List of scheduled monuments in Mendip

Mendip is a local government district of Somerset in England. The Mendip district covers a largely rural area of 285 square miles (738 km2)[1] ranging from the Mendip Hills through on to the Somerset Levels. It has a population of approximately 110,000.[1] The administrative centre of the district is Shepton Mallet but the largest town (with more than twice the population of Shepton Mallet) is Frome.[2][3]
A scheduled monument is a nationally important archaeological site or monument which is given legal protection by being placed on a list (or "schedule") by the Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport; Historic England takes the leading role in identifying such sites. The legislation governing this is the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Areas Act 1979. The term "monument" can apply to the whole range of archaeological sites, and they are not always visible above ground. Such sites have to have been deliberately constructed by human activity. They range from prehistoric standing stones and burial sites, through Roman remains and medieval structures such as castles and monasteries, to later structures such as industrial sites and buildings constructed for the World Wars or the Cold War.[4]
There are 234 scheduled monuments in Mendip. These include a large number of bowl and round barrows and other neolithic, Bronze and Iron Age tumuli such as the Priddy Circles and Priddy Nine Barrows and Ashen Hill Barrow Cemeteries.[5][6][7][8] There are also several Iron Age hill forts on the hill tops and lake villages on the lowlands such as Meare and Glastonbury Lake Villages.[9][10][11][12] The lake villages were often connected by timber trackways such as the Sweet Track. There are several Roman sites particularly around the Charterhouse Roman Town and lead mining.[13] Some later coal mining sites are also included in the list.
Two major religious sites in Mendip at Glastonbury Abbey and Wells Cathedral and their precincts and dispersed residences, tithe barns and The Abbot's Fish House, are included in the list.[14][15][16][17] Prehistoric defensive features such as Ponter's Ball Dyke were supplemented in the medieval period by motte-and-bailey castles such as Farleigh Hungerford, Nunney and Fenny Castle.[18][19][20][21] Commercial and industrial development is represented by the Old Iron Works at Mells and various market crosses.[22][23] The most recent site on the list is a World War II bombing decoy complex and anti-aircraft obstructions, which were built in 1940, on Black Down, the highest point of the Mendip Hills.[24] The monuments are listed below using the titles given in the Historic England data sheets.
Monuments
[edit]| Name | Location | Type | Completed [note 1] | Grid ref.[note 2] Geo-coordinates | Notes | Entry number [note 3] | Image | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| An area of the Romano-British linear village at Fosse Lane, Shepton Mallet | Shepton Mallet | Earthworks | Romano-British | ST 62920 42423 51°10′47″N 2°31′54″W / 51.1798°N 2.5318°W |
Earthworks from a Romano-British village next to the Fosse Way. | 1011635 |  Upload Photo |
[25] |
| Ashen Hill barrow cemetery: a group of eight round barrows 500 m southeast of Harptree Lodge | Priddy | Round barrows | Bronze Age | ST 53911 52055 51°15′46″N 2°39′45″W / 51.2628°N 2.6625°W |
Priddy Nine Barrows and Ashen Hill Barrow Cemeteries are a collection of round barrows, dating from the Bronze Age. The barrows sit on crests of land at either end of a field in an area of the Mendip Hills with several Neolithic remains. They are assumed to be related to the Priddy Circles which lie 750 metres (2,460 ft) to the north. Ashen Hill consists of six bowl barrows and two bell barrows aligned east to west while Priddy Nine Barrows divided into one group of seven round barrows and another pair slightly separated from the others. Excavations in 1815 uncovered cremation burials and grave goods. A geophysical magnetometry survey suggested that there may have been three further barrows. | 1010513 |  |
[6][7] [8] |
| Badger Hole, Wookey | St Cuthbert Out | Cave | Iron Age | ST 53247 47954 51°13′44″N 2°40′16″W / 51.2288°N 2.6710°W |
Badger Hole is a dry cave on the slopes above the Wookey ravine near the Wookey Hole Caves resurgence and contain in situ cave sediments laid down during the Ice Age. Just outside the cave the foundations of a 1st-century hut have been identified. These had been built on during the Roman era up to the end of the 4th century. | 1010294 |  Upload Photo |
[26][27] [28] |
| Barrow, 350 m east of Harptree Lodge | Chewton Mendip | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 54015 52388 51°16′08″N 2°39′38″W / 51.2688°N 2.6605°W |
A bowl barrow close to Priddy Circles. The mound is approximately 20 metres (66 ft) in diameter. | 1015921 |  Upload Photo |
[29] |
| Beckery Chapel and cemetery (site of) | Glastonbury | Cemetery | Middle Ages | ST 48405 38312 51°08′30″N 2°44′20″W / 51.1417°N 2.7389°W |
The site of a chapel, also known as St Brigid's Chapel, and medieval cemetery. The chapel was "in ruins" in 1791. Excavations in 1967 found the remains of 63 burials. | 1006147 |  Upload Photo |
[30] |
| Bell barrow south of Blackwell Tyning Plantation | Emborough | Bell barrow | Bronze Age | ST 60691 50278 51°15′01″N 2°33′53″W / 51.2503°N 2.5646°W |
A bell barrow which is approximately 32 metres (105 ft) in diameter. | 1008288 |  Upload Photo |
[31] |
| Bishop's palace | Wookey | Bishop's Palace | 13th century | ST 51784 45647 51°12′29″N 2°41′30″W / 51.2080°N 2.6916°W |
Earthworks from a medieval Bishop's Palace first documented in 1224 which may have been built by Jocelin of Wells. New buildings were added in the 1550s which included the only building which still survives and is used as Court Farmhouse. | 1013588 |  Upload Photo |
[32][33] [34] |
| Bishop's Palace ruined portions, walls and well house | Wells | Bishop's Palace | c. 1280 | ST5516845702 51°12′32″N 2°38′35″W / 51.208755°N 2.643159°W |
The Bishop's Palace and accompanying Bishops House is adjacent to Wells Cathedral and has been the home of the Bishops of the Diocese of Bath and Wells for 800 years. Building of the palace started around 1210 by Bishops Jocelin of Wells and Reginald Fitz Jocelin. The chapel and great hall were added by Bishop Robert Burnell between 1275 and 1292. The walls, gatehouse and moat were added in the 14th century by Bishop Ralph of Shrewsbury. The Bishops House was added in the 15th century by Bishop Thomas Beckington. The great hall later fell into disrepair and was partially demolished around 1830. The palace was originally surrounded by a medieval deer park. When the walls were built, streams were diverted to form the moat as a reservoir. In the 1820s, the grounds within the walls were planted and laid out as pleasure grounds by Bishop George Henry Law, who created a reflecting pond near the springs. Parts of the buildings are still used as a residence by the current bishop, however much of the palace is now used for public functions and as a tourist attraction. | 1006201 |  |
[35] |
| Bishop's tithe barn | Wells | Tithe barn | 15th century | ST 55090 45532 51°12′21″N 2°38′37″W / 51.2059°N 2.6435°W |
Local stone roughly squared, with Doulting ashlar dressings and a Westmorland slate roof. Royalist troops were quartered in the barn during the Bloody Assizes. | 1003247 |  |
[14][36] |
| Bolter's Bridge, Hornblotton | Ditcheat | Bridge | Middle Ages | ST 60604 33410 51°05′55″N 2°33′50″W / 51.0986°N 2.5640°W |
A medieval stone bridge, carrying a small road over the River Alham. The bridge is approximately 2 metres (6 ft 7 in) wide. | 1006231 |  |
[37] |
| Bowl barrow 20 m northwest of Whitestown Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52782 55227 51°17′39″N 2°40′43″W / 51.2942°N 2.6786°W |
A bowl barrow which is 19 metres (62 ft) in diameter. | 1011522 |  Upload Photo |
[38] |
| Bowl barrow 70 m east of Barrow House Farm | Chewton Mendip | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 60119 53250 51°16′37″N 2°34′23″W / 51.2770°N 2.5731°W |
A bowl barrow which is 19 metres (62 ft) in diameter. | 1011527 |  Upload Photo |
[39] |
| Bowl barrow 70 m northeast of King Down Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50892 54211 51°17′06″N 2°42′20″W / 51.2849°N 2.70553°W |
A bowl barrow which is 19 metres (62 ft) in diameter. | 1011531 |  Upload Photo |
[40] |
| Bowl barrow 70 m northwest of Hill View | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52180 52320 51°16′05″N 2°41′12″W / 51.2680°N 2.6868°W |
A bowl barrow which is 22 metres (72 ft) in diameter. | 1010390 |  Upload Photo |
[41] |
| Bowl barrow 70 m west of Rowberrow Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52000 52189 51°16′00″N 2°41′22″W / 51.2668°N 2.6894°W |
A bowl barrow which is 17 metres (56 ft) in diameter. | 1010425 |  Upload Photo |
[42] |
| Bowl barrow 90 m northeast of Hill View | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52299 52388 51°16′07″N 2°41′06″W / 51.2686°N 2.6851°W |
A bowl barrow which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1009747 |  Upload Photo |
[43] |
| Bowl barrow 100 m north east of Home Farm Cottage | Ston Easton | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 62202 54284 51°17′11″N 2°32′36″W / 51.2864°N 2.5434°W |
A bowl barrow which is 21 metres (69 ft) in diameter. | 1016296 |  |
[44] |
| Bowl barrow 120 m north west of Burnt Wood | Emborough | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 59873 49566 51°14′38″N 2°34′34″W / 51.2438°N 2.5762°W |
A bowl barrow which is 17 metres (56 ft) in diameter. | 1008079 |  Upload Photo |
[45] |
| Bowl barrow 130 m west of St Lawrence's Church | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52694 51406 51°15′35″N 2°40′45″W / 51.2598°N 2.6793°W |
A bowl barrow which is 24 metres (79 ft) in diameter. | 1009768 |  Upload Photo |
[46] |
| Bowl barrow 150 m north east of Victoria Farm | St Cuthbert Out | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 59619 48618 51°14′07″N 2°34′47″W / 51.2353°N 2.5798°W |
A bowl barrow which is 35 metres (115 ft) in diameter. | 1016236 |  Upload Photo |
[47] |
| Bowl barrow 150 m southwest of King Down Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50624 54034 51°17′00″N 2°42′34″W / 51.2833°N 2.7094°W |
A bowl barrow which is 19 metres (62 ft) in diameter. | 1011520 |  Upload Photo |
[48] |
| Bowl barrow 170 m south-east of Hunter's Lodge Inn | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 55094 50086 51°14′54″N 2°38′41″W / 51.2482°N 2.6448°W |
A bowl barrow which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1010648 |  Upload Photo |
[49] |
| Bowl barrow 180 m southwest of Yoxter Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 51047 53886 51°16′55″N 2°42′12″W / 51.2820°N 2.7033°W |
A bowl barrow which is 16 metres (52 ft) in diameter. | 1011532 |  Upload Photo |
[50] |
| Bowl barrow 180 m west of Ubley Warren Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 51108 55226 51°17′39″N 2°42′09″W / 51.2941°N 2.7026°W |
A bowl barrow which is 25 metres (82 ft) in diameter. | 1010160 |  Upload Photo |
[51] |
| Bowl barrow 220 m south west of Ubley Hill Farmhouse | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 51606 57202 51°18′43″N 2°41′45″W / 51.3119°N 2.6957°W |
A bowl barrow which is 14 metres (46 ft) in diameter. | 1010284 |  Upload Photo |
[52] |
| Bowl barrow 230 m north west of Hunter's Lodge Inn | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 54710 50191 51°14′57″N 2°39′01″W / 51.2491°N 2.6503°W |
A bowl barrow which is 10 metres (33 ft) in diameter. | 1010182 |  Upload Photo |
[53] |
| Bowl barrow 250 m northeast of King Down Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50941 54362 51°17′11″N 2°42′17″W / 51.2863°N 2.7048°W |
A bowl barrow which is 21 metres (69 ft) in diameter. | 1011530 |  Upload Photo |
[54] |
| Bowl barrow 250 m north west of Victoria Farm | St Cuthbert Out | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 59314 48669 51°14′09″N 2°35′03″W / 51.2357°N 2.5841°W |
A bowl barrow which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1016233 |  Upload Photo |
[55] |
| Bowl barrow 250 m south east of Redhill Farm | Emborough | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 60667 50669 51°15′14″N 2°33′54″W / 51.2538°N 2.5650°W |
A bowl barrow which is 30 metres (98 ft) in diameter. | 1016297 |  Upload Photo |
[56] |
| Bowl barrow 250 m west of Starve Lark Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 53251 55975 51°18′04″N 2°40′19″W / 51.3010°N 2.6719°W |
A bowl barrow which is 24 metres (79 ft) in diameter. | 1008078 |  Upload Photo |
[57] |
| Bowl barrow 260 m east of Templedown Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 51848 54848 51°17′27″N 2°41′31″W / 51.2907°N 2.6919°W |
A bowl barrow which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1011534 |  Upload Photo |
[58] |
| Bowl barrow 280 m south east of Ubley Hill Farmhouse | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52012 57325 51°18′47″N 2°41′24″W / 51.3130°N 2.6899°W |
A bowl barrow which is 12 metres (39 ft) in diameter. | 1010282 |  Upload Photo |
[59] |
| Bowl barrow 300 m north of Hazel Manor | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52749 57059 51°18′39″N 2°40′45″W / 51.3107°N 2.6793°W |
A bowl barrow which is 17 metres (56 ft) in diameter. | 1010265 |  Upload Photo |
[60] |
| Bowl barrow 300 m north east of Whitnell Corner | Emborough | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 59872 49026 51°14′20″N 2°34′34″W / 51.2390°N 2.5762°W |
A bowl barrow which is 10 metres (33 ft) in diameter. | 1011670 |  |
[61] |
| Bowl barrow 300 m south west of Harptree Lodge | Chewton Mendip | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 53553 52235 51°16′03″N 2°40′02″W / 51.2674°N 2.6671°W |
A bowl barrow which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1010287 |  Upload Photo |
[62] |
| Bowl barrow 300 m southwest of Moor View | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52107 49325 51°14′28″N 2°41′15″W / 51.2411°N 2.6875°W |
A bowl barrow which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1009773 |  Upload Photo |
[63] |
| Bowl barrow 300 m west of Newlands Farm | Chewton Mendip | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 57332 50604 51°15′11″N 2°36′46″W / 51.2530°N 2.6128°W |
A bowl barrow which is 25 metres (82 ft) in diameter. | 1008094 |  Upload Photo |
[64] |
| Bowl barrow 310 m southeast of Eastwater Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 53772 50538 51°15′08″N 2°39′50″W / 51.2521°N 2.6638°W |
A bowl barrow which is 22 metres (72 ft) in diameter. | 1009767 |  Upload Photo |
[65] |
| Bowl barrow 320 m east of Lodmore Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 53567 53914 51°16′57″N 2°40′02″W / 51.2825°N 2.6671°W |
A bowl barrow which is 15 metres (49 ft) in diameter. | 1010458 |  Upload Photo |
[66] |
| Bowl barrow 330 m north of Stoke Woods | Rodney Stoke | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 49160 51339 51°15′32″N 2°43′48″W / 51.2589°N 2.7300°W |
A bowl barrow which is 17 metres (56 ft) in diameter. | 1008086 |  Upload Photo |
[67] |
| Bowl barrow 340 m east of Templedown Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 51923 54875 51°17′28″N 2°41′27″W / 51.2910°N 2.6908°W |
A bowl barrow which is 16 metres (52 ft) in diameter. | 1011535 |  Upload Photo |
[68] |
| Bowl barrow 340 m north-east of Wellington Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 49267 54030 51°16′59″N 2°43′44″W / 51.2831°N 2.7288°W |
A bowl barrow which is 17 metres (56 ft) in diameter. | 1010644 |  Upload Photo |
[69] |
| Bowl barrow 350 m northeast of Cheddar Head Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50408 53068 51°16′29″N 2°42′44″W / 51.2746°N 2.7123°W |
A bowl barrow which is 12 metres (39 ft) in diameter. | 1010635 |  Upload Photo |
[70] |
| Bowl barrow 350 m northwest of Fernhill Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52523 55752 51°17′56″N 2°40′57″W / 51.2989°N 2.6824°W |
A bowl barrow which is 16 metres (52 ft) in diameter. | 1009745 |  Upload Photo |
[71] |
| Bowl barrow 350 m north west of Harptree Lodge | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 53444 52804 51°16′21″N 2°40′08″W / 51.2725°N 2.6688°W |
A bowl barrow which is 23 metres (75 ft) in diameter. | 1010286 |  Upload Photo |
[72] |
| Bowl barrow 365 m south west of Ubley Warren Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 51132 54900 51°17′28″N 2°42′08″W / 51.2911°N 2.7022°W |
A bowl barrow which is 40 metres (130 ft) in diameter. | 1008287 |  Upload Photo |
[73] |
| Bowl barrow 370 m east of Ubley Hill Farmhouse | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52119 57378 51°18′49″N 2°41′18″W / 51.3135°N 2.6884°W |
A bowl barrow which is 16 metres (52 ft) in diameter. | 1010281 |  Upload Photo |
[74] |
| Bowl barrow 380 m south east of Southfield Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 55186 49623 51°14′38″N 2°38′36″W / 51.2440°N 2.6434°W |
A bowl barrow which is 15 metres (49 ft) in diameter. | 1010178 |  Upload Photo |
[75] |
| Bowl barrow 380 m south east of Beechbarrow | St Cuthbert Out | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 57466 48871 51°14′15″N 2°36′38″W / 51.2374°N 2.6106°W |
A bowl barrow which is 15 metres (49 ft) in diameter. | 1020020 |  Upload Photo |
[76] |
| Bowl barrow 390 m northeast of Bristol Plain Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50691 52201 51°16′00″N 2°42′29″W / 51.2668°N 2.7081°W |
A bowl barrow which is 26 metres (85 ft) in diameter. | 1010483 |  Upload Photo |
[77] |
| Bowl barrow 390 m northwest of Fernhill Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52469 55772 51°17′57″N 2°40′59″W / 51.2991°N 2.6831°W |
A bowl barrow which is 15 metres (49 ft) in diameter. | 1009763 |  Upload Photo |
[78] |
| Bowl barrow 400 m north of Stoke Woods | Rodney Stoke | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 49419 51291 51°15′31″N 2°43′34″W / 51.2585°N 2.7262°W |
A bowl barrow which is 12 metres (39 ft) in diameter. | 1008087 |  Upload Photo |
[79] |
| Bowl barrow 400 m north-west of Starve Lark Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 53091 56075 51°18′07″N 2°40′27″W / 51.3019°N 2.6743°W |
A bowl barrow which is 20 metres (66 ft) in diameter. | 1008077 |  Upload Photo |
[80] |
| Bowl barrow 400 m south of Rookham | St Cuthbert Out | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 55211 49240 51°14′26″N 2°38′35″W / 51.2406°N 2.6430°W |
A bowl barrow which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1016298 |  Upload Photo |
[81] |
| Bowl barrow 400 m southwest of Moor View | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 51965 49326 51°14′28″N 2°41′22″W / 51.2411°N 2.6895°W |
A bowl barrow which is 9 metres (30 ft) in diameter. | 1010106 |  Upload Photo |
[82] |
| Bowl barrow 410 m northeast of Bristol Plain Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50742 52157 51°15′59″N 2°42′27″W / 51.2664°N 2.7074°W |
A bowl barrow which is 23 metres (75 ft) in diameter. | 1010486 |  Upload Photo |
[83] |
| Bowl barrow 420 m east of Bristol Plain Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50756 52106 51°15′58″N 2°42′26″W / 51.2660°N 2.7072°W |
A bowl barrow, previously known as Green Barrow, which is 15 metres (49 ft) in diameter. | 1010488 |  Upload Photo |
[84] |
| Bowl barrow 420 m north of Stoke Woods | Rodney Stoke | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 49276 51382 51°15′33″N 2°43′42″W / 51.2593°N 2.7283°W |
A bowl barrow, previously known as Green Barrow, which is 12 metres (39 ft) in diameter. | 1011918 |  Upload Photo |
[85] |
| Bowl barrow 430 m north of Whitnell Corner | Emborough | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 59788 49198 51°14′26″N 2°34′39″W / 51.2405°N 2.5774°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 25 metres (82 ft) in diameter. | 1008080 |  Upload Photo |
[86] |
| Bowl barrow 430 m north east of Stoke Woods | Rodney Stoke | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 49757 51180 51°15′27″N 2°43′17″W / 51.2576°N 2.7214°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 14 metres (46 ft) in diameter. | 1008088 |  Upload Photo |
[87] |
| Bowl barrow 430 m northwest of King Down Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50352 54230 51°17′06″N 2°42′48″W / 51.2850°N 2.7133°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 20 metres (66 ft) in diameter. | 1011519 |  Upload Photo |
[88] |
| Bowl barrow 430 m southwest of King Down Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50370 53922 51°16′56″N 2°42′47″W / 51.2823°N 2.7130°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 10 metres (33 ft) in diameter. | 1011521 |  Upload Photo |
[89] |
| Bowl barrow 435 m north west of Ivy Cottage | St Cuthbert Out | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 54435 48464 51°14′01″N 2°39′14″W / 51.2335°N 2.6540°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 9 metres (30 ft) in diameter. | 1020495 |  Upload Photo |
[90] |
| Bowl barrow 450 m east of Bristol Plain Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50782 52033 51°15′55″N 2°42′24″W / 51.2653°N 2.7068°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 21 metres (69 ft) in diameter. | 1010481 |  |
[91] |
| Bowl barrow 450 m north west of Harptree Lodge | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 53308 52803 51°16′21″N 2°40′15″W / 51.2725°N 2.6707°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 16 metres (52 ft) in diameter. | 1010285 |  Upload Photo |
[92] |
| Bowl barrow 450 m south-east of Red Quar Farm | Chewton Mendip | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 56517 51667 51°15′45″N 2°37′29″W / 51.2625°N 2.6246°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1008083 |  Upload Photo |
[93] |
| Bowl barrow 450 m southwest of Fernhill Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52440 55251 51°17′40″N 2°41′01″W / 51.2944°N 2.6835°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 23 metres (75 ft) in diameter. | 1011523 |  Upload Photo |
[94] |
| Bowl barrow, 455 m west of Brimble Pit Pool | Westbury | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST5033650796 51°15′15″N 2°42′47″W / 51.2542°N 2.7130°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 11 metres (36 ft) in diameter. | 1415590 | [95] | |
| Bowl barrow 460 m east of Charterhouse Warren Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50438 54861 51°17′27″N 2°42′44″W / 51.2907°N 2.7121°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 12 metres (39 ft) in diameter. | 1010640 |  Upload Photo |
[96] |
| Bowl barrow 470 m south east of Southfield Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 55490 49795 51°14′44″N 2°38′21″W / 51.2456°N 2.6391°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1010263 |  Upload Photo |
[97] |
| Bowl barrow 490 m north west of Pen Hill Farm | St Cuthbert Out | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 55349 48418 51°14′00″N 2°38′27″W / 51.2332°N 2.6409°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 14 metres (46 ft) in diameter. | 1020206 |  Upload Photo |
[98] |
| Bowl barrow 500 m north of East Water | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 53717 51462 51°15′37″N 2°39′53″W / 51.2604°N 2.6647°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 13 metres (43 ft) in diameter. | 1010637 |  Upload Photo |
[99] |
| Bowl barrow 510 m south east of Lodmore Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 53724 53754 51°16′52″N 2°39′54″W / 51.2810°N 2.6649°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 19 metres (62 ft) in diameter. | 1010427 |  |
[100] |
| Bowl barrow 520 m south-east of Red Quar Farm | Chewton Mendip | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 56551 51647 51°15′44″N 2°37′27″W / 51.2623°N 2.6241°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1008082 |  Upload Photo |
[101] |
| Bowl barrow, 540 m west of Brimble Pit Pool | Westbury | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST5025750847 51°15′17″N 2°42′51″W / 51.2546°N 2.7142°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 22 metres (72 ft) in diameter. | 1415589 |  Upload Photo |
[102] |
| Bowl barrow 550 m south of Bristol Plain Farm: part of a linear round barrow cemetery | Rodney Stoke | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50211 51421 51°15′35″N 2°42′54″W / 51.2598°N 2.7149°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 12 metres (39 ft) in diameter. | 1008090 |  |
[103] |
| Bowl barrow 550 m southwest of Nordrach | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50788 55768 51°17′56″N 2°42′26″W / 51.2989°N 2.7072°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1011529 |  Upload Photo |
[104] |
| Bowl barrow 550 m south east of Southfield Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 55554 49741 51°14′42″N 2°38′17″W / 51.2451°N 2.6381°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1010264 |  Upload Photo |
[105] |
| Bowl barrow 550 m south east of Brimble Pit Pool: one of a group of round barrows north and east of Foxhills Wood | Westbury | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 51123 50363 51°15′01″N 2°42′06″W / 51.2503°N 2.7017°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 13 metres (43 ft) in diameter. | 1016293 |  Upload Photo |
[106] |
| Bowl barrow 570 m south east of Lodmore Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 53759 53653 51°16′48″N 2°39′52″W / 51.2801°N 2.6644°W |
A bowl barrow which is 17 metres (56 ft) in diameter. | 1010424 |  Upload Photo |
[107] |
| Bowl barrow 570 m south east of Southfield Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 55529 49654 51°14′39″N 2°38′19″W / 51.2443°N 2.6385°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 15 metres (49 ft) in diameter. | 1010231 |  Upload Photo |
[108] |
| Bowl barrow 570 m west of Newlands Farm | Chewton Mendip | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 57030 50530 51°15′08″N 2°37′02″W / 51.2523°N 2.6171°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 30 metres (98 ft) in diameter. | 1008093 |  Upload Photo |
[109] |
| Bowl barrow 590 m south-east of Charterhouse Warren Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50581 54816 51°17′25″N 2°42′36″W / 51.2903°N 2.7101°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 20 metres (66 ft) in diameter. | 1008076 |  Upload Photo |
[110] |
| Bowl barrow 600 m east of Priddy Hill Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52037 52814 51°16′21″N 2°41′20″W / 51.2724°N 2.6889°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 22 metres (72 ft) in diameter. | 1010521 |  Upload Photo |
[111] |
| Bowl barrow 600 m north of Rookham Plantation | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 54538 49100 51°14′21″N 2°39′09″W / 51.2393°N 2.6526°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 21 metres (69 ft) in diameter. | 1009774 |  Upload Photo |
[112] |
| Bowl barrow 610 m northwest of Whitestown Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52238 55261 51°17′40″N 2°41′11″W / 51.2945°N 2.6864°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 30 metres (98 ft) in diameter. | 1011536 |  |
[113] |
| Bowl barrow 650 m northeast of Higher Pitts Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 54038 49468 51°14′33″N 2°39′35″W / 51.2425°N 2.6598°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 16 metres (52 ft) in diameter. | 1010649 |  Upload Photo |
[114] |
| Bowl barrow 700 m south of Bristol Plain Farm: part of a linear round barrow cemetery | Rodney Stoke | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50305 51291 51°15′31″N 2°42′49″W / 51.2586°N 2.7135°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 12 metres (39 ft) in diameter. | 1008084 |  Upload Photo |
[115] |
| Bowl barrow 730 m southeast of Bristol Plain Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50931 51694 51°15′44″N 2°42′17″W / 51.2623°N 2.7046°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1010490 |  Upload Photo |
[116] |
| Bowl barrow 750 m southwest of Dale Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 51939 50857 51°15′17″N 2°41′24″W / 51.2548°N 2.6901°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 16 metres (52 ft) in diameter. | 1008214 |  Upload Photo |
[117] |
| Bowl barrow 760 m southeast of Bristol Plain Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50960 51676 51°15′44″N 2°42′15″W / 51.2621°N 2.7042°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 13 metres (43 ft) in diameter. | 1010492 |  Upload Photo |
[118] |
| Bowl barrow 770 m south of Townsend Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 51689 51152 51°15′26″N 2°41′35″W / 51.2571°N 2.6930°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 15 metres (49 ft) in diameter. | 1009743 |  Upload Photo |
[119] |
| Bowl barrow 800 m south of Townsend Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 51735 51113 51°15′26″N 2°41′35″W / 51.2571°N 2.6930°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 16 metres (52 ft) in diameter. | 1009740 |  Upload Photo |
[120] |
| Bowl barrow 810 m southeast of Bristol Plain Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 51003 51646 51°15′42″N 2°42′13″W / 51.2618°N 2.7036°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 20 metres (66 ft) in diameter. | 1010499 |  Upload Photo |
[121] |
| Bowl barrow 820 m south of Bristol Plain Farm: part of a linear round barrow cemetery | Rodney Stoke | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50402 51182 51°15′27″N 2°42′44″W / 51.2576°N 2.7121°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 17 metres (56 ft) in diameter. | 1008089 |  Upload Photo |
[122] |
| Bowl barrow 850 m south of Bristol Plain Farm: part of a linear round barrow cemetery | Westbury | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50448 51142 51°15′26″N 2°42′41″W / 51.2573°N 2.7115°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 10 metres (33 ft) in diameter. | 1008085 |  Upload Photo |
[123] |
| Bowl barrow 850 m south of Townsend Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 51808 51046 51°15′23″N 2°41′31″W / 51.2565°N 2.6919°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 17 metres (56 ft) in diameter. | 1009741 |  Upload Photo |
[124] |
| Bowl barrow 850 m southeast of Bristol Plain Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 51036 51629 51°15′42″N 2°42′11″W / 51.2617°N 2.7031°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 15 metres (49 ft) in diameter. | 1010502 |  Upload Photo |
[125] |
| Bowl barrow 870 m southwest of Charterhouse Warren Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 49221 54528 51°17′15″N 2°43′46″W / 51.2876°N 2.7295°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 16 metres (52 ft) in diameter. | 1010642 |  Upload Photo |
[126] |
| Bowl barrow 870 m southwest of Dale Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 51701 50931 51°15′20″N 2°41′37″W / 51.2555°N 2.6935°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 26 metres (85 ft) in diameter. | 1008217 |  Upload Photo |
[127] |
| Bowl barrow 900 m south west of Bristol Plain Farm: part of a group of round barrows south and south west of Bristol Plain Farm | Rodney Stoke | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 49593 51435 51°15′35″N 2°43′26″W / 51.2598°N 2.7238°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 21 metres (69 ft) in diameter. | 1008784 |  Upload Photo |
[128] |
| Bowl barrow in the garden of Beechbarrow | St Cuthbert Out | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 57071 48924 51°14′16″N 2°36′59″W / 51.2379°N 2.6163°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 20 metres (66 ft) in diameter. | 1020019 |  Upload Photo |
[129] |
| Bowl barrow on Stock Hill: part of the Stock Hill round barrow cemetery | Chewton Mendip | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 55679 50914 51°15′21″N 2°38′11″W / 51.2557°N 2.6365°W |
A bowl barrow, which is 12.5 metres (41 ft) in diameter. | 1014239 |  |
[130] |
| Bracelet Cave | St Cuthbert Out | Cave | Palaeolithic | ST 52283 48340 51°13′56″N 2°41′05″W / 51.2322°N 2.6848°W |
A cave from which nine human skeletons have been uncovered, probably from the Bronze Age. Roman artefacts have also been identified. | 1012062 |  Upload Photo |
[131] |
| Browne's Gate | Wells | Gateway | 1451 | ST5494445852 51°12′36″N 2°38′47″W / 51.210086°N 2.646384°W |
Brown's Gatehouse (also known as the Dean's Eye) is an entrance gateway into a walled precinct, the Liberty of St Andrew, which encloses the twelfth century Cathedral, the Bishop's Palace, Vicar's Close and the residences of the clergy who serve the cathedral. The Brown's Gatehouse was built around 1451, by Bishop Thomas Beckington (also spelt Beckyngton), and provides the entrance to the Bishop's Place from Sadler Street. It is named after the shoemaker Richard Brown, who was the next door tenant in 1553. It is a two-storey building of Doulting ashlar stone, with a Welsh slate roof with coped gables behind parapets. | 1006198 |  |
[132][133][134] |
| Brownes' Hole | Stoke St Michael | Cave | Palaeolithic | ST 66928 47558 51°13′34″N 2°28′30″W / 51.2262°N 2.4750°W |
An extensive cave system believed to contain archaeological artefacts. | 1010709 |  Upload Photo |
[135] |
| Burial chamber (remains of), Murtry Hill, Orchardleigh Park | Buckland Dinham | Chamber tomb | Neolithic | ST 76297 50667 51°15′17″N 2°20′28″W / 51.2547°N 2.3410°W |
A probable burial chamber which was excavated in 1803 and 1804 when human bones and cremation urns were discovered. | 1006174 |  |
[136] |
| Camp 600 yd (548 m) E of Charterhouse | Priddy | Hillfort | Iron Age and Romano-British | ST 50405 55783 51°15′17″N 2°20′28″W / 51.2547°N 2.3410°W |
Charterhouse Camp is a univallate Iron Age hill fort. It is situated approximately 0.97 kilometres (0.6 mi) east from the village of Charterhouse. There is some evidence, in the form of burials in local caves, of human occupation since the late Neolithic times and the early Bronze Age. The site is associated with Charterhouse Roman Town and may have been the site of Iscalis. | 1006195 |  Upload Photo |
[137][138] |
| Central of three duck decoys on Walton Moor, south of Lord Bath's Drove | Walton | Duck decoy | 19th century | ST 45747 33772 51°06′03″N 2°46′34″W / 51.1007°N 2.7762°W |
An island within a square pool which was supplied by four "pipes". Used as a duck decoy | 1014449 |  Upload Photo |
[139] |
| Charterhouse lead works | Priddy | Lead mine | Romano-British | ST 49586 55184 51°17′37″N 2°43′28″W / 51.2935°N 2.7244°W |
The lead and silver mines at Charterhouse, were first operated on a large scale by the Romans, from at least A.D. 49. At first the lead/silver industries were tightly controlled by the Roman military, but within a short time the extraction of these metals was contracted out to civilian companies, probably because the silver content of the local ore was not particularly high. | 1006127 |  |
[140][141] [142][143] |
| Circular earthwork and barrows on Beacon Hill | Doulting | Earthworks | Neolithic | ST 63842 45913 51°12′41″N 2°31′08″W / 51.2113°N 2.5190°W |
Three bowl barrows. | 1006199 |  Upload Photo |
[144] |
| Deserted medieval hamlet E of Draycott | Rodney Stoke | Earthworks | Middle Ages | ST 48876 51586 51°15′40″N 2°44′03″W / 51.2611°N 2.7341°W |
A small medieval farmstead including the foundations of a building, and the surrounding field system. | 1006122 |  Upload Photo |
[145] |
| Deserted medieval farmstead and field system NW of Ebbor Wood | Priddy | Earthworks | Middle Ages | ST 51510 49353 51°14′29″N 2°41′46″W / 51.2413°N 2.6960°W |
The site of medieval farmsteads. The more recent was built around 1788 and was ruined by 1886. | 1006138 |  Upload Photo |
[146] |
| Deserted medieval site SW of Tytherington Bridge | Selwood | Earthworks | Middle Ages | ST 76981 44781 51°12′06″N 2°19′51″W / 51.2018°N 2.3309°W |
A deserted medieval village. | 1006123 |  Upload Photo |
[147][148][149] |
| Deserted medieval site W of Lower Batch Farm | Lamyatt | Earthworks | Middle Ages | ST 65117 35944 51°07′18″N 2°29′59″W / 51.1217°N 2.4998°W |
Earthworks from a deserted medieval village. | 1003749 |  Upload Photo |
[150] |
| Disc barrow 610 m northeast of Drove Cottage | Priddy | Disc barrow | Bronze Age | ST 55910 50083 51°14′54″N 2°37′59″W / 51.2482°N 2.6331°W |
A disc barrow which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter. | 1009746 |  Upload Photo |
[151] |
| Dovecote 220 m north of St Philip and St James's Church | Norton St Philip | Dovecote | 15th century | ST 77130 55926 51°18′07″N 2°19′46″W / 51.3020°N 2.3294°W |
A 15th century Doulting stone dovecote containing approximately 660 nesting boxes. | 1019896 |  Upload Photo |
[152][153] |
| Drying house at The Coach House, Willow Vale | Frome | Drying house | 18th or 19th century | ST 77896 48142 51°13′55″N 2°19′05″W / 51.2320°N 2.3180°W |
A circular stone building, about 5 metres (16 ft) in diameter used for drying cloth from the local woolen industry. | 1016955 |  Upload Photo |
[154] |
| Duck decoy 1 km south east of Manor Farm | Godney | Duck decoy | Before 1736 | ST 47776 41530 51°10′14″N 2°44′54″W / 51.1706°N 2.7484°W |
A duck decoy which survives as waterlogged hollows up to 50 metres (160 ft) in length. | 1014442 |  Upload Photo |
[155] |
| Duck decoy, 590 m south west of Rice Farm | Sharpham | Duck decoy | ? | ST 46779 40362 51°09′36″N 2°45′45″W / 51.1600°N 2.7624°W |
The site of a four pipe duck decoy with two small islands in a square pool. The site was dredged in 1984 and 1985 and still attracts water fowl. | 1014447 |  Upload Photo |
[156] |
| Duck decoy, 820 m SSW of Little Huckham Farm: the western of three decoys on Walton Moor | Walton | Duck decoy | 1823 | ST 44731 34328 51°06′20″N 2°47′27″W / 51.1056°N 2.7908°W |
A duck decoy which survives as an oval pool. | 1014448 |  Upload Photo |
[157] |
| Duck decoy, 950 m south west of junction of Westhay Moor Drove and Lewis's Drove | Meare | Duck decoy | Before 1736 | ST 45807 43087 51°11′04″N 2°46′36″W / 51.1844°N 2.7768°W |
A six pipe duck decoy from which a rectangular pool area can be seen. | 1014435 |  Upload Photo |
[158] |
| Duck decoy east of Barrow Wood Lane | Westbury | Duck decoy | Late 18th or early 19th century | ST 47869 48501 51°14′00″N 2°44′53″W / 51.2333°N 2.7480°W |
A duck decoy with a complex arrangement of ditches and channels, probably used from the late 18th or early 19th century but out of use by 1840. | 1014453 |  Upload Photo |
[159] |
| Duck decoy in Sharpham Park, 600 m south west of Avalon Farm | Sharpham | Duck decoy | ? | ST 46326 38220 51°08′27″N 2°46′07″W / 51.1407°N 2.7686°W |
The site of a four pipe duck decoy with an oval pool approximately 40 metres (130 ft) long with an oval island. The site was dredged in 1985 and still attracts water fowl. | 1014450 |  Upload Photo |
[160] |
| Early Christian settlement and monastic site at Marchey Farm | Wookey | Earthworks | Romano-British to Middle Ages | ST 47960 46211 51°12′46″N 2°44′47″W / 51.2127°N 2.7464°W |
Earthworks from a Christian settlement which was also occupied during the Roman period and Middle Ages. The remains of a rectangular building which is thought to have been a chapel have been identified surrounded by a bank and ditch. The site which was known as Martinsey or Martin's Island and was connected with Glastonbury Abbey. | 1011266 |  Upload Photo |
[161] |
| Earthwork N of Stubbs Wood, Merehead | Wanstrow | Earthworks | Roman or Iron Age | ST 69561 43681 51°11′29″N 2°26′13″W / 51.1915°N 2.4370°W |
An earthwork bank and ditch which may related to a promontory hill fort. | 1006150 |  Upload Photo |
[162] |
| Earthworks S of Tadhill Farm | Downhead | Earthworks | Iron Age | ST 67634 45810 51°12′38″N 2°27′53″W / 51.2106°N 2.4647°W |
A possible camp, cattle enclosure or homestead which may have been occupied during the Iron Age. | 1006169 |  Upload Photo |
[163] |
| Farleigh Hungerford Castle | Farleigh Hungerford | Castle | 14th century | ST8007957661 51°19′04″N 2°17′14″W / 51.317704°N 2.287232°W |
Farleigh Hungerford Castle was built in two phases: the inner court was constructed between 1377 and 1383 by Sir Thomas Hungerford. His son, Sir Walter Hungerford, extended the castle with an additional, outer court, enclosing the parish church in the process. In the English Civil War in 1642, the castle was seized by Royalist forces in 1643, but recaptured by Parliament without a fight near the end of the conflict in 1645. By the 18th century the castle fell into disrepair; in 1730 it was bought by the Houlton family, when much of it was broken up for salvage. In the 1915 Farleigh Hungerford Castle was sold to the Office of Works and a restoration programme began. It is now owned by English Heritage, who operate it as a tourist attraction. | 1015871 |  |
[19][164] |
| Fenny Castle: a motte and bailey castle | Wookey | Motte-and-bailey castle | Middle Ages | ST 50767 43585 51°11′22″N 2°42′19″W / 51.1895°N 2.7053°W |
Fenny Castle is the remains of a motte and bailey castle sited on a natural hillock of Lias approximately 20 metres (66 ft) above the surrounding flat land on the edge of the Somerset Levels. Little remains of the stonework, and there is evidence of extensive quarrying. The mound is now covered in grass and scrub with a few trees. | 1015496 |  |
[21][165] |
| Fenny Castle Cross: a medieval wayside cross 20 m north west of Castle Farm, Castle | Wookey | Cross | 14th century | ST 50838 44078 51°11′38″N 2°42′18″W / 51.1938°N 2.7049°W |
The remains of a wayside cross with three square steps. | 1015797 |  |
[166][167] |
| Five bowl barrows 500 m north west of Cuckoo Cleeves: part of the Stock Hill round barrow cemetery | Chewton Mendip | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST 55708 50973 51°15′22″N 2°38′10″W / 51.2561°N 2.6361°W |
Five bowl barrows which range from 10 metres (33 ft) to 27 metres (89 ft) in diameter. | 1014775 |  Upload Photo |
|
| Four round barrows SE of Miners' Arms Inn, Chewton Rabbit Warren | Chewton Mendip | Round barrow | Bronze Age | ST 54612 51688 51°15′45″N 2°39′06″W / 51.2625°N 2.6518°W |
A group of round barrows. | 1006215 |  Upload Photo |
[168][169] [169][170] |
| Fussell's Lower Works: an iron edge tool works, 210 m south east of Wadbury | Mells | Iron works | 1740s | ST 73903 48879 51°14′16″N 2°22′36″W / 51.2378°N 2.3767°W |
The Old Iron Works is a 0.25 hectare biological Site of Special Scientific Interest. The site is a ruined iron works, which mainly produced agricultural edge-tools which were exported all over the world, and is now, in addition to its unique and major importance in relation to industrial archaeology, used as a breeding site by horseshoe bats. It is included in the Heritage at Risk Register produced by Historic England. | 1019796 |  |
[22][171] [172][173] [174] |
| Glastonbury Abbey | Glastonbury | Abbey | pre Norman Conquest | ST5005838781 51°08′46″N 2°42′55″W / 51.146101°N 2.71534°W |
Glastonbury Abbey was a monastery founded in the 7th century and enlarged in the 10th, before a major fire in 1184 destroyed the buildings. It was rebuilt and by the 14th century was one of the richest and most powerful monasteries in England. The abbey was suppressed during the Dissolution of the Monasteries under King Henry VIII of England. The last abbot, Richard Whiting (Whyting), was hanged, drawn and quartered as a traitor on Glastonbury Tor in 1539. From at least the 12th century the Glastonbury area was frequently associated with the legend of King Arthur, a connection promoted by medieval monks who asserted that Glastonbury was Avalon. Christian legends have also claimed that the abbey was founded by Joseph of Arimathea in the 1st century. The ruins of Glastonbury Abbey were purchased by the Bath and Wells Diocesan Trust in 1908 and are now the property of and managed by the Glastonbury Abbey trust. | 1021077 |  |
[175][176][177] |
| Glastonbury Lake Village | near Godney | Crannog | Iron Age | ST 49286 40757 51°09′49″N 2°43′33″W / 51.1636°N 2.7258°W |
Glastonbury Lake Village was an Iron Age village on a 'crannog' or man made island in the Somerset Levels. It has been described as "the best preserved prehistoric village ever found in the United Kingdom". The site covered an area of 122 metres (400 ft) north to south by 91 metres (300 ft) east to west. It was first constructed 250 B.C. by laying down timber and clay. Wooden houses and barns were then built on the clay base and occupied by up to 200 people at any time until the village was abandoned around 50 B.C. | 1006156 |  |
[9][10][178] [179][180] [181][182] [183][184][185] |
| Group of round barrows 750 m north west of Ivy Cottage | St Cuthbert Out | Round barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 54217 48700 51°14′08″N 2°39′26″W / 51.2356°N 2.6572°W |
Four round barrows which range from 10 metres (33 ft) to 23 metres (75 ft) in diameter. | 1020494 |  Upload Photo |
[186] |
| Group of seven round barrows 380 m east of East Water Drove (Part of Priddy Nine Barrows Cemetery) | Priddy | Round barrows | Bronze Age | ST 53911 52055 51°15′46″N 2°39′45″W / 51.2628°N 2.6625°W |
Priddy Nine Barrows and Ashen Hill Barrow Cemeteries are a collection of round barrows, dating from the Bronze Age. The barrows sit on crests of land at either end of a field in an area of the Mendip Hills with several Neolithic remains. They are assumed to be related to the Priddy Circles which lie 750 metres (2,460 ft) to the north. Ashen Hill consists of six bowl barrows and two bell barrows aligned east to west while Priddy Nine Barrows divided into one group of seven round barrows and another pair slightly separated from the others. Excavations in 1815 uncovered cremation burials and grave goods. A geophysical magnetometry survey suggested that there may have been three further barrows. | 1010506 |  |
[6][7][8] |
| Group of three bowl barrows and one long barrow 90 m northeast of Barrow House Farm | Chewton Mendip | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 60096 53286 51°16′38″N 2°34′25″W / 51.2773°N 2.5735°W |
Three bowl barrows and a long barrow which vary between 18 metres (59 ft) and 24 metres (79 ft) in diameter. | 1011528 |  Upload Photo |
[187] |
| Hales Castle: a ringwork and associated earthworks on Coles Hill | Frome | Motte-and-bailey castle | Middle Ages | ST 79748 44223 51°11′50″N 2°17′28″W / 51.1971°N 2.291°W |
Hales Castle was a medieval castle was built, probably in the years immediately after the Norman conquest of England in 1066. The circular ringwork is 37 metres (120 ft) in diameter and stands on the northern slope of Roddenbury Hill, close to the Iron Age Roddenbury Hillfort. It comprises banks and outer ditches and has an unfinished bailey. | 1008805 |  |
[188] |
| Henge 370 m north east of Drove Cottage | Priddy | Henge | Neolithic | ST 55915 49786 51°14′45″N 2°38′00″W / 51.2457°N 2.6332°W |
Drove Cottage Henge is situated in a valley. The bank circumscribing the henge is about 11.5 metres (38 ft) thick and 0.4 metres (1.3 ft) high, with a diameter of around 54 metres (177 ft) when measuring from the outsides of the banks. Just inside this bank is a ditch 6 metres (20 ft) wide and 0.3 metres (0.98 ft) deep, enclosing a circular central area about 19 metres (62 ft) in diameter. In the northern portion of this central area is a low-lying mound in front of the exit, which appears as a break in the outside bank. | 1015795 |  Upload Photo |
[189][190] |
| Hillfort at Fox Covert, 550 m north east of Lamyatt Lodge | Lamyatt | Earthworks | Iron Age | ST 66610 36648 51°07′41″N 2°28′43″W / 51.1281°N 2.4785°W |
An early Iron Age earthwork, probably a stock enclosure but known as Fox Covert, occupies 3.25 hectares (8.0 acres) on a spur of Creech Hill overlooking the River Alham valley. | 1016303 |  Upload Photo |
[191][192][193] |
| Hillfort on Roddenbury Hill | Selwood | Hill fort | Iron Age | ST 79782 43925 51°11′42″N 2°17′28″W / 51.195°N 2.2911°W |
Roddenbury Hillfort is a univallate Iron Age hillfort. The site covers 0.84 hectares (2.1 acres). It some places the protective bank has been destroyed in others it remains up to 1.6 metres (5.2 ft) high and has a 1.8 metres (5.9 ft) ditch below it. | 1008804 |  |
[194] |
| Kingsdown camp, Mells Down | Buckland Dinham | Univallate hill fort | Iron Age | ST 71837 51733 51°15′51″N 2°24′12″W / 51.2642°N 2.4033°W |
Kingsdown Camp is an Iron Age hill fort. It is a univallate fort with an area of 0.15 hectares (0.37 acres), and is approximately quadrilateral in shape. In the Iron Age or Roman period a drystone wall was constructed, possibly 4 metres (13 ft) high and 2.5 metres (8 ft) wide. There is an entrance on the northeast side. The fort continued to be used by the Romans. | 1006219 |  Upload Photo |
[195][196] |
| King's Castle enclosures, Iron Age defended settlement | St Cuthbert Out | Hill fort | Iron Age | ST 56882 45641 51°12′30″N 2°37′09″W / 51.2084°N 2.6191°W |
King's Castle is an Iron Age enclosed hilltop settlement at the south-western edge of the Mendip Hills. It consists of two or three interlinked sub-enclosures, with what appears to be a field system extending to the east; an unusual layout, the site remains relatively little studied and has not been archaeologically excavated. It is a scheduled monument, and shares its name with the surrounding King's Castle Wood—today a Somerset Wildlife Trust nature reserve—though this name is probably a modern invention. | 1008807 |  Upload Photo |
[197][198] [199][200][201] |
| Lake villages NW of Oxenpill | Meare | Crannog | Iron Age | ST 44388 42200 51°10′35″N 2°47′44″W / 51.1764°N 2.7956°W |
Meare Lake Village is the site of an Iron Age settlement on the Somerset Levels. In prehistoric times there were two villages situated within the now-drained Meare Pool, occupied at different times between 300 B.C. and 100 AD. The villages were built on a morass on an artificial foundation of timber filled with brushwood, bracken, rubble and clay. | 1006160 |  Upload Photo |
[11][12] [202][203] [204][205] |
| Lime Kiln Hill Quarry Cave | Mells | Cave | Palaeolithic | ST 73062 48659 51°14′11″N 2°23′14″W / 51.2365°N 2.3872°W |
A cave from which Pleistocene faunal remains and a Middle Palaeolithic chert hand axe have been recovered. | 1012068 |  Upload Photo |
[206] |
| Linear barrow cemetery comprising six bowl barrows 510 m south west of Townsend Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST 51528 51658 51°15′43″N 2°41′46″W / 51.2620°N 2.6961°W |
Six bowl barrows in a line. Each is between 10 metres (33 ft) and 23 metres (75 ft) in diameter. | 1009744 |  Upload Photo |
[207] |
| Linear earthwork in Butleigh Wood | Butleigh | Earthworks | Iron Age or Middle Ages | ST 50396 33139 51°05′43″N 2°42′35″W / 51.0954°N 2.7097°W |
The New Ditch is a linear earthwork of possible Iron Age or Medieval construction. Its construction is similar to Ponter's Ball Dyke 4.8 kilometres (3 mi) to the northeast, with the dyke on the south east of the embankment, but of less massive construction. Both were probably part of a more extensive defence scheme. It is nearly 0.8 kilometres (0.5 mi) in length and was probably of greater extent originally, but as it stands, New Ditch cannot be termed a cross-ridge dyke although it does seem to be a boundary work. It is debatable whether this site is ancient because it is located close to a medieval woodland and a deer park. | 1006152 |  |
[208][209] |
| Long barrow 180 m north of Lime House | Chewton Mendip | Long barrow | Neolithic | ST 60095 53061 51°16′31″N 2°34′25″W / 51.2753°N 2.5735°W |
A long barrow which is 48 metres (157 ft) long and 27 metres (89 ft) wide. | 1011526 |  Upload Photo |
[210] |
| Long barrow 230 m east of Chewton Plot | Chewton Mendip | Long barrow | Neolithic | ST 61113 52907 51°16′26″N 2°33′32″W / 51.2740°N 2.5588°W |
A long barrow which is 28 metres (92 ft) long and 12 metres (39 ft) wide | 1011524 |  Upload Photo |
[211] |
| Long barrow 370 m south-south-east of Castle Farm | Chewton Mendip | Long barrow | Neolithic | ST 54519 52548 51°16′13″N 2°39′12″W / 51.2703°N 2.6533°W |
A long barrow which is 30 metres (98 ft) long and 14 metres (46 ft) wide. | 1011525 |  Upload Photo |
[212] |
| Long barrow and bowl barrow 430 m north west of the Mendip Nature Research Station | St Cuthbert Out | Long barrow and bowl barrow | Neolithic | ST 58589 49575 51°14′38″N 2°35′41″W / 51.2438°N 2.5946°W |
A long barrow which is 29 metres (95 ft) long and 12 metres (39 ft) wide and a bowl barrow which is 11 metres (36 ft) in diameter. | 1020548 |  Upload Photo |
[213] |
| Long barrow 600 m east north east of Brimble Pit Pool | Priddy | Long barrow | Neolithic | ST 51412 50909 51°15′19″N 2°41′51″W / 51.2553°N 2.6976°W |
A long barrow which is 30 metres (98 ft) long and 11 metres (36 ft) wide. | 1010389 |  Upload Photo |
[214] |
| Long barrow, round barrow and cairn on Pen Hill | St Cuthbert Out | Long barrow | Neolithic | ST 56348 48679 51°14′08″N 2°37′36″W / 51.2356°N 2.6266°W |
A long barrow which is 44 metres (144 ft) long and 13 metres (43 ft) wide, a round barrow and a cairn. | 1020018 |  Upload Photo |
[215] |
| Maesbury Castle small multivallate hillfort | Croscombe | Hill fort | Iron Age | ST 60994 47168 51°13′20″N 2°33′35″W / 51.2222°N 2.5597°W |
Maesbury Castle is an Iron Age hill fort. The enclosure has an area of 2.5 hectares (6.2 acres), and lies at a height of 292 metres (958 ft). The fort has a single rampart up to 6 metres (20 ft) high, with an outer ditch (univallate). Entrances are to the south-east and north-east (with possible outworks). | 1015494 |  |
[143][216][217] |
| Market cross in the market place | Shepton Mallet | Market cross | 16th century | ST 61887 43652 51°11′27″N 2°32′48″W / 51.1908°N 2.5468°W |
The hexagonal market cross was built in the early 16th century. The central column is surrounded by six segmental arches which were added around 1700. Six rebels from the Monmouth Rebellion were executed at the site in 1685. | 1019974 |  |
[23] |
| Marston Moat | Trudoxhill | Earthwork | 12th century | ST 76753 43814 51°11′43″N 2°20′24″W / 51.1953°N 2.3400°W |
Marston Moat is the site of a fortified manor house built before 1195. The 7.0 metres (23 ft) wide moat which measures 33 metres (108 ft) by 57 metres (188 ft) has a 3.0 metres (10 ft) wide and 0.30 metres (1 ft) high bank on its south and east sides. | 1016302 |  Upload Photo |
[218][219][220] |
| Medieval and post-medieval coal mining remains in Harridge Wood and Edford Wood South | Ashwick | Earthworks | Middle Ages | ST 65397 48181 51°13′54″N 2°29′49″W / 51.2318°N 2.4970°W |
Earthworks including mounds, spoil tips and bell pits from coal mining which continued at the site until the 17th or 18th century. | 1019023 |  Upload Photo |
[221] |
| Medieval coal mining remains immediately south of Benter Cross | Ashwick | Earthworks | Middle Ages | ST 64823 48884 51°14′17″N 2°30′19″W / 51.2380°N 2.5053°W |
Earthworks including spoil mounds and shafts from coal mining in the medieval period which may have start as early as the Roman occupation of Britain. | 1019022 |  Upload Photo |
[222] |
| Medieval wayside cross at Bodden | Doulting | Cross | Middle Ages | ST 63977 44050 51°11′40″N 2°31′01″W / 51.1945°N 2.5169°W |
A square base with the 0.4 metres (1 ft 4 in) remains of the shaft of a cross. | 1015798 |  Upload Photo |
[223] |
| Medieval farmstead, E of Butleigh Wood | Butleigh | Earthworks | Middle Ages | ST 50674 33451 51°05′54″N 2°42′21″W / 51.0982°N 2.7058°W |
Earthworks from a deserted medieval settlement. | 1006132 |  Upload Photo |
[224] |
| Medieval standing cross 50 m west of St Peter's Church | Evercreech | Market cross | 15th century | ST 64891 38681 51°08′47″N 2°30′12″W / 51.1463°N 2.5033°W |
The market cross stands on four steps and a 3 metres (9.8 ft) high shaft. In the 19th century the cruciform head was restored. | 1016232 |  |
[225][226] |
| Medieval standing cross 80 m south of St Mary's Church | Croscombe | Cross | 14th century | ST5904144349 51°11′49″N 2°35′15″W / 51.1969°N 2.5876°W |
An octagonal base of three steps supports the shaft of the cross. The lower 0.3 metres (1 ft 0 in) of the shaft is original. The upper part is more recent. | 1015796 |  |
[227] |
| Moated manor house site, Spargrove Farm | Batcombe | Earthwork | Middle Ages | ST 67044 37918 51°08′23″N 2°28′21″W / 51.1396°N 2.4724°W |
Earthwork remains of a deserted medieval village surrounded by a moat. It was deserted in the 16th century. | 1006151 |  Upload Photo |
[228] |
| Murtry Old Bridge | Buckland Dinham | Bridge | 15th century | ST 76436 49915 51°14′52″N 2°20′20″W / 51.2479°N 2.3390°W |
A stone arch bridge. Two of the arches are original the other has been replaced. | 1006176 |  Upload Photo |
[229] |
| Nunney Castle | Nunney | Castle | 14th century | ST 73671 45731 51°12′37″N 2°22′43″W / 51.2103°N 2.3786°W |
Nunney Castle was built in the late 14th century by Sir John Delamare on the profits of his involvement in the Hundred Years' War, the moated castle's architectural style, possibly influenced by the design of French castles, has provoked considerable academic debate. Remodelled during the late 16th century, Nunney Castle was damaged during the English Civil War and is now ruined. The architectural historian Nikolaus Pevsner has described Nunney as "aesthetically the most impressive castle in Somerset." | 1014716 |  |
[20] |
| Outlook Cave | Ebbor Gorge | Cave | Neolithic | ST 52464 48644 51°14′06″N 2°40′56″W / 51.2350°N 2.6823°W |
Human and animal bones from the Neolithic were recovered from the cave in 1907. | 1010711 |  Upload Photo |
[230] |
| Pair of bowl barrows 350 m NNE of Whitnell Corner | Emborough | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 59818 49081 51°14′22″N 2°34′37″W / 51.2395°N 2.5770°W |
Two bowl barrows, one of which is 30 metres (98 ft) in diameter and the other 18 metres (59 ft). | 1008081 |  |
[231] |
| Pair of bowl barrows 405 m east of East Water Drove (Part of Priddy Nine Barrows Cemetery) | Chewton Mendip | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST 53866 51730 51°15′46″N 2°39′45″W / 51.2629°N 2.6626°W |
Priddy Nine Barrows and Ashen Hill Barrow Cemeteries include two bowl barrows which are separated from the others. Similarly to the other seven they are around 20 metres (66 ft) in diameter and rise to between 2.5 metres (8 ft 2 in) and 3 metres (9.8 ft) high. | 1010503 |  |
[8] |
| Pair of bowl barrows 640 m south of Bristol Plain Farm: part of a linear round barrow cemetery | Rodney Stoke | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 50252 51353 51°15′33″N 2°42′51″W / 51.2592°N 2.7143°W |
Two bowl barrows, one of which is 19 metres (62 ft) in diameter and the other 20 metres (66 ft). | 1008091 |  Upload Photo |
[232] |
| Part of the Hospital of St Mary Magdalene, Magdalene Street | Glastonbury | Almshouses | 1444 | ST 49885 38659 51°08′42″N 2°43′04″W / 51.1450°N 2.7178°W |
In the 1070s St Margaret's Chapel was built on Magdelene Street, originally as a hospital and later as almshouses for the poor. The building dates from 1444. The roof of the hall is thought to have been removed after the Dissolution, and some of the building was demolished in the 1960s. It is Grade II* listed, and a scheduled monument. In 2010 plans were announced to restore the building. | 1020789 |  |
[233][234] [235][236][237] |
| Ponter's Ball linear earthwork | Glastonbury | Dyke | Possibly 3rd century B.C. or post-Roman | ST 53200 37632 51°08′17″N 2°40′06″W / 51.1380°N 2.6682°W |
Ponter's Ball Dyke is a linear earthwork. It consists of an embankment with a ditch on the east side. The current visible remains extend to just over 1 kilometre (0.62 mi). Interpretation of the site is not clear. It is possible that it was part of a longer defensive barrier associated with New Ditch three miles to the south-west which is built in a similar manner. It has been suggested that it is part of a great Celtic sanctuary, probably 3rd century B.C., while others date it to the post-Roman period and connect it with the Dark Age occupation on Glastonbury Tor. The 1970 excavation suggests the 12th century or later. | 1006154 |  |
[238][239] [18][240] |
| Priddy Circle and barrow cemetery 400 m north of Castle of Comfort Inn | Priddy | Earthwork enclosures | Neolithic | ST 54011 52781 51°16′21″N 2°39′39″W / 51.2725°N 2.6608°W |
Priddy Circles are a linear arrangement of four circular earthwork enclosures. They are described as 'probable Neolithic ritual or ceremonial monuments similar to a henge'. | 1015501 |  Upload Photo |
[143] [241][242] |
| Priddy Glebe Barrow: a bowl barrow 25 m north of St. Lawrence's Church | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52817 51415 51°15′36″N 2°40′39″W / 51.2599°N 2.6776°W |
A bowl barrow which is 25 metres (82 ft) in diameter. | 1009765 |  Upload Photo |
[243] |
| Rhinoceros Hole, Wookey | St Cuthbert Out | Cave | Paleolithic | ST 53238 47930 51°13′43″N 2°40′16″W / 51.2286°N 2.6711°W |
A collapsed rock shelter which was used by humans between 100,000 and 40,000 years ago. | 1010292 |  Upload Photo |
[244] |
| Rode Bridge | Rode | Bridge | c. 1777 | ST 80237 54309 51°17′15″N 2°17′05″W / 51.2876°N 2.2848°W |
A stone two-arch bridge over the River Frome. | 1006180 |  |
[245] |
| Roman amphitheatre 1/2 mile (800 m) N of Charterhouse | Charterhouse | Amphitheatre | Romano-British | ST 49887 56506 51°18′20″N 2°43′13″W / 51.3055°N 2.7203°W |
The amphitheatre stood west of Charterhouse Roman Town. It is the only one in England to exist at a lead mine. It measures 32 metres (105 ft) by 24.4 metres (80 ft) and the banks for the seating survive 4.5 metres (15 ft) above the arena. It was probably a place of entertainment for the soldiers at the Roman fort which was established here. | 1006193 |  Upload Photo |
[246][247][248] |
| Roman building 270 m north east of Priddy church | Priddy | Earthwork | Romano-British | ST 53095 51461 51°15′37″N 2°40′25″W / 51.2604°N 2.6736°W |
The site of as Roman building. Artefacts from the 1st to 3rd centuries have been uncovered. | 1015497 |  Upload Photo |
[249] |
| Roman building 600 yd (549 m) SW of Lower Sutton Farm | Ditcheat | Earthwork | Romano-British | ST 61784 33297 51°05′52″N 2°32′50″W / 51.0977°N 2.5471°W |
Earthworks from a Roman settlement. Pottery from the 3rd and 4th centuries has been uncovered. | 1002956 |  Upload Photo |
[250] |
| Roman building at Lamyatt Beacon, Creech Hill | Lamyatt | Earthwork | Romano-British | ST 67009 36213 51°07′27″N 2°28′22″W / 51.1242°N 2.4728°W |
Lamyatt Beacon marks the highest area of Creech Hill. It is the site of a Romano-Celtic temple, which was in use from 250 A.D. to 375 A.D. | 1003748 |  Upload Photo |
[251] |
| Roman settlement at Town Field | Priddy | Earthwork | Romano-British | ST 50112 56275 51°18′12″N 2°43′01″W / 51.3034°N 2.7170°W |
Charterhouse Roman Town grew up around the north-western edge of prehistoric lead and silver mines, which were exploited by the Romans. Extraction is thought to have begun as early as 49 A.D. and continued until at least the 4th century. | 1006194 |  Upload Photo |
[141][252] |
| Romano-British settlement on Stoke Moor | Rodney Stoke | Earthwork | Romano-British | ST 45999 48984 51°14′15″N 2°46′30″W / 51.2375°N 2.7749°W |
Earthworks from a 18.5 hectares (46 acres) Roman settlement. Coins and pottery from the 1st to 3rd centuries have been uncovered. | 1011125 |  Upload Photo |
[253] |
| Roman villa complex, 330 m south-west of St Algar's Farm | Selwood | Roman villa | Romano-British | ST7832341854 51°10′32″N 2°18′41″W / 51.1755°N 2.3115°W |
Earthworks from a Roman villa surrounded by an enclosure with a ditch surrounding 100 square metres (1,100 sq ft) from which a large number of artefacts have been recovered. | 1006153 |  Upload Photo |
[254] |
| Roman villa NW of Port Way | Hemington | Roman villa | Romano-British | ST 76283 53104 51°16′36″N 2°20′29″W / 51.2766°N 2.3414°W |
Earthworks from a Roman villa. | 1006140 |  Upload Photo |
[255] |
| Roman villa NW of Two Acre Plantation | Street | Roman villa | Romano-British | ST 48882 34624 51°06′31″N 2°43′54″W / 51.1086°N 2.7316°W |
Earthworks from a Roman villa. | 1006182 |  Upload Photo |
[256] |
| Round barrow cemetery 470 m and 400 m north of Pen Hill Farm | St Cuthbert Out | Round barrow | Bronze Age | ST 55718 48611 51°14′06″N 2°38′08″W / 51.2350°N 2.6356°W |
A round barrow cemetery consisting of five bowl barrows and two cairns. | 1020207 |  Upload Photo |
[257] |
| Round barrow 1435 m SE of Miners' Arms Inn | Chewton Mendip | Round barrow | Bronze Age | ST 55633 51528 51°15′40″N 2°38′14″W / 51.2612°N 2.6372°W |
A mound which may be a barrow or a spoil heap. | 1006216 |  Upload Photo |
[258] |
| Round barrow in Beacon Plantation | Doulting | Round barrow | Bronze Age | ST 64093 45873 51°12′39″N 2°30′54″W / 51.2109°N 2.515°W |
A group of six round barrows. | 1006178 |  Upload Photo |
[259] |
| Round barrow on Beacon Hill | Ashwick | Round barrow | Bronze Age | ST 63564 46118 51°12′47″N 2°31′23″W / 51.2131°N 2.5230°W |
Three round barrows. | 1003030 | [260] | |
| Round barrows in and near Wright's Piece | Priddy | Round barrow | Bronze Age | ST 52550 54693 51°17′22″N 2°40′54″W / 51.2894°N 2.6818°W |
A collection of round barrows. | 1006218 |  |
[261] |
| Round barrows SW of Cleeve's Plantation | Chewton Mendip | Round barrow | Bronze Age | ST 56255 50731 51°15′15″N 2°37′42″W / 51.2541°N 2.6282°W |
A probable bowl barrow. | 1003027 |  Upload Photo |
[262] |
| Rowberrow: a bowl barrow 40 m north of Hill View | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST 52248 52340 51°16′06″N 2°41′09″W / 51.2682°N 2.6858°W |
A bowl barrow which is 22 metres (72 ft) in diameter. | 1010391 |  Upload Photo |
[263] |
| Savory's Hole | St Cuthbert Out | Cave | Palaeolithic | ST 52863 48811 51°14′11″N 2°40′36″W / 51.2365°N 2.6766°W |
A cave in Ebbor Gorge from which human bones have been recovered. | 1012061 |  Upload Photo |
[264] |
| Section of medieval road, south of Pomparles Bridge, north of Street | Street | Road | Middle Ages | ST 48672 37514 51°08′05″N 2°44′06″W / 51.1346°N 2.7350°W |
The site of a medieval road. | 1014443 |  Upload Photo |
[265] |
| Section of the Abbot's Way trackway, 500 m WSW of Honeygar Farm | Meare | Timber trackway | Neolithic | ST 41979 42583 51°10′46″N 2°49′53″W / 51.1795°N 2.8314°W |
The site of the preserved remains of the Abbot's Way a corduroy timber trackway which was built between 2630 and 2280 B.C. | 1014432 |  Upload Photo |
[265] |
| Sections of the Sweet Track and Post Track, 240 m south west of Sunnyside Farm | Meare | Timber trackway | 3807 or 3806 B.C. | ST 42865 41721 51°10′19″N 2°49′07″W / 51.1719°N 2.8186°W |
A section of the Sweet Track, an ancient causeway built in either 3807 or 3806 B.C. and the earlier structure, the Post Track. Construction was of crossed wooden poles, driven into the waterlogged soil to support a walkway that consisted mainly of planks of oak, laid end-to-end. The track was only used for a period of around 10 years and was then abandoned, probably due to rising water levels. | 1014440 |  Upload Photo |
[266] |
| Sections of the Sweet Track and Post Track, 250 m ESE of Station House | Meare | Timber trackway | 3807 or 3806 B.C. | ST 42590 41139 51°10′00″N 2°49′21″W / 51.1666°N 2.8225°W |
A section of the Sweet Track, an ancient causeway built in either 3807 or 3806 B.C. and the earlier structure, the Post Track. Construction was of crossed wooden poles, driven into the waterlogged soil to support a walkway that consisted mainly of planks of oak, laid end-to-end. The track was only used for a period of around 10 years and was then abandoned, probably due to rising water levels. | 1014831 |  Upload Photo |
[267] |
| Small Down Knoll camp | Evercreech | Hill fort | Bronze Age | ST 66623 40624 51°09′51″N 2°28′49″W / 51.1642°N 2.4803°W |
Small Down Knoll, or Small Down Camp, is a Bronze Age hill fort. Finds of flints indicate a prehistoric Mesolithic occupation. The fort has multiple ramparts (multivallate) following the contours of the hilltop, enclosing an area of about 2.4 ha (6 acres). Most of the perimeter is a double rampart, but the flatter eastern side has an extra counterscarp rampart with well-defined double ditches. There are two entrances to the south-east: one is a simple opening with evidence of a guardhouse; and the other shows linear features of a holloway. The fort contains about 14 round barrows (tumuli), which form a line of burials running east–west along the crest of the hill. The fort and the barrows appear to be Bronze Age, but excavations have found some Iron Age pottery in the barrows and the ditches. | 1006175 | 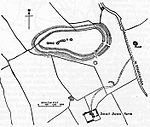 |
[268][269][270] |
| Small multivallate promontory fort on Blacker's Hill | Chilcompton | Hill fort | Iron Age | ST 63666 50051 51°14′58″N 2°31′20″W / 51.2494°N 2.5222°W |
Blacker's Hill is roughly rectangular and is a promentary type. It covers 6 hectares (15 acres) and originally had two ramparts and two ditches, but on the west and south sides it was defended by the steep drop. In some places the ramparts survive to a considerable height but on the north east side the inner rampart and ditch have been destroyed. There are three gaps but only that on the east seems to be original. | 1015493 |  Upload Photo |
[271][272] |
| St Cuthbert's and Chewton lead mines and Fair Lady Well | Priddy | Lead mines | Roman to late 19th century | ST 54555 50561 51°15′09″N 2°39′09″W / 51.2524°N 2.6526°W |
The remains of lead mines used between the Romano-British era until the late 19th century. It consists of a series of earthen banks and pools; however the buildings no longer exist. Fair Lady Well is a stone chamber over a spring which was constructed in the Middle Ages. | 1421084 |  Upload Photo |
[273] |
| St Michael's Church, monastic remains, and other settlement remains on Glastonbury Tor | Glastonbury Tor | Ruined church tower | 13th century | ST5121838615 51°08′41″N 2°41′55″W / 51.144709°N 2.698735°W |
Several buildings have been constructed on the summit of Glastonbury Tor during the Saxon and early medieval periods; they have been interpreted as an early church and monks' hermitage. The head of a wheel cross dating from the 10th or 11th century has been recovered. The original wooden church was destroyed by an earthquake in 1275, and the stone Church of St Michael built on the site in the 14th century. Its tower remains, although it has been restored and partially rebuilt several times. Archaeological excavations during the 20th century sought to clarify the background of the monument and church, but some aspects of their history remain unexplained. | 1019390 |  |
[274][275] |
| Stow Barrow : a bowl barrow 700 m southwest of Haydon Grange Farm | Priddy | Bowl barrow | Neolithic to Bronze Age | ST 52065 53537 51°16′44″N 2°41′19″W / 51.2789°N 2.6886°W |
A bowl barrow which is 35 metres (115 ft) in diameter. | 1010522 |  Upload Photo |
[276] |
| Tedbury Camp | Great Elm | Multivallate hill fort | Iron Age | ST 74347 48794 51°14′16″N 2°22′05″W / 51.2378°N 2.3681°W |
Promontory hill fort defended by two parallel banks. Also the site of Roman occupation and a coin hoard. | 1006163 |  |
[277][278] |
| The Abbey Barn at Abbey Farm | Glastonbury | Barn | 14th century | ST5036138551 51°08′39″N 2°42′40″W / 51.14406°N 2.710977°W |
The Tithe Barn is now the venue for the Somerset Rural Life Museum. It is a museum of the social and agricultural history of Somerset, housed in buildings surrounding a 14th-century barn once belonging to Glastonbury Abbey. It was used as a Tithe barn for the storage of arable produce, particularly wheat and rye, from the abbey's home farm of approximately 212 hectares (524 acres). Threshing and winnowing would also have been carried out in the barn. The barn which was built from local shelly limestone, with thick timbers supporting the stone tiling of the roof. After the Dissolution of the Monasteries in 1539 the barn was given to the Duke of Somerset. By the early 20th century it was being used as a farm store by the Mapstone family. In 1974 they donated it to Somerset County Council and between 1976 and 1978 underwent restoration. | 1019389 |  |
[16][279] |
| The Abbot's Fish House and fishponds | Meare | Fish house | 14th century | ST4580441729 51°10′20″N 2°46′36″W / 51.172219°N 2.776593°W |
The Abbot's Fish House was built in the 14th century. It is the only surviving monastic fishery building in England. Fishing was an important source of food for the monks of Glastonbury Abbey. Fishing was carried out in artificial ponds, which were mentioned at Meare in the Domesday Book and from the River Brue and Meare Pool. The present rectangular stone building was constructed by the abbot between 1322 and 1335 for the storage and processing of the fish and as a residence for the chief fisherman. After the Dissolution of the Monasteries the building fell into disrepair and it was seriously damaged by fire in the 1880s. Some restoration has been undertaken during the 20th century, including the replacement of the roof in the 1920s. | 1008018 |  |
[17][280][281] |
| The Devil's Bed and Bolster long barrow | Beckington | Long barrow | Neolithic | ST 81495 53333 51°16′44″N 2°16′00″W / 51.2788°N 2.2667°W |
The long barrow is 35 metres (115 ft) long and 21 metres (69 ft) wide. | 1017897 |  |
[282] |
| The easternmost of three duck decoys on Walton Moor | Walton | Duck decoy | 19th century | ST 46078 33855 51°06′05″N 2°46′17″W / 51.1014°N 2.7715°W |
The remains of a duck decoy with a central island. | 1014446 |  Upload Photo |
[283] |
| The Falconry, Farleigh Hungerford | Norton St Philip | Falconry | 14th or 15th century | ST 79676 58022 51°19′15″N 2°17′35″W / 51.3209°N 2.2930°W |
A rectangular stone two-storey cartshed and falconry. | 1006172 |  Upload Photo |
[284] |
| The tithe barn | Doulting | Tithe barn | 15th century | ST 64725 43024 51°11′07″N 2°30′20″W / 51.1854°N 2.5056°W |
The Tithe Barn was built in the 15th century. Tithe barns were used to store tithes, from the local farmers to the ecclesiastical landlords. In this case the landlord was Glastonbury Abbey. | 1003025 |  |
[285] |
| Tithe Barn, Pilton | Pilton | Tithe barn | 14th century | ST5890140630 51°09′48″N 2°35′21″W / 51.163432°N 2.589142°W |
The Tithe Barn in Pilton was built in the 14th century as a tithe barn to hold produce for Glastonbury Abbey. It was damaged by fire in 1963 and it remained a wreck until Michael Eavis, organiser of the Glastonbury Festival, bought it in 1995, and presented the barn to the Pilton Barn Trust. The project was made possible with a grant of £400,000 from English Heritage. The Glastonbury festival contributed a further £100,000. | 1006224 |  |
[15][286][287][288] |
| The Tribunal | Glastonbury | House | 15th century | ST4993438961 51°08′52″N 2°43′02″W / 51.147709°N 2.717137°W |
The Tribunal was built in the 15th century as a merchant's house. The history of the building is not well documented, although the majority of the present stone house was constructed in the 15th century on the site of a 12th-century wooden building. The current front wall was added in the 16th century. It has been used as a merchant's house and possibly a shop and school. The building is currently in the guardianship of English Heritage and used as a tourist information centre. On the first floor is the museum of the Glastonbury Antiquarian Society which houses artefacts from Glastonbury Lake Village. | 1014714 |  |
[289][290] |
| Three bowl barrows at Green Ore, two 150 m south east and one 420 m south west of Newlands Farm | St Cuthbert Out | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST 57267 50230 51°14′59″N 2°36′49″W / 51.2496°N 2.6136°W |
Three bowl barrows each around 15 metres (49 ft) in diameter. | 1020546 |  Upload Photo |
[291] |
| Three bowl barrows 400 m north west of Haydon Hut | St Cuthbert Out | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST 57865 48927 51°14′17″N 2°36′18″W / 51.2380°N 2.6049°W |
A bowl barrow which is 22 metres (72 ft) in diameter. | 1020021 |  Upload Photo |
[292] |
| Three bowl barrows in Big Plantation, 690 m south west of Beechbarrow | St Cuthbert Out | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST 56696 48511 51°14′03″N 2°37′18″W / 51.2341°N 2.6216°W |
Three bowl barrows each around 12 metres (39 ft) in diameter. | 1020205 |  Upload Photo |
[293] |
| Three of the Priddy Circles and one barrow, 400 m west of Castle Farm | Priddy | Earthwork and enclosures | Neolithic | ST 54011 52781 51°16′21″N 2°39′39″W / 51.2725°N 2.6608°W |
Priddy Circles are a linear arrangement of four circular earthwork enclosures. They are described as 'probable Neolithic ritual or ceremonial monuments similar to a henge'. | 1015498 | 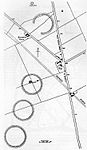 |
[143] [242][294] |
| Timber trackway site, 700 m west of Honeygar Farm | Meare | Timber trackway | Neolithic | ST 41793 42773 51°10′52″N 2°50′03″W / 51.1812°N 2.8341°W |
The remains of a brushwood track built between 3650 and 3500 B.C. | 1014434 |  Upload Photo |
[295] |
| Tinney's trackways, west of Sharpham Bridge | Sharpham | Timber trackway | Neolithic | ST 46708 38088 51°08′23″N 2°45′47″W / 51.1396°N 2.7631°W |
The route of several brushwood tracks. | 1014436 |  Upload Photo |
[296] |
| Two bell barrows and a bowl barrow 370 m east of Clover Farm: part of a group of round barrows west of Cranmore railway station | Cranmore | Bell barrows and a bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST 65847 42744 51°10′58″N 2°29′24″W / 51.1829°N 2.4900°W |
The bell barrows are 30 metres (98 ft) and 25 metres (82 ft) in diameter while the bowl barrow is 11 metres (36 ft). | 1016304 |  Upload Photo |
[297] |
| Two bowl barrows 350 m south of Brimble Pit Pool: part of a group of round barrows north and east of Foxhills Wood | Westbury | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST 50828 50469 51°15′05″N 2°42′21″W / 51.2513°N 2.7059°W |
Two bowl barrows one of which is 17 metres (56 ft) in diameter and the other 12 metres (39 ft). | 1016295 |  Upload Photo |
[298] |
| Two bowl barrows 550 m south west of Haydon House | St Cuthbert Out | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST 57876 47893 51°13′43″N 2°36′17″W / 51.2287°N 2.6047°W |
Two bowl barrows each approximately 13 metres (43 ft) in diameter. | 1020208 |  Upload Photo |
[299] |
| Two bowl barrows 850 m south east of Brimble Pit Pool: part of a group of round barrows north and east of Foxhills Wood | Westbury | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST 51219 50056 51°14′51″N 2°42′01″W / 51.2476°N 2.7003°W |
Two bowl barrows one of which is 10 metres (33 ft) in diameter and the other 11.5 metres (38 ft). | 1016294 |  Upload Photo |
[300] |
| Two bowl barrows on Barren Down, 250 m north west of Princes Lodge | Shepton Mallet | Bowl barrow | Bronze Age | ST 62097 44147 51°11′43″N 2°32′38″W / 51.1953°N 2.5438°W |
Two bowl barrows, one of which is 18 metres (59 ft) in diameter and the other 11 metres (36 ft). | 1019422 |  Upload Photo |
[301] |
| Two round barrows on Beacon Hill | Ashwick | Round barrow | Bronze Age | ST 63408 46142 51°15′05″N 2°35′48″W / 51.2513°N 2.5966°W |
Two round barrows each around 12 metres (39 ft) in diameter. | 1006200 |  Upload Photo |
[302] |
| Two round barrows SE of Castle of Comfort Inn | Chewton Mendip | Round barrow | Bronze Age | ST 54486 52935 51°16′25″N 2°39′14″W / 51.2737°N 2.6538°W |
A long mound believed to be two adjacent round barrows. | 1006217 |  Upload Photo |
[303] |
| Two round barrows 600 yd (550 m) ENE of Green Ore | Chewton Mendip | Round barrow | Bronze Age | ST 58461 50413 51°15′05″N 2°35′48″W / 51.2514°N 2.5966°W |
Two mounds which are believed to be round barrows, surrounded by several other mounds which are thought to be spoil heaps. | 1002959 |  Upload Photo |
[304] |
| Vobster Breach colliery, 890 m ENE of Tweed Farm | Leigh-on-Mendip | Coal mine | 19th century | ST 69755 48900 51°14′19″N 2°26′05″W / 51.2385°N 2.4346°W |
The remains of a coal mine including the coking ovens, shafts, drainage adits and branch railway. | 1014867 |  Upload Photo |
[305] |
| Wadbury Camp | Mells | Univallate hill fort | Iron Age | ST 73753 48859 51°14′21″N 2°22′49″W / 51.2391°N 2.3803°W |
A promontory hill fort covering 30 hectares (74 acres) surrounded by a bank and scarp. | 1006162 |  Upload Photo |
[306][307] |
| Westbury Beacon, a bell barrow 720 m west of Brimble Pit Pool | Westbury | Bell barrow | Bronze Age | ST5004950748 51°15′13″N 2°43′02″W / 51.2537°N 2.7171°W |
A bell barrow approximately 28 metres (92 ft) in diameter. | 1006177 |  Upload Photo |
[308] |
| Westbury Camp, slight univallate hillfort, 750 m north of Stokewood Cottage | Rodney Stoke | Hill fort | Iron Age | ST 49201 51126 51°15′30″N 2°43′37″W / 51.2583°N 2.7269°W |
Westbury Camp is a univallate Iron Age hill fort. The camp is largely situated in a hill slope. The north east defences has largely been destroyed by small quarries over the years. The narrow top of the hill bank suggests that it may have been surmounted by a dry stone wall. Along part of the east side of the camp there are traces of a berm between the bank and the outer ditch and at the western angle shallow quarry pits occur internally and externally set back from the 'rampart'. | 1015500 |  Upload Photo |
[309][310][311] |
| Westbury village cross | Westbury | Cross | 15th century | ST 50048 48806 51°14′10″N 2°43′01″W / 51.2362°N 2.7169°W |
A 1.9 metres (6 ft 3 in) high shaft of a cross on a six step octagonal base. | 1016292 |  |
[312] |
| Whatley Combe Roman villa | Nunney | Earthworks | Romano-British | ST 74316 47005 51°13′18″N 2°22′09″W / 51.2217°N 2.3692°W |
Earthworks from a multi-room Roman villa, with a bath suite, occupied during the 4th century. | 1006188 |  Upload Photo |
[313] |
| Witham Priory | Witham Friary | Monastery | 12th century | ST 75795 41646 51°10′25″N 2°20′51″W / 51.1735°N 2.3476°W |
Earthworks from a Carthusian monastery which was occupied between the 12th and 16th centuries. | 1006161 |  |
[314] |
| World War II bombing decoy complex, anti-aircraft obstructions and Beacon Batch round barrow cemetery on Black Down | Priddy | Earthworks | 1940 | ST 47960 57110 51°18′42″N 2°44′30″W / 51.3116°N 2.7417°W |
Earthworks from a World War II bombing decoy town. The decoy, known under the code name Starfish used fires of creosote and water to simulate incendiary bombs exploding. The site was home to a Z battery of anti aircraft rockets. Piles of stones (known as cairns) were also created to prevent enemy aircraft from using the hilltop as a landing site. | 1020995 |  |
[315][316] [24][317] |
See also
[edit]- Scheduled Monuments in Somerset
- Grade I listed buildings in Mendip
- Grade II* listed buildings in Mendip
Notes
[edit]- ^ The date given is the date used by Historic England as significant for the initial building or that of an important part in the structure's description.
- ^ Sometimes known as OSGB36, the grid reference is based on the British national grid reference system used by the Ordnance Survey.
- ^ The "List Entry Number" is a unique number assigned to each listed building and scheduled monument by Historic England.
References
[edit]- ^ a b "A Portrait of Mendip". Mendip District Council. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Shepton Mallet Parish". Neighbourhood Statistics. Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 2 January 2014. Retrieved 1 January 2014.
- ^ "Frome Parish". Neighbourhood Statistics. Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 2 January 2014. Retrieved 1 January 2014.
- ^ "Sites of Special Scientific Interest and historical monuments". Gov.uk. Natural England. Retrieved 25 April 2015.
- ^ "PRIDDY CIRCLES". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 15 April 2011.
- ^ a b c "Group of seven round barrows 380 m east of East Water Drove (Part of Priddy Nine Barrows Cemetery)". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 13 April 2014.
- ^ a b c "Ashen Hill barrow cemetery: a group of eight round barrows 500 m southeast of Harptree Lodge". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 13 April 2014.
- ^ a b c d "Pair of bowl barrows 405 m east of East Water Drove (Part of Priddy Nine Barrows Cemetery)". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 13 April 2014.
- ^ a b "Glastonbury Lake Village". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 16 March 2011.
- ^ a b "Glastonbury Lake Village". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Retrieved 18 November 2007.
- ^ a b "Iron-age settlement (Meare West), Meare". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 10 February 2011.
- ^ a b "Iron-age settlement (Meare East), Meare". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 10 February 2011.
- ^ Elkington, H D H (1976). "The Mendip Lead Industry". The Roman West Country: Classical Culture and Celtic Society.
- ^ a b "The Bishop's Barn". historicengland.org.uk. Historic England. Retrieved 4 March 2009.
- ^ a b "Former Tithe Barn in farmyard at Cumhill Farm". National heritage list for England. Historic England. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
- ^ a b "Abbey Tithe Barn, including attached wall to east". National heritage list for England. Historic England. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
- ^ a b "The Abbot's Fish House". National heritage list for England. Historic England. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
- ^ a b "Ponters Ball BALL". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 12 April 2011.
- ^ a b "Farleigh Hungerford Castle". National heritage list for England. Historic England. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
- ^ a b "Nunney Castle". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 1 July 2011.
- ^ a b "Fenny Castle". PastScape. Historic England. Archived from the original on 25 March 2012. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ a b "South West England". Heritage at Risk. Historic England. p. 183. Retrieved 25 April 2015.
- ^ a b "Market cross in the market place". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 11 February 2015.
- ^ a b "World War II bombing decoy complex, anti-aircraft obstructions and Beacon Batch round barrow cemetery on Black Down, Priddy / Cheddar — Mendip". Heritage at Risk. Historic England. Archived from the original on 27 July 2014. Retrieved 14 October 2013.
- ^ "An area of the Romano-British linear village at Fosse Lane, Shepton Mallet". National heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- ^ "Wookey Hole" (PDF). SSSI citation. English Nature. Retrieved 20 November 2008.
- ^ "Prehistoric and Roman occupation, Hole Ground, Wookey Hole". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 9 December 2013.
- ^ "Badger Hole, Wookey". National heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- ^ "Barrow, 350 m east of Harptree Lodge". National heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- ^ "St Brigid's Chapel". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- ^ "Bell barrow south of Blackwell Tyning Plantation". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- ^ "Bishop's palace". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- ^ "Court Farmhouse". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- ^ Bush, Robin (1994). Somerset: The complete guide. Wimborne, Dorset: Dovecote Press. ISBN 1-874336-27-X.
- ^ "Bishop Burnell's Great Hall". National heritage list for England. Historic England. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
- ^ Bush, Robin (1994). Somerset: The complete guide. Wimborne, Dorset: Dovecote Press. pp. 221. ISBN 1-874336-26-1.
- ^ "Monument No. 200137". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 20 m northwest of Whitestown Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 70 m east of Barrow House Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 70 m northeast of King Down Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 70 m northwest of Hill View". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 70 m west of Rowberrow Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 90 m northeast of Hill View". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 100 m north east of Home Farm Cottage". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 120 m north west of Burnt Wood". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 130 m west of St Lawrence's Church". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 150 m north east of Victoria Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 150 m southwest of King Down Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 170 m south-east of Hunter's Lodge Inn". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 180 m southwest of Yoxter Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 26 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 180 m west of Ubley Warren Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 220 m south west of Ubley Hill Farmhouse". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 230 m north west of Hunter's Lodge Inn". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 250 m northeast of King Down Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 250 m north west of Victoria Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 250 m south east of Redhill Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 250 m west of Starve Lark Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 260 m east of Templedown Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 280 m south east of Ubley Hill Farmhouse". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 300 m north of Hazel Manor". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 300 m north east of Whitnell Corner". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 300 m south west of Harptree Lodge". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 300 m southwest of Moor View". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 300 m west of Newlands Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 310 m southeast of Eastwater Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 320 m east of Lodmore Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 330 m north of Stoke Woods". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 340 m east of Templedown Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 340 m north-east of Wellington Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 350 m northeast of Cheddar Head Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 350 m northwest of Fernhill Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 350 m north west of Harptree Lodge". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 365 m south west of Ubley Warren Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 370 m east of Ubley Hill Farmhouse". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 27 January 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 380 m south east of Southfield Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 380 m south east of Beechbarrow". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 390 m northeast of Bristol Plain Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 390 m northwest of Fernhill Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 400 m north of Stoke Woods". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 400 m north-west of Starve Lark Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 400 m south of Rookham". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 400 m southwest of Moor View". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 410 m northeast of Bristol Plain Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 420 m east of Bristol Plain Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 420 m north of Stoke Woods". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 430 m north of Whitnell Corner". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 430 m north east of Stoke Woods". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 430 m northwest of King Down Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 430 m southwest of King Down Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 435 m north west of Ivy Cottage". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 450 m east of Bristol Plain Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 450 m north west of Harptree Lodge". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 450 m south-east of Red Quar Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 450 m southwest of Fernhill Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow, 455 m west of Brimble Pit Pool". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 460 m east of Charterhouse Warren Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 470 m south east of Southfield Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 490 m north west of Pen Hill Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 500 m north of East Water". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 510 m south east of Lodmore Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 520 m south-east of Red Quar Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow, 540 m west of Brimble Pit Pool". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 550 m south of Bristol Plain Farm: part of a linear round barrow cemetery". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 550 m southwest of Nordrach". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 550 m south east of Southfield Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 550 m south east of Brimble Pit Pool: one of a group of round barrows north and east of Foxhills Wood". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 570 m south east of Lodmore Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 570 m south east of Southfield Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 570 m west of Newlands Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 590 m south-east of Charterhouse Warren Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 600 m east of Priddy Hill Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 600 m north of Rookham Plantation". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 610 m northwest of Whitestown Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 650 m northeast of Higher Pitts Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 700 m south of Bristol Plain Farm: part of a linear round barrow cemetery". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 730 m southeast of Bristol Plain Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 750 m southwest of Dale Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 760 m southeast of Bristol Plain Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 770 m south of Townsend Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 800 m south of Townsend Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 810 m southeast of Bristol Plain Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 820 m south of Bristol Plain Farm: part of a linear round barrow cemetery". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 850 m south of Bristol Plain Farm: part of a linear round barrow cemetery". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 850 m south of Townsend Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 850 m southeast of Bristol Plain Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 870 m southwest of Charterhouse Warren Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 870 m southwest of Dale Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow 900 m south west of Bristol Plain Farm: part of a group of round barrows south and south west of Bristol Plain Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow in the garden of Beechbarrow". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bowl barrow on Stock Hill: part of the Stock Hill round barrow cemetery". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 6 February 2015.
- ^ "Bracelet Cave". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- ^ "Brown's Gatehouse". National heritage list for England. Historic England. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
- ^ Bush, Robin (1994). Somerset: The complete guide. Wimborne, Dorset: Dovecote Press. pp. 222. ISBN 1-874336-26-1.
- ^ "Brown's Gatehouse, Wells". historicengland.org.uk. Historic England. Retrieved 13 January 2009.
- ^ "Brownes' Hole". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- ^ "Orchard Leigh Stones". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- ^ "Iscalis". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- ^ "Mendip Hills: An Archaeological Survey of the Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty" (PDF). Somerset County Council Archaeological Projects. Retrieved 15 January 2011.
- ^ "Central of three duck decoys on Walton Moor, south of Lord Bath's Drove". National heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- ^ "Industrial archaeology — mine workings". British Geological Survey. Retrieved 5 February 2015.
- ^ a b Havinden, Michael (1981). The Somerset Landscape. The making of the English landscape. London: Hodder and Stoughton. pp. 58–59. ISBN 0-340-20116-9.
- ^ "Major Romano-British Settlement Charterhouse on Mendip, Avon". Roman Britain.org. Archived from the original on 27 September 2006. Retrieved 28 October 2006.
- ^ a b c d Firth, Hannah (2007). Mendip from the air. Taunton: Somerset County Council. ISBN 978-0-86183-390-0.
- ^ "Monument No. 200264". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 7 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 194703". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Rams Pits". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 202902". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 202903". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Marston". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "MONUMENT NO. 199946". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Disc barrow 610 m northeast of Drove Cottage". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Dovecote 220 m north of St Philip and St James's Church". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Dovecote". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Drying house at The Coach House, Willow Vale". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Duck decoy 1 km south east of Manor Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Duck decoy, 590 m south west of Rice Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Duck decoy, 820 m SSW of Little Huckham Farm: the western of three decoys on Walton Moor". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Duck decoy, 950 m south west of junction of Westhay Moor Drove and Lewis's Drove". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Duck decoy east of Barrow Wood Lane". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Duck decoy in Sharpham Park, 600 m south west of Avalon Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 8 February 2015.
- ^ "Early Christian settlement and monastic site at Marchey Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 200361". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 200178". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ^ Kightly, Charles. (2006) Farleigh Hungerford Castle. London: English Heritage. ISBN 1-85074-997-3.
- ^ "Fenny Castle". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 13 May 2011.
- ^ "Fenny Castle Cross, Castle". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 8 September 2014.
- ^ "Fenny Castle Cross: a medieval wayside cross 20 m north west of Castle Farm, Castle". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 9 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 197584". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 2 March 2015.
- ^ a b "Monument No. 197592". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 2 March 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 197587". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 2 March 2015.
- ^ "English Nature citation sheet" (PDF). 2006. Retrieved 25 July 2006.
- ^ Atthill, Robin (1964). Old Mendip. Newton Abbott: David and Charles. ISBN 0-7153-5171-0.
- ^ "The Fussell ironworks at Wadbury, Wells" (PDF). James Fussell. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ Mark Adler (December 2010). "When Fussells had the edge". Mendip Times. 6 (7): 89.
- ^ "Glastonbury Abbey". National heritage list for England. Historic England. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
- ^ Rahtz, Phillip; Watts, Lorna (2003). Glastonbury Myth and archaeology. Stroud: Tempus. ISBN 978-0752425481.
- ^ Carley, James P. (1988). Glastonbury Abbey: The Holy House at the Head of the Moors Adventurous. Guild Publishing. ISBN 0-85115-460-3.
- ^ Adkins, Lesley; Roy Adkins (1992). A field guide to Somerset archeology. Wimborne: Dovecote Press. pp. 69–70. ISBN 978-0-946159-94-9.
- ^ Webster, C.J. (2007). "The Archaeology of South West England South West Archaeological Research Framework" (PDF). Somerset County Council. p. 133. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Lake village". Glastonbury Antiquarians. Retrieved 15 May 2015.
- ^ Kennedy, Maev (7 October 2005). "Britain's ancient sites destroyed by agriculture". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ Fell, V. (1995). "Metallographic examination of Iron Age tools from Somerset". Historical Metallurgy. 29 (1): 1–11. Retrieved 15 May 2015.
- ^ "Glastonbury Lake Village". BBC History Trails. BBC. Retrieved 15 May 2015.
- ^ "Glastonbury lake village, Godney — Mendip". Heritage at Risk. Historic England. Archived from the original on 26 August 2014. Retrieved 14 October 2013.
- ^ Brunning, Richard (2006). Wet and Wonderful: The Heritage of the Avalon Marshes. Somerset County Council. ISBN 978-0861833801.
- ^ "Group of round barrows 750 m north west of Ivy Cottage". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ^ "Group of three bowl barrows and one long barrow 90 m northeast of Barrow House Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ^ "Hales Castle". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 22 July 2011.
- ^ "Drove Cottage Henge". Henge in England in Somerset. Megalithic Portal. Retrieved 25 April 2015.
- ^ "Henge 370 m NE of Drove Cottage, Hillgrove Road, Priddy". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 2 January 2011.
- ^ "Hillfort at Fox Covert, Milton Clevedon". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 16 January 2011.
- ^ "Fox Covert". Fortified England. Archived from the original on 11 July 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2011.
- ^ "Hillfort at Fox Covert, 550 m north east of Lamyatt Lodge". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ^ "Roddenbury Hillfort, Longleat Wood, Selwood". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 15 January 2011.
- ^ "Kingsdown Camp". PastSacpe. Historic England. Retrieved 24 March 2011.
- ^ "Kingsdown Camp, Mells Down, Mells". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 24 March 2011.
- ^ "King's Castle enclosures, iron age defended settlement, Wells". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. September 1985. Retrieved 30 April 2014.
- ^ "Kings Castle". PastScape. Historic England. Archived from the original on 29 April 2014. Retrieved 29 April 2014.
- ^ "King's Castle Wood Nature Reserve". Somerset Wildlife Trust. Retrieved 29 April 2014.
- ^ Gathercole, Clare (2003). "An Archaeological Assessment of Wells" (PDF). Somerset Extensive Urban Survey. Somerset County Council. pp. 3–6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 April 2014. Retrieved 29 April 2014.
- ^ Pyne, William. "An Iron Age Hamlet at King's Castle". Academia.edu. Retrieved 29 April 2014.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Rippon, Stephen (2004). "Making the Most of a Bad Situation? Glastonbury Abbey, Meare, and the Medieval Exploitation of Wetland Resources in the Somerset Levels" (PDF). Medieval Archaeology. 48. Maney Publishing: 119. doi:10.1179/007660904225022816. hdl:10036/20952. S2CID 161985196.
- ^ Godwin, H.; Macfadyen, W. A. (1955). "Studies of the Post-Glacial History of British Vegetation. XIII. The Meare Pool Region of the Somerset Levels". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. 239 (662). Royal Society: 161–190. Bibcode:1955RSPTB.239..161G. doi:10.1098/rstb.1955.0008.
- ^ Cunliffe, Barry (2005). Iron Age Communities in Britain (4th Ed). Abingdon, Oxon: Routledge. p. 266. ISBN 0-415-34779-3.
- ^ "Meare Lake Villages". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 10 February 2011.
- ^ "Lime Kiln Hill Quarry Cave". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ^ "Linear barrow cemetery comprising six bowl barrows 510 m south west of Townsend Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 10 February 2015.
- ^ "New Ditch". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 15 April 2011.
- ^ "New Ditch, Butleigh Wood, Butleigh". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 15 January 2011.
- ^ "Long barrow 180 m north of Lime House". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 11 February 2015.
- ^ "Long barrow 230 m east of Chewton Plot". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 11 February 2015.
- ^ "Long barrow 370 m south-south-east of Castle Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 11 February 2015.
- ^ "Long barrow and bowl barrow 430 m north west of the Mendip Nature Research Station". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 11 February 2015.
- ^ "Long barrow 600 m east north east of Brimble Pit Pool". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 11 February 2015.
- ^ "Long barrow, round barrow and cairn on Pen Hill". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 11 February 2015.
- ^ "Maesbury Castle Hillfort, Croscombe". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 30 December 2010.
- ^ Tratman, E.K. (1959). "Maesbury Castle, Somerset" (PDF). Proceedings of the University of Bristol Spelaeological Society. 8 (3): 172–178.
- ^ "Marston Moat". Heritage at Risk. Historic England. Archived from the original on 21 October 2017. Retrieved 21 October 2017.
- ^ "Marston Moat". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 25 August 2011.
- ^ "Marston Moat". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 11 February 2015.
- ^ "Medieval and post-medieval coal mining remains in Harridge Wood and Edford Wood South". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ^ "Medieval coal mining remains immediately south of Benter Cross". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ^ "Medieval wayside cross at Bodden". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 196819". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 13 February 2015.
- ^ "Medieval standing cross 50 m west of St Peter's Church". National Heritage list for England. Historic England. Retrieved 30 April 2015.
- ^ "Village Cross to West of Church of St Peter". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
- ^ "Medieval standing cross 80 m south of St Mary's Church". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No, 199945". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
- ^ "Murty Bridge". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 14 February 2015.
- ^ "Outlook Cave". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 15 February 2015.
- ^ "Pair of bowl barrows 350 m NNE of Whitnell Corner". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 15 February 2015.
- ^ "Pair of bowl barrows 640 m south of Bristol Plain Farm: part of a linear round barrow cemetery". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 15 February 2015.
- ^ "St Margaret's Chapel". St Margaret's Chapel. Archived from the original on 19 June 2010. Retrieved 5 July 2010.
- ^ "Almshouses and Chapel of St Mary Magdalene's Hospital". historicengland.org.uk. Historic England. Retrieved 5 July 2010.
- ^ "Hospital of St Mary, Chapel and Men's Almshouses, Magdalene Street, Glastonbury". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 5 July 2010.
- ^ Adler, Mark (October 2010). "Icon John and the refuge from "The madding World"". Mendip Times. 6 (5): 65.
- ^ "Part of the Hospital of St Mary Magdalene, Magdalene Street". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 15 February 2015.
- ^ Allcroft, Arthur Hadrian (1908). Earthwork of England: Prehistoric, Roman, Saxon, Danish, Norman and Mediæval. Nabu Press. p. 496. ISBN 978-1-178-13643-2. Retrieved 12 April 2011.
- ^ Morgan, Vicky (10 December 2002). "Ponter's Ball Dyke". Ancient Village or Settlement in England in Somerset. Megalithic Portal. Retrieved 12 April 2011.
- ^ "Ponters Ball (linear earthwork), Havyatt". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 12 April 2011.
- ^ "Priddy Circle 2". PastSacpe. Historic England. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ a b "Priddy Circle 1". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ "Priddy Glebe Barrow: a bowl barrow 25 m north of St. Lawrence's Church". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- ^ "Rhinoceros Hole, Wookey". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- ^ "Rode Bridge". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 21 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 194337". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ Dunning, Robert (1983). A History of Somerset. Chichester: Phillimore & Co. ISBN 978-0-85033-461-6.
- ^ Adkins, Lesley and Roy (1992). A field Guide to Somerset Archeology. Stanbridge: Dovecote press. pp. 37–39. ISBN 0-946159-94-7.
- ^ "Roman building 270 m north east of Priddy church". National Heritage List for England. Historic England.
- ^ "Monument No. 200162". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 199898". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Charterhouse on Mendip Roman Mining Settlement". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Romano-British settlement on Stoke Moor". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Roman villa complex, 330 m south-west of St Algar's Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 203149". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 193981". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Round barrow cemetery 470 m and 400 m north of Pen Hill Farm". National heritage List for England. Historic England.
- ^ "Monument No. 197530". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 200267". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 200259". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 197603". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 197504". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Rowberrow: a bowl barrow 40 m north of Hill View". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Savory's Hole". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ a b "Section of medieval road, south of Pomparles Bridge, north of Street". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Sections of the Sweet Track and Post Track, 240 m south west of Sunnyside Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Sections of the Sweet Track and Post Track, 250 m ESE of Station House". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Excavation (1904), Small Down Camp, Evercreech". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 1 January 2011.
- ^ "Small Down Camp Hillfort". Digital Digging. 28 November 2013. Retrieved 25 April 2015.
- ^ "Small Down Knoll camp". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Iron age promontory fort, Blackers Hill, Chilcompton". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 20 November 2010.
- ^ "Geophysical Survey (1999), Blackers Hill fort, Chilcompton". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- ^ "St Cuthbert's and Chewton lead mines and Fair Lady Well". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "St Michaels church tower, Tor Hill". National heritage list for England. Historic England. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
- ^ "St Michael's Church, monastic remains, and other settlement remains on Glastonbury Tor". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Stow Barrow : a bowl barrow 700 m southwest of Haydon Grange Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
- ^ "Tedbury Camp, Elm". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 15 January 2011.
- ^ "Tedbury Camp". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 16 March 2011.
- ^ "Abbey Tithe Barn, including attached wall to east". historicengland.org.uk. Retrieved 29 September 2007.
- ^ "The Abbot's Fish House and Fishponds". National heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 10 January 2015.
- ^ "Meare Fish House". Historic England. Retrieved 11 January 2015.
- ^ "The Devil's Bed and Bolster long barrow". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "The easternmost of three duck decoys on Walton Moor". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 202971". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Tithe Barn in farmyard at Manor Farm". historicengland.org.uk. Historic England. Retrieved 17 March 2008.
- ^ "Michael Eavis talks". BBC Somerset. BBC. Retrieved 2 November 2008.
- ^ "Pilton Tithe Barn". Glastonbury Festival. 29 April 2009. Retrieved 25 April 2015.
- ^ "Former Tithe Barn in farmyard at Cumhill Farm". historicengland.org.uk. Historic England. Retrieved 2 November 2008.
- ^ "The Tribunal". National heritage list for England. Historic England. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
- ^ "The Tribunal". historicengland.org.uk. Historic England. Retrieved 20 August 2008.
- ^ "Three bowl barrows at Green Ore, two 150 m south east and one 420 m south west of Newlands Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Three bowl barrows 400 m north west of Haydon Hut". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Three bowl barrows in Big Plantation, 690 m south west of Beechbarrow". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Priddy Circle 2". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
- ^ "Timber trackway site, 700 m west of Honeygar Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Tinney's trackways, west of Sharpham Bridge". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Two bell barrows and a bowl barrow 370 m east of Clover Farm: part of a group of round barrows west of Cranmore railway station". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Two bowl barrows 350 m south of Brimble Pit Pool: part of a group of round barrows north and east of Foxhills Wood". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Two bowl barrows 550 m south west of Haydon House". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Two bowl barrows 850 m south east of Brimble Pit Pool: part of a group of round barrows north and east of Foxhills Wood". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Two bowl barrows on Barren Down, 250 m north west of Princes Lodge". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 197551". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Chewton Mendip 3A and 3B (Grinsell)". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ "Monument No. 197551". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Vobster Breach colliery, 890 m ENE of Tweed Farm". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Wadbury Camp". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- ^ "Wadbury Hillfort, Wadbury". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 14 May 2011.
- ^ "Westbury Beacon, a bell barrow 720 m west of Brimble Pit Pool". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Westbudy Camp". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 26 March 2011.
- ^ "Westbury Camp hillfort, N of Stoke Woods, Rodney Stoke". Somerset Historic Environment Record. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 16 January 2011.
- ^ "Westbury Camp". Fortified England. Archived from the original on 11 July 2011. Retrieved 16 January 2011.
- ^ "Westbury village cross". National Heritage List for England. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Monument No.202781". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ "Witham Priory". PastScape. Historic England. Retrieved 1 March 2015.
- ^ Adkins, Lesley and Roy (1992). A field Guide to Somerset Archeology. Stanbridge: Dovecote press. p. 24. ISBN 0-946159-94-7.
- ^ Brown, Donald (1999). Somerset v Hitler: Secret Operations in the Mendips 1939–1945. Newbury: Countryside Books. ISBN 1-85306-590-0.
- ^ "Mendip Hills An Archaeological Survey of the Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty" (PDF). Somerset County Council Archaeological Projects. Somerset County Council. Retrieved 16 January 2011.


