List of provinces and commanderies of the Han dynasty
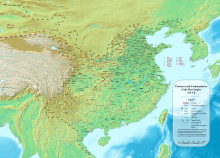
Local governments in the Han dynasty (202 BC – 220 AD) consisted of three levels of administrative divisions: provinces (cishibu 刺史部, or zhou), commanderies (jun) and counties (xian). The early Han dynasty inherited a two-tiered system of government composed of commanderies and counties from the Warring States (5th century BC – 221 BC) and the Qin dynasty (221 BC – 206 BC),[1] while 13 provinces were created on top of the existing hierarchy in 106 BC.
In each province, the central government assigned an Inspector (cishi, 刺史) to audit the administration of commanderies and kingdoms, from 106 BC to 1 BC and from 42 AD to 188 AD. In other periods, the position was replaced by a Governor (mu, 牧, literally "shepherd"), a higher-ranked official.[2] A commandery was under a Commandery Administrator (junshou, 郡守, before 148 BC) or a Grand Administrator (taishou, 太守, after 148 BC).[3] A county was governed by a Magistrate (ling, 令, for larger counties) or a Chief (zhang, 長, for smaller counties), who were the lowest local officials directly appointed by the central government. A special type of county, known as march (dao, 道), was used to administer certain areas with "barbarian" populations, especially on the frontiers of the empire.[4]
In early Han dynasty, chief followers and relatives of the emperor were granted kingdoms. However, independence of the kings gradually diminished. After the failed Rebellion of the Seven States, drastic measures were instated to limit the power of the kings.[5] From 145 BC onward, the central government controlled the appointment of all important officials in the kingdoms. Larger kingdoms were divided, and eventually the government of a kingdom became identical to that of a commandery. For example, the Chancellor (xiang, 相) was equivalent to a Grand Administrator.[5] Similarly, marquessates were administered in the same way as counties.[6]
By the end of the Western Han dynasty, the empire had 103 kingdoms and commanderies, as well as 1,587 counties. The Eastern Han census in 140 AD documented 99 kingdoms and commanderies, and 1,179 counties.[3][4]
Provinces
[edit]There were 13 provinces in the Han Empire. The capital region, although similar to a province in size, was not assigned an Inspector, but was instead inspected by the Colonel Director of Retainers (Sili xiaowei, 司隸校尉).[2] The region was therefore often known as "Sili".
During the Western Han dynasty, the Inspectors were agents of the central government, and did not permanently reside in the provinces. The Inspectors/Governors were transferred to the local government only in 35 AD.[7]
Apart from the capital region, the 13 provinces are:
| Province | Extent | |
|---|---|---|
| Yuzhou | 豫州 | S. and E. Henan, N. Anhui, N. Jiangsu, SW. Shandong |
| Jizhou | 冀州 | S. Hebei |
| Yanzhou | 兗州 | W. Shandong, NE. Henan |
| Qingzhou | 青州 | N. and E. Shandong, SE. Hebei |
| Xuzhou | 徐州 | N. Jiangsu, NE. Anhui, SE. Shandong |
| Jingzhou | 荊州 | S. Henan, Hubei, Hunan, parts of Guangdong and Guangxi |
| Yangzhou | 揚州 | S. Jiangsu, S. Anhui, Zhejiang, Fujian, parts of Henan and Hubei |
| Yizhou | 益州 | Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, Guizhou, S. Shaanxi, parts of Hubei and Gansu |
| Liangzhou | 涼州 | Gansu, Ningxia, NE. Qinghai |
| Bingzhou | 并州 | Shanxi, parts of Shaanxi and Inner Mongolia |
| Shuofang[note 1] | 朔方 | N. Shaanxi, Ordos and Hetao regions in Inner Mongolia |
| Youzhou | 幽州 | N. Hebei, Beijing, Tianjin, Liaoning, northern Korea |
| Jiaozhi[note 2] | 交趾 | Northern and central Vietnam, Guangxi, Guangdong, SE. Fujian |
Commanderies
[edit]| Commandery | Seat | First established [8][9] |
Last dissolved [8][9] |
Population (2 AD census)[10] |
No. of counties (Book of Han)[10] |
Population (140 AD census)[11] |
No. of counties (Book of Later Han)[11] |
Province | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Chinese | Name | Chinese | |||||||
| Jingzhao [note 1] |
京兆 | Chang'an | 長安 | 104 BC | – | 682,468 | 12 | 285,574 | 10 | Sili |
| Zuopingyi [note 1] |
左馮翊 | Chang'an → Gaoling |
長安 高陵 |
104 BC | – | 917,822 | 24 | 145,195 | 13 | Sili |
| Youfufeng [note 1] |
右扶風 | Chang'an → Huaili |
長安 槐里 |
104 BC | – | 836,070 | 21 | 93,091 | 15 | Sili |
| Weinan | 渭南 | 206 BC | 198 BC | – | – | – | – | – | ||
| Heshang | 河上 | 206 BC | 198 BC | – | – | – | – | – | ||
| Zhongdi | 中地 | 205 BC | 198 BC | – | – | – | – | – | ||
| Taichang [note 2] |
太常 | Chang'an | 長安 | c. 145 BC | 41 BC | – | – | – | – | Sili |
| Henan [note 1] |
河南 | Luoyang | 雒陽 | 4th century BC | – | 1,740,279 | 22 | 1,010,827 | 21 | Sili |
| Henei | 河內 | Huai | 懷 | Emperor Gao's reign | – | 1,067,097 | 18 | 801,558 | 18 | Sili |
| Hedong | 河東 | Anyi | 安邑 | 3rd century BC | – | 962,912 | 24 | 570,803 | 20 | Sili |
| Hongnong | 弘農 | Hongnong | 弘農 | 113 BC | – | 475,954 | 11 | 199,113 | 9 | Sili |
| Yingchuan | 潁川 | Yangdi | 陽翟 | 230 BC | – | 2,210,973 | 20 | 1,436,513 | 17 | Yuzhou |
| Runan | 汝南 | Pingyu | 平輿 | Emperor Gao's reign | – | 2,596,148 | 37 | 2,100,788 | 37 | Yuzhou |
| Xiping | 西平 | Xiping | 西平 | 82 AD | 88 AD | – | – | – | – | Yuzhou |
| Yiyang | 弋陽 | Yiyang | 弋陽 | 213 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Yuzhou |
| Dang/ Liang |
碭 梁 |
Dang → Suiyang |
碭 睢陽 |
225 BC | – | 106,752 | 8 | 431,283 | 9 | Yuzhou |
| Pei | 沛 | Xiang | 相 | Emperor Jing's reign | – | 2,030,480 | 37 | 1,251,393 [note 3] |
21 | Yuzhou |
| Qiao | 譙 | Qiao | 譙 | 213 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Yuzhou |
| Huaiyang/ Chen |
淮陽 陳 |
Chen | 陳 | 224 BC | – | 981,423 | 9 | 547,572 [note 3] |
9 | Yanzhou → Yuzhou |
| Xue/ Lu |
薛 魯 |
Lu | 魯 | 224 BC | – | 607,381 | 6 | 411,590 | 6 | Yuzhou |
| Wei | 魏 | Ye | 鄴 | 152 BC | – | 909,655 | 18 | 695,660 | 15 | Jizhou |
| Julu | 鉅鹿 | Julu → Yingtao |
鉅鹿 廮陶 |
228 BC | – | 827,177 | 20 | 602,096 | 15 | Jizhou |
| Guangping → Pinggan |
廣平 平干 |
Guangping | 廣平 | Emperor Wu's reign | 82 AD[note 4] | 198,558 | 16 | – | – | Jizhou |
| Guangzong | 廣宗 | 93 AD | 93 AD | – | – | – | – | Jizhou | ||
| Hengshan/ Changshan |
恆山 常山 |
Yuanshi | 元氏 | 228 BC | – | 677,956 | 18 | 631,184 | 13 | Jizhou |
| Zhending | 真定 | Zhending | 真定 | 113 BC | 37 AD | 178,616 | 4 | – | – | Jizhou |
| Zhongshan | 中山 | Lunu | 盧奴 | 154 BC | – | 668,080 | 14 | 658,195 | 13 | Jizhou |
| Boling | 博陵 | Boling | 博陵 | 158 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Jizhou |
| Xindu/ Lecheng/ Anping |
信都 樂成 安平 |
Xindu | 信都 | 154 BC | – | 304,384 | 17 | 655,118 | 13 | Jizhou |
| Hejian | 河間 | Lecheng | 樂成 | Emperor Gao's reign | –[note 5] | 187,662 | 4 | 634,421 | 11 | Jizhou |
| Zhangwu | 章武 | Dongpingshu | 東平舒 | c. 213 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Jizhou |
| Qinghe/ Ganling |
清河 甘陵 |
Qingyang → Ganling |
清陽 甘陵 |
Emperor Gao's reign | – | 875,422 | 14 | 760,418 | 17 | Jizhou |
| Guangchuan | 廣川 | Guangchuan | 廣川 | 107 AD | 121 AD | – | – | – | – | Jizhou |
| Handan/ Zhao |
邯鄲 趙 |
Handan | 邯鄲 | 228 BC | – | 349,952 | 4 | 188,381 | 5 | Jizhou |
| Bohai | 勃海 | Fuyang → Nanpi |
浮陽 南皮 |
165 BC | – | 905,119 | 26 | 1,106,500 | 8 | Youzhou → Jizhou |
| Jichuan/ Chenliu/ Jiyang |
濟川 陳留 濟陽 |
Jiyang → Chenliu |
濟陽 陳留 |
144 BC | – | 1,509,050 | 17 | 869,433 | 17 | Yanzhou |
| Dong | 東 | Puyang | 濮陽 | 242 BC | – | 1,659,028 | 22 | 603,393 | 15 | Yanzhou |
| Jiyin/ Dingtao |
濟陰 定陶 |
Dingtao | 定陶 | 144 BC | – | 1,386,278 | 9 | 657,554 | 11 | Yanzhou |
| Chengyang | 城陽 | Ju → Dongwu |
莒 東武 |
Emperor Gao's reign | –[note 6] | 205,784 | 4 | – | – | Yanzhou → Qingzhou |
| Jidong/ Dahe/ Dongping |
濟東 大河 東平 |
Wuyan | 無鹽 | 144 BC | – | 607,976 | 7 | 448,270 | 7 | Yanzhou |
| Rencheng | 任城 | Rencheng | 任城 | 84 AD | – | – | – | 194,156 | 3 | Yanzhou |
| Taishan | 泰山 | Fenggao | 奉高 | 122 BC | – | 726,604 | 24 | 437,317 | 12 | Yanzhou |
| Ying | 嬴 | Ying | 嬴 | Emperor Xian's reign | Unknown | – | – | – | – | Yanzhou |
| Jibei | 濟北 | Boyang → Lu |
博陽 盧 |
Qin dynasty | – | – | – | 235,897 | 5 | Yanzhou |
| Shanyang/ Changyi |
山陽 昌邑 |
Changyi | 昌邑 | 144 BC | – | 801,288 | 23 | 606,091 | 10 | Yanzhou |
| Boyang/ Jinan |
濟南 | Boyang → Dongpingling |
博陽 東平陵 |
201 BC | – | 642,884 | 14 | 453,308 | 10 | Qingzhou |
| Pingyuan | 平原 | Pingyuan | 平原 | Emperor Jing's reign | – | 664,543 | 19 | 1,002,658 | 9 | Qingzhou → Jizhou |
| Laoling | 樂陵 | Yanci | 厭次 | 213 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Jizhou |
| Qiansheng/ Le'an |
千乘 樂安 |
Qiansheng → Linji |
千乘 臨濟 |
110 BC | – | 490,720 | 15 | 424,075 | 9 | Qingzhou |
| Linzi/ Qi |
臨菑 齊 |
Linzi | 臨淄 | 221 BC | – | 554,444 | 12 | 491,765 | 6 | Qingzhou |
| Beihai | 北海 | Yingling → Ju |
營陵 勮 |
156 BC | – | 593,159 | 26 | 853,604 | 18 | Qingzhou |
| Zichuan | 菑川 | Ju | 勮 | 164 BC | 37 AD | 227,031 | 3 | – | – | Qingzhou |
| Jiaoxi/ Gaomi |
膠西 高密 |
Gaomi | 高密 | 201 BC | 37 AD | 205,784 | 4 | – | – | Qingzhou |
| Jiaodong | 膠東 | Jimo | 即墨 | 219 BC | 37 AD | 323,331 | 8 | – | – | Qingzhou |
| Donglai | 東萊 | Ye → Huang |
掖 黃 |
Emperor Jing's reign | – | 502,693 | 17 | 484,393 | 13 | Qingzhou |
| Changguang | 長廣 | Changguang | 長廣 | 198 AD | Unknown | – | – | – | – | Qingzhou |
| Langya | 琅邪 | Langya → Dongwu → Kaiyang |
琅邪 東武 開陽 |
221 BC | – | 1,079,010 | 51 | 570,967 | 13 | Xuzhou |
| Dongguan | 東莞 | Dongguan | 東莞 | 198 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Xuzhou |
| Dong'an | 東安 | Emperor Xian's reign | Unknown | – | – | – | – | Xuzhou | ||
| Donghai | 東海 | Tan | 郯 | Qin dynasty | – | 1,559,357 | 38 | 706,416 | 13 | Xuzhou |
| Licheng | 利城 | Licheng | 利城 | 198 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Xuzhou |
| Changlü | 昌慮 | Changlü | 昌慮 | 198 AD | 206 AD | – | – | – | – | Xuzhou |
| Pengcheng/ Chu |
彭城 楚 |
Pengcheng | 彭城 | Qin dynasty | – | 497,804 | 7 | 493,027 | 8 | Xuzhou |
| Linhuai | 臨淮 | Xu | 徐 | 117 BC | 79 AD | 1,237,764 | 29 | – | – | Xuzhou |
| Xiapi | 下邳 | Xiapi | 下邳 | 72 AD | – | – | – | 611,083 | 17 | Xuzhou |
| Dongcheng | 東城 | Emperor Xian's reign | Unknown | – | – | – | – | Xuzhou | ||
| Dongyang/ Guangling |
東陽 廣陵 |
Guangling | 廣陵 | Emperor Gao's reign | – | 140,722 | 4 | 410,190 | 11 | Xuzhou |
| Sishui | 泗水 | Ling | 淩 | 114 BC | 37 AD | 119,114 | 3 | – | – | Xuzhou |
| Nanyang | 南陽 | Wan | 宛 | 272 BC | – | 1,942,051 | 36 | 2,439,618 | 37 | Jingzhou |
| Zhangling | 章陵 | Zhangling | 章陵 | Emperor Xian's reign | – | – | – | – | – | Jingzhou |
| Nanxiang | 南鄉 | Nanxiang | 南鄉 | Emperor Xian's reign | – | – | – | – | – | Jingzhou |
| Nan/ Linjiang/ Jiangling |
南 臨江 江陵 |
Jiangling | 江陵 | 278 BC | – | 718,540 | 18 | 747,604 | 17 | Jingzhou |
| Xiangyang | 襄陽 | Xiangyang | 襄陽 | 208 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Jingzhou |
| Linjiang/ Yidu |
臨江 宜都 |
Yidu | 宜都 | 208 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Jingzhou |
| Hengshan | 衡山 | Zhu | 邾 | Qin dynasty | 121 BC | – | – | – | – | – |
| Jiangxia | 江夏 | Xiling → Shiyang/ Shaxian |
西陵 石陽 沙羨 |
121 BC | – | 219,218 | 14 | 265,464 | 14 | Jingzhou |
| Qichun | 蘄春 | Qichun | 蘄春 | 208 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Yangzhou |
| Xiling | 西陵 | Yangxin | 陽新 | 214 AD | Unknown | – | – | – | – | Jingzhou |
| Wuchang | 武昌 | Wuchang | 武昌 | 220 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Jingzhou |
| Lingling | 零陵 | Lingling → Quanling |
零陵 泉陵 |
111 BC | – | 139,378 | 10 | 1,001,578 | 10 | Jingzhou |
| Guiyang | 桂陽 | Chen | 郴 | Emperor Gao's reign | – | 156,488 | 11 | 501,403 | 11 | Jingzhou |
| Wuling | 武陵 | Suo → Linyuan |
索 臨沅 |
4th century BC | – | 185,758 | 13 | 250,913 | 12 | Jingzhou |
| Changsha | 長沙 | Linxiang | 臨湘 | 221 BC | – | 235,823 | 13 | 1,059,372 | 12 | Jingzhou |
| Hanchang | 漢昌 | Hanchang | 漢昌 | 210 AD | Unknown | – | – | – | – | Jingzhou |
| Jiujiang/ Huainan |
九江 淮南 |
Shouchun | 壽春 | 223 BC | – | 780,525 | 15 | 432,426 | 14 | Yangzhou |
| Fuling | 阜陵 | Fuling | 阜陵 | 73 AD | 206 AD | – | – | – | – | Yangzhou |
| Zhang/ Danyang |
鄣 丹陽 |
Guzhang → Wanling → Jianye |
故鄣 宛陵 建業 |
Qin dynasty | – | 405,171 | 17 | 630,545 | 16 | Yangzhou |
| Xindu | 新都 | Shixin | 始新 | 208 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Yangzhou |
| Linchuan | 臨川 | Emperor Xian's reign | Unknown | – | – | – | – | Yangzhou | ||
| Lujiang | 廬江 | Poyang | 鄱陽 | 219 BC | 121 BC | – | – | – | – | – |
| Lujiang [note 7] |
廬江 | Shu → Wan |
舒 皖 |
121 BC | – | 457,333 | 12 | 424,683 | 14 | Yangzhou |
| Lu'an | 六安 | Lu | 六 | 121 BC | 37 AD | 178,616 | 5 | – | – | Yangzhou |
| Kuaiji | 會稽 | Wu → Shanyin |
吳 山陰 |
222 BC | – | 1,032,604 | 26 | 481,196 | 14 | Yangzhou |
| Wu | 吳 | Wu | 吳 | 129 AD | – | – | – | 700,782 | 13 | Yangzhou |
| Yuzhang | 豫章 | Nanchang | 南昌 | 202 BC | – | 351,965 | 18 | 1,668,906 | 21 | Yangzhou |
| Luling | 廬陵 | Xichang | 西昌 | 195 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Yangzhou |
| Pengze | 彭澤 | 208 AD | Unknown | – | – | – | – | Yangzhou | ||
| Poyang | 鄱陽 | Poyang | 鄱陽 | 210 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Yangzhou |
| Hanzhong/ Hanning |
漢中 漢寧 |
Xicheng → Nanzheng |
西城 南鄭 |
312 BC | – | 300,614 | 12 | 267,402 | 9 | Yizhou |
| Xicheng | 西城 | Xicheng | 西城 | 215 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Jingzhou |
| Shangyong | 上庸 | Shangyong | 上庸 | 215 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Jingzhou |
| Fangling | 房陵 | Fangling | 房陵 | 215 – 219 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Jingzhou |
| Ba/ Yongning |
巴 永寧 |
Jiangzhou | 江州 | 316 BC | – | 708,148 | 11 | 1,086,049 | 14 | Yizhou |
| Badong Dependent States [note 8] |
巴東屬國 | Fuling | 涪陵 | 201 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Yizhou |
| Ba/ Baxi |
巴 巴西 |
Anhan → Langzhong |
安漢 閬中 |
195 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Yizhou |
| Dangqu | 宕渠 | Dangqu | 宕渠 | 218 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Yizhou |
| Guling/ Badong |
固陵 巴東 |
Yufu | 魚復 | 195 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Yizhou |
| Guanghan | 廣漢 | Zitong → Luo |
梓潼 雒 |
201 BC | – | 662,249 | 13 | 509,438 | 11 | Yizhou |
| Zitong | 梓潼 | Zitong | 梓潼 | 217 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Yizhou |
| Guanghan Dependent States/ Yinping [note 8] |
廣漢屬國 陰平 |
Yinping | 陰平 | 108 AD | – | – | – | 205,652 | 3 | Yizhou |
| Shu | 蜀 | Chengdu | 成都 | 316 BC | – | 1,245,929 | 15 | 1,350,476 | 11 | Yizhou |
| Shu Commandery Dependent States/ Hanjia [note 8] |
蜀郡屬國 漢嘉 |
Hanjia | 漢嘉 | 123 AD | – | – | – | 475,629 | 4 | Yizhou |
| Shenli | 沈黎 | Zuodu | 筰都 | 111 BC | 97 BC | – | – | – | – | Yizhou |
| Yuesui | 越巂 | Qiongdu | 邛都 | 111 BC | – | 408,405 | 15 | 623,418 | 11 | Yizhou |
| Wudu | 武都 | Wudu → Xiabian |
武都 下辯 |
111 BC | – | 235,560 | 9 | 81,728 | 7 | Yizhou → Liangzhou |
| Wenshan | 汶山 | Wenjiang | 汶江 | 111 BC | – | – | – | – | – | Yizhou |
| Qianwei | 犍為 | Bi → Bodao → Wuyang |
鄨 僰道 武陽 |
135 BC | – | 489,486 | 12 | 411,378 | 9 | Yizhou |
| Jiangyang | 江陽 | Jiangyang | 江陽 | 213 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Yizhou |
| Qianwei Dependent States/ Zhuti [note 8] |
犍為屬國 朱提 |
Zhuti | 朱提 | 107 AD | – | – | – | 37,187 | 2 | Yizhou |
| Zangke | 牂牁 | Gujulan | 故且蘭 | 111 BC | – | 153,360 | 17 | 267,253 | 16 | Yizhou |
| Yizhou | 益州 | Dianchi | 滇池 | 109 BC | – | 580,463 | 24 | 110,802 | 17 | Yizhou |
| Yongchang | 永昌 | Suitang → Buwei |
巂唐 不韋 |
69 AD | – | – | – | 1,897,344 [note 9] |
8 | Yizhou |
| Longxi | 隴西 | Didao → Xiangwu → Didao |
狄道 襄武 狄道 |
279 BC | – | 236,824 | 11 | 29,637 | 11 | Liangzhou |
| Jincheng | 金城 | Jincheng → Yunwu |
金城 允吾 |
81 BC | – | 149,648 | 13 | 18,947 | 10 | Liangzhou |
| Xiping | 西平 | Xidu | 西都 | Emperor Xian's reign | – | – | – | – | – | Liangzhou |
| Tianshui/ Hanyang |
天水 漢陽 |
Pingxiang → Ji |
平襄 冀 |
114 BC | – | 261,348 | 16 | 130,138 | 13 | Liangzhou |
| Nan'an | 南安 | Huandao | 豲道 | 188 AD | 214 AD | – | – | – | – | Liangzhou |
| Yongyang | 永陽 | Shanggui | 上邽 | 193 AD | 214 AD | – | – | – | – | Liangzhou |
| Anding | 安定 | Gaoping → Meiyang → Linjing |
高平 美陽 臨涇 |
114 BC | – | 143,294 | 21 | 29,060 | 8 | Liangzhou |
| Xinping | 新平 | Qi | 漆 | 194 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Liangzhou |
| Jiuquan | 酒泉 | Lufu | 祿福 | Emperor Wu's reign | – | 76,726 | 9 | 12,706 | 9 | Liangzhou |
| Zhangye | 張掖 | Lude | 觻得 | Emperor Wu's reign | – | 88,731 | 10 | 26,040 | 8 | Liangzhou |
| Zhangye Dependent States [note 8] |
張掖屬國 | Emperor An's reign | – | – | – | 16,952 | 5 | Liangzhou | ||
| Zhangye Juyan Dependent States/ Xihai [note 8] |
張掖居延屬國 西海 |
Juyan | 居延 | Emperor An's reign | – | – | – | 4,733 | 1 | Liangzhou |
| Xi | 西 | Rile | 日勒 | 195 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Liangzhou |
| Dunhuang | 敦煌 | Dunhuang | 敦煌 | Emperor Wu's reign | – | 38,335 | 6 | 29,170 | 6 | Liangzhou |
| Wuwei | 武威 | Guzang | 姑臧 | Emperor Xuan or Emperor Yuan's reign | – | 76,419 | 10 | 34,226 | 14 | Liangzhou |
| Shangdang | 上黨 | Zhangzi | 長子 | 5th century BC | – | 337,766 | 14 | 127,403 | 13 | Bingzhou |
| Leping | 樂平 | Zhan | 沾 | c. 215 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Bingzhou |
| Taiyuan | 太原 | Jinyang | 晉陽 | 247 BC | – | 680,488 | 21 | 200,124 | 16 | Bingzhou |
| Xinxing | 新興 | Jiuyuan | 九原 | 215 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Bingzhou |
| Yanmen | 雁門 | Shanwu → Yinguan |
善無 陰館 |
c. 300 BC | – | 293,454 | 14 | 31,862 | 14 | Bingzhou |
| Dai | 代 | Sanggan → Dai → Gaoliu |
桑乾 代 高柳 |
c. 300 BC | – | 278,754 | 18 | 20,123 | 11 | Bingzhou → Youzhou |
| Yunzhong | 雲中 | Yunzhong | 雲中 | c. 300 BC | 215 AD | 173,270 | 11 | 26,430 | 11 | Bingzhou |
| Dingxiang | 定襄 | Chengle | 成樂 | 196 BC | 215 AD | 163,144 | 12 | 13,571 | 5 | Bingzhou |
| Wuyuan | 五原 | Jiuyuan | 九原 | 127 BC | 215 AD | 231,328 | 16 | 22,957 | 10 | Shuofang → Bingzhou |
| Shuofang | 朔方 | Shuofang → Linrong → Wuyuan |
朔方 臨戎 五原 |
127 BC | 215 AD | 136,628 | 10 | 7,843 | 6 | Shuofang → Bingzhou |
| Shang | 上 | Fushi → Ya → Fushi → Xiayang |
膚施 衙 膚施 夏陽 |
c. 5th century BC | 215 AD | 606,658 | 23 | 28,599 | 10 | Shuofang → Bingzhou |
| Xihe | 西河 | Pingding → Lishi |
平定 離石 |
125 BC | Emperor Ling's reign | 698,836 | 36 | 20,838 | 13 | Shuofang → Bingzhou |
| Beidi | 北地 | Maling → Fuping → Chiyang → Fuping → Duiyu |
馬領 富平 池陽 富平 祋祤 |
271 BC | – | 210,688 | 19 | 18,637 | 6 | Shuofang → Liangzhou |
| Zhuo | 涿 | Zhuo | 涿 | 117 BC | – | 782,764 | 29 | 633,754 | 7 | Youzhou |
| Shanggu | 上谷 | Juyang | 沮陽 | 283 BC | – | 117,762 | 15 | 51,204 | 8 | Youzhou |
| Guangyang | 廣陽 | Ji | 薊 | 222 BC | –[note 10] | 70,658 | 4 | 280,600 | 5 | Youzhou |
| Yuyang | 漁陽 | Yuyang | 漁陽 | 283 BC | – | 264,116 | 12 | 435,740 | 9 | Youzhou |
| Youbeiping | 右北平 | Wuzhong → Pinggang → Tuyin |
無終 平剛 土垠 |
c. 3rd century BC | – | 320,780 | 16 | 53,475 | 4 | Youzhou |
| Liaoxi | 遼西 | Yangle | 陽樂 | c. 3rd century BC | – | 352,325 | 14 | 81,714 | 5 | Youzhou |
| Liaodong | 遼東 | Xiangping | 襄平 | c. 3rd century BC | – | 272,539 | 18 | Unknown | 11 | Youzhou |
| Liaodong Dependent States [note 8] |
遼東屬國 | Changli | 昌黎 | Emperor An's reign | – | – | – | Unknown | 6 | Youzhou |
| Xuantu (Hyŏnto) | 玄菟 | Fuzu (Pucho) → Gaogouli (Koguryŏ) |
夫租 高句驪 |
108 BC | – | 221,845 | 3 | 43,163 | 6 | Youzhou |
| Lelang (Rakrang) | 樂浪 | Chaoxian (Chosŏn) | 朝鮮 | 108 BC | – | 406,748 | 25 | 257,050 | 18 | Youzhou |
| Lintun (Imtun) | 臨屯 | Dongyi (Tongni) | 東暆 | 108 BC | 82 BC | – | – | – | – | Youzhou |
| Zhenfan (Chinpŏn) | 真番 | Shou (Sap) | 霅 | 108 BC | 82 BC | – | – | – | – | Youzhou |
| Canghai (Ch'anghae) | 蒼海 | 128 BC | 126 BC | – | – | – | – | Youzhou | ||
| Daifang (Taepang) | 帶方 | Daifang (Taepang) | 帶方 | c. 213 AD | – | – | – | – | – | Youzhou |
| Xiang | 象 | Linchen | 臨塵 | 214 BC | 76 BC | – | – | – | – | Yizhou |
| Nanhai | 南海 | Panyu | 番禺 | 214 BC | – | 94,253 | 6 | 250,282 | 7 | Jiaozhi |
| Cangwu | 蒼梧 | Guangxin | 廣信 | 111 BC | – | 146,160 | 10 | 466,975 | 11 | Jiaozhi |
| Yulin | 鬱林 | Bushan | 布山 | 111 BC | – | 71,162 | 12 | Unknown | 11 | Jiaozhi |
| Hepu | 合浦 | Xuwen → Hepu |
徐聞 合浦 |
111 BC | – | 78,980 | 5 | 86,617 | 5 | Jiaozhi |
| Gaoxing/ Gaoliang |
高興 高涼 |
Gaoliang → Siping |
高涼 思平 |
Emperor Huan's reign | –[note 11] | – | – | – | – | Jiaozhi |
| Jiaozhi (Giao Chỉ) | 交趾 | Leilou (Luy Lâu) → Longbian (Long Biên) |
羸𨻻 龍編 |
204 BC | – | 746,237 | 10 | Unknown | 12 | Jiaozhi |
| Jiuzhen (Cửu Chân) | 九真 | Xupu (Tư Phố) | 胥浦 | 204 BC | – | 166,013 | 7 | 209,894 | 5 | Jiaozhi |
| Rinan (Nhật Nam) | 日南 | Zhuwu (Chu Ngô) → Xiquan (Tây Quyển) |
朱吾 西捲 |
111 BC | – | 69,485 | 5 | 100,676 | 5 | Jiaozhi |
| Zhuya | 珠崖 | Shendu | 瞫都 | 110 BC | 46 BC | – | – | – | – | Jiaozhi |
| Dan'er | 儋耳 | Dan'er | 儋耳 | 110 BC | 46 BC | – | – | – | – | Jiaozhi |
- ^ a b c d While usually listed alongside commanderies, Jingzhao, Zuopingyi, Youfufeng were not commanderies themselves. Instead, Jingzhao was governed by the Intendant of the Capital. Zuopingyi and Youfufeng were also titles of the officials that administer the two regions. The three regions in the Guanzhong Plain, collectively known as "Sanfu" (三輔), were briefly divided into regular commanderies (Weinan, Heshang and Zhongdi) in the first years of the Former Han. From 198 BC to 104 BC, they were overseen by the Clerk of the Capital (Neishi 內史). There were two Clerks of the Capital ("left", Zuo Neishi; and "right", You Neishi) from Emperor Wen's reign onward, who were in charge of the northern and southern halves of the region, respectively.[12] Henan was administered in a similar way to Jingzhao during the Eastern Han period.
- ^ A special commandery in charge of imperial mausoleums[13]
- ^ a b Corrected based on commentary in 曹金华 (2014). 后汉书稽疑. p. 1511.
- ^ Dissolved in 37 AD, reestablished in 60 AD
- ^ Dissolved in 37 AD, reestablished in 90 AD
- ^ Dissolved in 37 AD, reestablished in 198 AD
- ^ A separate commandery from the first Lujiang Commandery
- ^ a b c d e f g Dependent States were institutions that governed non-Han peoples in the empire. Their chief officials were known as Chief Commandants (duwei, 都尉). Most Dependent States were subordinate to commanderies. However, six important Dependent States were elevated to full commandery status during Emperor An's reign.[14]
- ^ Disputed
- ^ Dissolved in 37 AD, reestablished in 96 AD
- ^ Dissolved during Emperor Ling's reign, reestablished in 220 AD
See also
[edit]References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ Lewis 1999, p. 614.
- ^ a b Bielenstein 1980, p. 90.
- ^ a b Bielenstein 1980, p. 92.
- ^ a b Bielenstein 1980, pp. 99–100.
- ^ a b Bielenstein 1980, pp. 105–107.
- ^ Bielenstein 1980, p. 108.
- ^ Bielenstein 1980, pp. 91–92.
- ^ a b Zhou 1987, pp. 259–302.
- ^ a b Li 1999, pp. 282–365.
- ^ a b Book of Han, Chapter 28.
- ^ a b Book of Later Han, Chapters 110–113.
- ^ Zhou 1987, pp. 129–132.
- ^ Zhou 1987, pp. 129–134.
- ^ Li 1999, pp. 118–119.
Sources
[edit]- Bielenstein, Hans (1980). The Bureaucracy of Han Times. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-511-75972-7.
- Lewis, Mark E. (1999). "Warring States: Political History". In Loewe, Michael; Shaughnessy, Edward L. (eds.). The Cambridge History of Ancient China. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 587–650. ISBN 978-0-521-47030-8.
- Li Xiaojie (1999). Donghan Zhengqu Dili [Administrative Geography of the Eastern Han Dynasty] (in Chinese). Jinan: Shandong Education Press. ISBN 978-7-532-82841-8.
- Zhou Zhenhe (1987). Xihan Zhengqu Dili [Administrative Geography of the Western Han Dynasty] (in Chinese). Beijing: People's Press. ISBN 978-7-100-12898-8.


