well as to the Kunar (Chitral) River and its tributaries. Along the Indus, it inhabits both banks from Jalkot (Kohistan District) upstream to near the Tungas village (Baltistan), with Gakuch being its western limit up the Gilgit River, Chalt up the Hunza River, and the Parishing Valley up the Astore River. It has been said to occur on the right side of the Yasin Valley (Gilgit District), though this is unconfirmed. The flare-horned markhor is also found around Chitral and the border areas with Afghanistan, where it inhabits a number of valleys along the Kunar River (Chitral District), from Arandu on the west bank and Drosh on the east bank, up to Shoghor along the Lutkho River, and as far as Barenis along the Mastuj River. The largest population is currently found in Chitral National Park in Pakistan.[2]
Bukharan markhor
[edit]Although the Bukharan markhor or Tajik markhur[19] (Capra falconeri heptneri) formerly lived in most of the mountains stretching along the north banks of the Upper Amu Darya and the Pyanj Rivers from Turkmenistan to Tajikistan, two to three scattered populations now occur in a greatly reduced distribution. It is limited to the region between lower Pyanj and the Vakhsh Rivers near Kulyab in Tajikistan (near 38°N 70°E / 38°N 70°E), and in the Kugitangtau Range in Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan (around 37°30′N 66°40′E / 37.500°N 66.667°E). This subspecies may possibly exist in the Darwaz Peninsula of northern Afghanistan near the border with Tajikistan. Before 1979, almost nothing was known of this subspecies or its distribution in Afghanistan, and no new information has been established in Afghanistan since that time.[2]
Kabul markhor
[edit]The Kabul markhor (Capra falconeri megaceros) has horns with a slight corkscrew, as well as a twist. A junior synonym is Capra falconeri jerdoni.[9]
Until 1978, the Kabul markhor survived in Afghanistan only in the Kabul Gorge and the Kohe Safi area of Kapissa, and in some isolated pockets in between. It now lives the most inaccessible regions of its once wider range in the mountains of Kapissa and Kabul Provinces, after having been driven from its original habitat by intensive poaching. In Pakistan, its present range consists only of small isolated areas in Baluchistan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KPK) province and in Dera Ghazi Khan District (Punjab Province). The KPK Forest Department considered that the areas of Mardan and Sheikh Buddin were still inhabited by the subspecies. At least 100 animals are thought to live on the Pakistani side of the Safed Koh range (Districts of Kurram and Khyber).[2]
Relationship with the domestic goat
[edit]Certain authors have postulated that the markhor is the ancestor of some breeds of domestic goat. The Angora goat has been regarded by some as a direct descendant of the Central Asian markhor.[20][21] Charles Darwin postulated that modern goats arose from crossbreeding markhor with wild goats.[22] Evidence for markhors crossbreeding with domestic goats has been found. One study suggested that 35.7% of captive markhors in the analysis (ranging from three different zoos) had mitochondrial DNA from domestic goats.[23] Other authors have suggested that markhor may have been the ancestor of some Egyptian goat breeds, based on their similar horns, though the lack of an anterior keel on the horns of the markhor belies any close relationship.[24] The Changthangi domestic goat of Ladakh and Tibet may derive from the markhor.[25] The Girgentana goat of Sicily is thought to have been bred from markhor,[26] as is the Bilberry goat of Ireland.[27] The Kashmiri feral herd of about 200 individuals on the Great Orme limestone headland of Wales are derived from a herd maintained at Windsor Great Park belonging to Queen Victoria.[28]
Fecal samples taken from markhor and domestic goats indicate that there is a serious level of competition for food between the two species. The competition for food between herbivores is believed to have significantly reduced the standing crop of forage in the Himalaya–Karkoram–Hindukush ranges. Domestic livestock have an advantage over wild herbivores since the density of their herds often pushes their competitors out of the best grazing areas, and decreased forage availability has a negative effect on female fertility.[29]
Threats
[edit]Hunting for meat as a means of subsistence or trade in wildlife parts adds to the growing problem for wildlife managers in many countries. Poaching, with its indirect impacts as disturbance, increasing fleeing distances and resulting reduction of effective habitat size, is by far the most important factor threatening the survival of the markhor populations.[30] The most important types of poachers seem to be local inhabitants, state border guards, the latter usually relying on local hunting guides, and Afghans, illegally crossing the border. Poaching causes fragmentation of the population into small islands where the remaining subpopulations are prone to extinction.[30] The markhor is a valued trophy hunting prize for its spiral horns. The Pakistani government issued several tags in an attempt to save the species, which since the introduction of hunting the species has seen a remarkable rebound. The continuing declines of markhor populations finally caught the attention of the international community.[31]
Hunting
[edit]
In British India, markhor were considered to be among the most challenging game species, because of the danger involved in stalking and pursuing them in high, mountainous terrain.[32] According to Arthur Brinckman in his The Rifle in Cashmere, "a man who is a good walker will never wish for any finer sport than ibex or markhoor shooting".[33] Elliot Roosevelt wrote of how he shot two markhor in 1881, his first on 8 July, his second on 1 August.[34] Although it is illegal to hunt markhor in Afghanistan, they have been traditionally hunted in Nuristan and Laghman Provinces, and this may have intensified during the War in Afghanistan. In Pakistan, hunting markhor is legal as part of a conservation process: expensive hunting licenses are available from the Pakistani government that allow the hunting of old markhors, which are no longer good for breeding purposes.[35] In India, it is illegal to hunt markhor but they are poached for food and for their horns, which are thought to have medicinal properties.[36] Markhor have also been successfully introduced to private game ranches in Texas. Unlike the aoudad, blackbuck, nilgai, ibex, and axis deer, however, markhor have not escaped in sufficient numbers to establish free-range wild populations in Texas.
The International Union for the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources currently classifies the markhor as a near threatened species, because of its relatively small population (2013 estimate: ~5,800 individuals), the absence of a projected total population decline, and its reliance on ongoing conservation efforts to maintain population levels.[2] There are reservations in Tajikistan to protect the markhors. In 1973, two reservations were established. The Dashtijum Strict Reserve (also called the Zapovednik in Russian) offers markhor protect across 20,000 ha. The Dashtijum Reserve (called the Zakasnik in Russian) covers 53,000 ha. Though these reserves exist to protect and conserve the markhor population, the regulations are poorly enforced making poaching common as well as habitat destruction.[2][11] Although markhors still face ongoing threats, recent studies have shown considerable success with regards to the conservation approach. The approach began in the 1900s when a local hunter was convinced by a hunting tourist to stop poaching markhors. The local hunter established a conservancy that inspired two other local organizations called Morkhur and Muhofiz. The two organizations expect that their conversations will not only protect, but allow them to sustainably exploit the markhor species. This approach has been effective compared to the protection of lands that lack enforcement and security.[11] In India, the markhor is a fully protected (Schedule I) species under Jammu and Kashmir's Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1978.[36]
In culture
[edit]The markhor is the national animal of Pakistan.[37] It was one of the 72 animals featured on the World Wide Fund for Nature Conservation Coin Collection in 1976. Markhor marionettes are used in the Afghan puppet shows known as buz-baz. The markhor has also been mentioned in a Pakistani computer-animated film known as Allahyar and the Legend of Markhor.[38]
Etymology
[edit]The name is thought to be derived from Persian language — a conjunction of mâr (مار, "snake, serpent") and the suffix khor (خور, "-eater"), interpreted to represent the animal's alleged ability to kill snakes, or as a reference to its corkscrew-like horns, which are somewhat reminiscent of coiling snakes.[7]
In folklore the markhor is believed to kill and eat serpents. Thereafter, while chewing the cud, a foam-like substance comes out of its mouth that drops on the ground and dries. This foam-like substance is sought after by the local people, who believe it is useful in extracting the poison from snakebites.[39]
References
[edit]- ^ Grubb, P. (2005). "Species Capra falconeri". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 701. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Michel, S. & Rosen Michel, T. (2016) [errata version of 2015 assessment]. "Capra falconeri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2015: e.T3787A97218336. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-4.RLTS.T3787A82028427.en. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
- ^ "American hunter pays $100,000 to kill rare Himalayan 'screw-horned' goat". The Independent. 2019. Retrieved 9 October 2019.
- ^ Sharma, S. D. (1990). Semantics and Syntax: Indian Loan Words in English : a Linguistic, Cultural, Literary & Historical Study. Prakash Book Depot. p. 83.
- ^ "International Day of the Markhor".
- ^ "Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 2 May 2024 | 78/278. International Day of the Markhor". United Nations.
- ^ a b c d e "Capra falconeri" Markhor, An Ultimate Ungulate fact sheet Archived 2007-12-20 at the Wayback Machine. Ultimateungulate.com. Retrieved on 2011-07-10.
- ^ Fedosenko, A. K. & Blank, D. A. (2001). "Capra sibirica" (PDF). Mammalian Species. 675: 1–13. doi:10.1644/1545-1410(2001)675<0001:CS>2.0.CO;2. S2CID 198969400.
- ^ a b c "NATURAL HISTORY OF THE MAMMALIA OF INDIA AND CEYLON" by Robert A. Sterndale, published by CALCUTTA: THACKER, SPINK, AND CO., BOMBAY: THACKER AND CO., LIMITED., LONDON: W. THACKER AND CO. 1884. Gutenberg.org (2006-10-16). Retrieved on 2011-07-10.
- ^ Frederick Markham (1854). Shooting in the Himalayas: a journal of sporting adventures and travel in Chinese Tartary, Ladac, Thibet, Cashmere, &c. R. Bentley.
- ^ a b c d Michel, S.; Michel, T.; Saidov, A.; Karimov, K.; Alidodov, M.; Kholmatov, I. (2014). "Population status of Heptner's markhor Capra falconeri heptneri in Tajikistan: challenges for conservation" (PDF). Oryx. 49 (3): 506–513. doi:10.1017/s0030605313000860. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 July 2014.
- ^ Ahmad, R.; Sharma, N.; Mishra, C.; Singh, N. J.; Rawat, G.S.; Bhatnagar, Y.V. (2017). "Security, size, or sociality: what makes markhor (Capra falconeri) sexually segregate?". Journal of Mammalogy. 99 (1): 55–63. doi:10.1093/jmammal/gyx155.
- ^ Lyngdoh, S. B.; Habib, B.; Shrotriya, S. (2019). "Dietary spectrum in Himalayan wolves: comparative analysis of prey choice in conspecifics across high-elevation rangelands of Asia" (PDF). Down to Earth. Retrieved 7 August 2020.
- ^ Sajjad, A. "Conservation and status of Markhor (Capra falconeri) in the northern parts of North West Frontier Province, Pakistan" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 December 2010.
- ^ Wagner, J.A. (1839). "Beschreibung einiger neuer oder wenig bekannter Säugethiere, welche von Herrn Baron von Hügel in Indien gesammelt wurden". Gelehrte Anzeigen der Königlich Bayerischen Akademie der Wissenschaften zu München. 9 (183): 429–432.
- ^ Damm & Franco, CIC Caprinae Atlas of the World, CIC/Rowland Ward, 2014
- ^ Richard Lydekker (1900). The great and small game of India, Burma, and Tibet. Asian Educational Services. ISBN 978-81-206-1162-7. Retrieved 10 July 2011.
- ^ Ahmad, R., Sharma, N., Mishra, C., Singh, N. J., Rawat, G. S., & Bhatnagar, Y. V. (2018). Security, size, or sociality: what makes markhor (Capra falconeri) sexually segregate?. Journal of Mammalogy, 99(1), 55–63.
- ^ Castello J. R. (2016) Bovids of the World: Antelopes, Gazelles, Cattle, Goats, Sheep, and Relatives. — Princeton University Press. — Pp. 320—325. — 664 p. — ISBN 978-0-691-16717-6
- ^ John Lord Hayes (1868). The Angora goat: its origin, culture and products. Boston, 1868
- ^ Olive Schreiner (1898). Angora goat ... : and, A paper on the ostrich ... London : Longmans, 1898
- ^ The Variation of Animals and Plants Under Domestication by Charles Darwin, Publisher O. Judd & company, 1868
- ^ Hammer, Sabine (2008). "Evidence for introgressive hybridization of captive markhor (Capra falconeri) with domestic goat: cautions for reintroduction". Biochemical Genetics. 46 (3/4): 216–226. doi:10.1007/s10528-008-9145-y. PMID 18228130. S2CID 7408515.
- ^ Juliet Clutton-Brock (1999). A natural history of domesticated mammals. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-63495-4. Retrieved 10 July 2011.
- ^ M Menrad; C.-H Stier; H Geldermann; C.F. Gall (2002). "A study on the Changthangi pashmina and the Bakerwali goat breeds in Kashmir: I. Analysis of blood protein polymorphisms and genetic variability within and between the populations". Small Ruminant Research. 43 (1): 3–14. doi:10.1016/S0921-4488(01)00265-6.
- ^ La Capra Girgentana. Capragirgentana.it. Retrieved on 2011-07-10.
- ^ "Between a rock and a goat's place in Waterford". Irish Times. August 2009.
- ^ The Great Orem in Llandudno North Wales Archived 2010-09-08 at the Wayback Machine. Llandudno.com. Retrieved on 2011-07-10.
- ^ Ashraf, N. (2014). "Competition for food between the markhor and domestic goat in Chitral, Pakistan". Turkish Journal of Zoology. 38 (2): 191–198. doi:10.3906/zoo-1306-6.
- ^ a b Michel, Stefan. "CONSERVATION OF TAJIK MARKHOR (Capra falconeri heptneri) AND URIAL (Ovis vignei) IN TAJIKISTAN AND ADJACENT AFGHANISTAN" (PDF).
- ^ Rosser, Naseer; Nigel; Alison M., Tareen & Leader-Williams. "Chapter 4: The Precautionary Principle, Uncertainty And Trophy Hunting: A Review Of The Torghar Population Of Central Asian Markhor Capra Falconeri". Points of View Reference Center. Retrieved 22 October 2014.
- ^ Hindu-Koh: Wanderings and Wild Sport on and Beyond the Himalayas (1853–1854) by Donald Macintyre, published by Asian Educational Services, 1996, ISBN 81-206-0851-8
- ^ Arthur Brinckman (1862). The rifle in Cashmere: a narrative of shooting expeditions in Ladak, Cashmere, Punjaub, etc., with advice on travelling, shooting, and stalking : to which are added notes on army reform and Indian politics. Smith, Elder. pp. 148–. Retrieved 10 July 2011.
- ^ Theodore Roosevelt IV (27 October 2008). Hunting in Many Lands. Clapham Press. ISBN 978-1-4437-7183-2. Retrieved 10 July 2011.
- ^ "A $55,000 wild Markhor chase". dailytimes.com.pk. 31 March 2006. Retrieved 25 December 2012.
- ^ a b "The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Retrieved 26 October 2018.
- ^ Taus-Bolstad, Stacy (2003). Pakistan in Pictures. Twenty-First Century Books. p. 15. ISBN 978-0822546825. Retrieved 25 December 2012.
- ^ IMDB(2018)https://www.imdb.com/title/tt7955106/
- ^ "Markhor". Museo de la Caza Los Yebenes. Retrieved 9 April 2017.
External links
[edit]- Mueenuddin, N. (2020). Himalayan Lynx Filmed Hunting Markhor in Pakistan for First Time (Motion picture). WWF Pakistan. Archived from the original on 22 December 2021.
- Markhor Pakistan National Animal

