List of nature parks in Germany
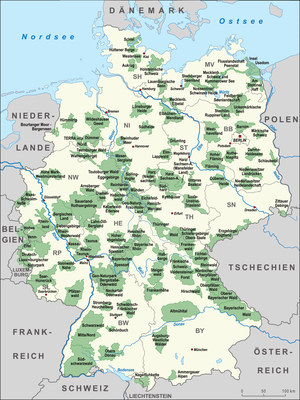
Nature parks in Germany (German: Naturparks) have been established under section 22, paragraph 4 of that country's Federal Nature Conservation Act (BNatSchG). As of 2020[update] there were 103 nature parks, comprising about 27 percent of the total land area of Germany and are brought together under the Association of German Nature Parks.[1] In total there are 23,159 Protected Areas in Germany.[2]
Parks that overlap into neighbouring countries are led by Europarc.[3]
The oldest nature park is Lüneburg Heath Nature Park, whose core area was established in 1921 as a nature reserve; by 2007, it had expanded to more than four times its original area.[4] As of 2020[update] the largest nature reserve in Germany, with 3,940 square kilometres (1,520 sq mi), is the Southern Black Forest Nature Park.[5]
The surface area of nature parks in Germany increased by 42% between 1998 and the end of 2019 (this corresponds to around 3.0 million hectares).[6]
The 16 national parks of Germany, under paragraph 24 of the Federal Nature Conservation Act, are not listed here. See List of national parks of Germany.
Nature parks
[edit]| Name | State |
Year |
Area (km²) |
Summary | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altmühl Valley Nature Park | 1969 | 2962 | The park is characterized by gently undulating plateaus and steep valleys with precipitous cliffs, and half of the park is wooded. The Altmühl flows through a spectacular valley from west to east. | 
| |
| Arnsberg Forest | 1961 | 482 | The park includes the Arnsberg Forest in the west and the Warstein Forest in the east. It is an area of low, forested mountains with several ridges. It is bordered by the Möhne in the north and the valley cut by the Ruhr in the south. | 
| |
| Augsburg-Western Woods | 1974 | 1175 | This park is bordered by the Danube, Wertach, Schmutter, Flossach and Mindel. The biggest part of the nature park is located in Augsburg (district) and extends to the edge of the districts Unterallgäu, Günzburg (district) and Dillingen (district). The gentle, hilly landscape of streams is fragmented by the gravel left behind by ice age Alpine glaciers and is nearly half forested. | 
| |
| Aukrug | 1970 | 384 | The park includes a flat and loamy ground moraine landscape with low hills and forests. In the south, the landscape is shaped by the river Stör, with moraines, heath, forest, and numerous ponds. | 
| |
| Barnim | 1999 | 749 | The park includes the Barnim heath habitats dating back to the ice age. It lies between the glacial valleys of Eberswalde in the north and Berlin in the south, and is more than half forested. The region is shaped by many individual lakes and meltwater gullies. | 
| |
| Bavarian Rhön | 1967 | 1245 | The park includes the area of the Rhön Mountains and lies amongst many low mountain ranges. In the south it extends to the Franconian Saale, and in its treeless Long Rhön shares a part of the central region of the High Rhön. The gently undulating surface is partially offset by basalt hills. | 
| |
| Bavarian Spessart | 1963 | 1710 | The park is underlain by Buntsandstein, gently inclined to the south. It includes the largest contiguous broadleaf/mixed forest in Germany, and is characterized by deep valleys, gentle slopes and heights. | 
| |
| Bavarian Forest | 1967 | 3008 | The park lies between the Danube and the heights of the Bavarian Forest. The park, nearly half forested, includes the peaks of the mountains as well as the southwestern slope, and is crossed by deep valleys and bordered by the Bavarian Forest National Park. | 
| |
| Bergisches Land | 1973 | 1917 | The park includes the northern part of the Rhenish Massif and the northern Siegerland and is a typical forested low mountain range. It rises gradually from west to east, and includes a densely populated valley. | 
| |
| Bergstraße-Odenwald Nature Park | 1960 | 3500 | The park includes the wooded low mountains of the Odenwald and extends east to the Maintal. It is bordered by the rivers Rhine, Main and Neckar. The region has stone runs formed by huge granite blocks (Felsenmeer) and bizarre rock formations. | 
| |
| Central/North Black Forest | 2000 | 3750[7] | The park is characterized by a varied landscape typical of the Black Forest with deeply incised valleys, rocks, streams and large, contiguous forested area. The crests themselves are treeless. In the south, the Central/North Black Forest Nature Park blends into the Southern Black Forest Nature Park. | 
| |
| Bourtanger Moor-Bargerveen | 2006 | 140 | The park includes the Bourtanger Moor, the largest contiguous raised bog in Europe. It has a variegated landscape and is characterized by heath regions, farming land, expanses of water and peat digs. | 
| |
| Dahme-Heideseen | 1998 | 594 | The park is characterized by the lake-dominated landscape of the river Dahme and numerous streams. The region is littered with sandy valley plains, moors, distinctive terminal moraines and wind-generated inland dunes. | 
| |
| Diemelsee | 1965 | 334 | The park is part of the Rothaar Mountains and is characterized by large, contiguous areas of forest. In the southeast and east it is bounded by the Waldecker Plain, in the north and northwest by the high plain of Paderborn and the Arnsberger Wald. | 
| |
| Drömling | 1990 | 278 | The park is a marsh, which previously comprised mainly wetlands. The landscape today is characterized by drainage and cultivation carried out in the 18th century and includes vast grasslands and dense forestry as well as a dense system of ditches. | 
| |
| Düben Heath | 1992 | 788 | The park includes the greater part of the Düben Heath (Dübener Heide) with about two thirds of it forested. The landscape is characterized by a varied hilly heath formed in the ice age. It lies between the riverbeds of Elbe and Mulde. | 
| |
| Dümmer | 1972 | 472 | The park includes the Dammer Berge, the Dümmer, the Stemweder Berg and numerous moors. The high ground in the area is crisscrossed by shallow dips created by the glaciers of the Saalian Stage and the moraines they left behind. | 
| |
| Ebbegebirge | 1964 | 777 | This nature park lies within the diverse Ebbegebirge, with two thirds of it covered by forest. It contains several dams such as the Biggertalsperre and numerous rivers such as the Lenne. | 
| |
| Eichsfeld-Hainich-Werratal | 1990 | 870 | The park is characterized by the hills of the Hainich and the plateaus of the Eichsfeld. The river Werra has shaped and cut deeply into the area in the southwest of the landscape. | 
| |
| Elbhöhen-Wendland | 1968 | 750 | The park includes two rather different major landscapes, the forested Drawehn ridge and the banks of the river Elbe. It is characterized by a varied relief with numerous slopes and valley on the Drawehn and the wide glacial valley of the Elbe (the Elbe-Urstromtal). | 
| |
| Elm-Lappwald | 1976 | 470 | The park includes the northern portion of the mid-German Harz mountains and the forested ridges of the Lappwald, Dorm and Elm, as well as the Helmstedter Mulde in the east. It is characterized by undulating hills. The chalk deposits of the local mountains are rich in fossils. | 
| |
| Feldberg Lake District | 1997 | 345 | The park is some 38 percent forested and dominated by hills, valleys and sandy plains. The western part of the region formed in the ice age, with ground moraines, terminal moraines, sandurs, and glacial valleys, belongs to Müritz National Park. | 
| |
| Fichtel Mountains | 1971 | 1028 | The park includes the wooded highlands of the Fichtel Mountains and the adjacent agricultural lands of the plateaux. It is bounded by the Thuringian Forest, Franconian Forest, Upper Palatine Forest and the Ore Mountains. The region is characterized by extensive rock formations and pillars such as the Luisenburg Rock Labyrinth. | 
| |
| Fläming | 2005 | 824 | The park includes the region between the Elbe and, in the north, the neighbouring High Fläming Nature Park. The gentle hills of the southern Fläming gradually lower themselves towards the city of Wittenberg. | 
| |
| Franconian Heights (Frankenhöhe) | 1974 | 1105 | This nature park is part of the cuesta in the southwest of Germany and descends steeply towards both west and east towards the Hohenlohe Plain and the Tauberland, respectively. To the southeast and the Central Franconian Basin the descent is more gentle. | 
| |
| Franconian Forest | 1971 | 1022 | The park is immediately adjacent to the Thuringian Forest and the Thuringian Slate Mountains-Upper Saale Nature Parks. It consists of an undulating plateau, overlooked by individual mountain tops with more than half its area forested. | 
| |
| Franconian Switzerland-Veldenstein Forest Nature Park | 1968 | 2346 | The park includes varied valleys and plateaus of the Franconian Jura, with some bizarrely shaped rock formations. Erosion has created numerous caves in the area. In the central area lies Franconian Switzerland. | 
| |
| German-Luxembourg | 1958 | 432 | The park includes the western side of the South Eifel. It is characterized by a hilly, gently rolling landscape with deeply incised valleys and craggy rocks. The park is part of the international German-Luxembourg Nature Park. | 
| |
| Habichtswald | 1962 | 474 | The park includes the Habichtswald, a forested low mountain range, which is located in the northern part of the extensive West Hesse Highlands. To the south and southwest, the landscape gradually descends into the valley of the river Eder. | 
| |
| Harz | 1960 | 2335 | The park includes the Harz mountains, except for some of the highest portions, which belong to Harz National Park. It is characterized by densely forested areas and short, steep valleys which alternate with mountain ridges and solitary mountains. | 
| |
| Haßberge | 1974 | 804 | The park is characterized by the hilly landscape of the Haßberge. The long ridge slopes steeply towards the west but more gently towards the east due to the makeup of the geological rock layers. In the south, it is bordered by the valley of the river Main. | 
| |
| Hessian Rhön | 1963 | 700 | The park includes the northwestern Rhön as well as parts of its foreland. The border with the Bavarian Rhön Nature Park runs through the high, elongated plain. The landscape of low mountains is characterized by wooded summits and high areas free of forest. | 
| |
| Hessian Spessart | 1962 | 729 | The park is characterized by oak and beech forests, deep valleys, gentle slopes, and the Spessart, which continues into Bavaria in the south. In the north it borders the Kinzig. | 
| |
| Hirschwald | 2006 | 278 | The park was once the hunting ground of a prince-elector and is the smallest nature park in Bavaria. It is one of the oldest and largest forested areas in the entire region. It is characterized by riparian forests and steep slopes towards Vils and the river Lauterach. | 
| |
| Hohe Mark | 1964 | 1040 | The park includes the wooded ridges of the Haltern Hills - the Hohe Mark (together with its western foothills the Rekener Berge and Die Berge), Haard and Borkenberge - with their gentle summits and which are located in the southern Münsterland. The region is characterised by a varied and changing landscape. It is bordered by the Haard and the Borkenberge hills. | 
| |
| High Fläming | 1997 | 827 | The park includes two different regions: in the north the flat lowlands of the Belziger Landschaftswiesen and in the south the hilly and wooded landscape of the High Fläming. The region is characterized by large, contiguous forest areas and a network of springs and burns. | 
| |
| High Vogelsberg | 1958 | 384 | The park includes the central range of the Vogelsberg, a former shield volcano complex with the largest basalt mass in Europe. It is characterized by broadleaf/mixed forest, some 34%, as well as grasslands and wetlands. | 
| |
| Hohes Venn – Eifel | 1960 | 1751 | The park includes the Eifel with the High Eifel and the High Fens. The southern High Eifel is characterized by forested ridges which are intersected by the rivers Prüm and Kyll. The foreland of the Fens has gentle hills. | 
| |
| Holstein Switzerland | 1986 | 753 | The park includes a multitude of lakes, such as the Lake of Plön, which were created during the last ice age and lie within the Schleswig-Holstein Uplands, crisscrossed by the rivers Schwentine and Kossau. | 
| |
| Homert | 1965 | 550 | The park lies between valley of the Ruhr in the northeast and the valley of the Lenne in the southwest. This varied, forested region is characterized by hills and ridges, river valleys, bizarre cliff and rock formations. | 
| |
| Hütten Hills | 1970 | 219 | The park includes the Hütten Hills, the northernmost hill country in Germany, and is largely part of the Schleswig Geestland. This landscape was created by rubble left behind by the glaciers during the last ice age. | ||
| Kellerwald-Edersee | 2001 | 406 | The park is characterized by a low mountain range as well as gentle valleys and hills. It includes part of the Kellerwald and stretches to the Edersee. It is dissected by the Eder river. The Naturpark comprises one of the largest protected beech forests in Europe. | 
| |
| Kyffhäuser | 1990 | 305 | The park is characterized by the geologically very different regions of the Kyffhäuser, the Windleite and the Hainleite. To the south the nature park borders the Goldene Aue. It is completely forested and show several cliffs reaching 100 meters. | 
| |
| Lahn-Dill Highlands | 2007 | 874 | The park includes the region Lahn-Dill Highlands. In the northwest the park borders the Rothaar Mountains, in the southwest it borders the Westerwald and in the south the Taunus. The park is more than half forested and partly streaked with rocky landscapes. To the northwest it is bordered by the Rothaar Mountain Nature Park. | 
| |
| Lauenburg Lakes | 1960 | 474 | The park includes the Lauenburg lakes such as the Ratzeburger See and the Schaalsee; roughly a quarter of the park is forest. It is characterized by terminal moraine heights and in the south by gently undulating sandur plains. | 
| |
| Lower Lusatian Heath | 1996 | 484 | The park is characterized by ground moraine and terminal moraine ridges, as well as glacial valleys and sandy areas, dating from the Wolstonian Stage. In the north vast contiguous forested areas extend on sandy plateaus. | 
| |
| Lower Lusatian Ridge | 1997 | 586 | The park includes ridge of the Niederlausitzer Landrücken, a typical terminal moraine landscape from the ice age. The region is crossed by the northwesterly extending Glogau-Baruther Urstromtal, an ancient ice-parallel meltwater channel, toward which the park slopes steeply downward. | 
| |
| Lower Saale Valley | 2005 | 408 | The park includes the lower Saale valley and is characterized by ice age deposits and round hills of porphyry. The lowlands are interrupted by rocky mountain ridges with steep bluffs and slopes. | 
| |
| Lüneburg Heath (Lüneburger Heide) |
1921 | 1130 | The park includes the Lüneburg Heath, that includes typical vast heath regions; the Wümme has its source there, and runs through the park. The hilly landscape was formed by ice age glaciers. Large areas of the region are covered by pine forest. | 
| |
| Maas-Schwalm-Nette | 1965 | 435 | The park spans the border with the Netherlands; the borderland is characterized by vast forests. The region has quite varied terrain, crossed by the eponymous rivers Schwalm and Nette and including the areas Süchtelner Höhen and Hardter Wald. | 
| |
| Märkische Schweiz | 1990 | 205 | The park includes a varied hilly area, the Buckow Forest, and numerous lakes which were created by the glaciers of the last ice age. The region is dissected by valleys, and the nature park is divided by the Buckower Rinne, which was cut by meltwater of glaciers. | 
| |
| Mecklenburg Switzerland and Lake Kummerow | 1997 | 673 | The nature park is only sparsely forested, it comprises several lakes including Lake Malchin, Lake Kummerow and Lake Teterow. The Peene river flows through the park. The region is characterized by hill chains in the centre of the park and valleys formed by glaciers of the ice age. | 
| |
| Mecklenburg Elbe Valley | 1998 | 426 | The park includes the pristine river-formed landscape of the Elbe and its tributaries. The landscape is characterized by inland dune regions with specialized vegetation and the steep Elbe riverbed slopes. The region is criss-crossed by forests and heath. | 
| |
| Meißner-Kaufungen Forest | 1962 | 421 | The park includes parts of the Kaufunger Wald, the Söhre and of the Hoher Meißner. It is characterized by a varied hilly mountain landscape bordering the Münden Nature Park to the north, and lies between Werra and Fulda. | 
| |
| Münden | 1959 | 374 | The park includes the northern part of the Kaufungen Forest, the Bramwald and the Dransfeld Municipal Forest. Its southern border adjoins the Meißner-Kaufung Forest Nature Park. It is characterized by hills and plateaus and vast, contiguous forested areas. | 
| |
| Nassau | 1963 | 590 | The nature park lies in the Rhenish Massif and is dissected from east to west by the deeply incised, winding Lahn. Several tributary valleys steeply climb to the heights of the Westerwald. | 
| |
| Neckar Valley-Odenwald | 1980 | 1292 | The park includes the heavily forested low mountain landscape of the Odenwald, with deeply incised valleys. Bordering landscapes are the Bauland (a mostly unwooded area with good soils) in the east, the Bergstraße in the west and the deeply incised Neckar valley in the south. | 
| |
| Northern Upper Palatinate Forest (Oberpfälzer Wald) |
1975 | 1380 | The park includes the hilly low mountain landscape of the northern Upper Palatinate Forest. In the west this gives way to forests, fields, meadows, and pastures. In the east are the higher altitudes of the Bavarian Forest. | 
| |
| Nossentiner/Schwinzer Heath | 1994 | 365 | The park is at least 60 percent forested and contains nearly 60 partly infilled lakes and includes a wide flat landscape, with only a few hills rising above. The region is characterized by sandy land, which in places forms wind-formed dunes. | 
| |
| Nuthe-Nieplitz | 1999 | 623 | The park is characterized by the wet lowlands of the rivers Nuthe and Nieplitz and beech forests close to their natural state. The central area of the region was formed as a glacial meltwater feeder channel (Zwischenurstromtal) by a melting glacier at the end of the last glacial period. | 
| |
| Ore Mountains/Vogtland | 1990 | 1495 | The park includes the Ore Mountains and the Vogtland and forms a diversified landscape. A forested area runs along an undulating plateau in the Vogtland, which rises gently to the south. Deeply sunken valleys run across the Ore Mountains. | 
| |
| Palatine Forest | 1958 | 1798 | With a forested area of 76 percent the park forms the largest contiguous forest in Germany. It is characterized by a varied and impressive landscape of Buntsandstein rocks found nowhere else in Germany. | 
| |
| Rhine-Taunus | 1968 | 808 | The park includes the western part of the Taunus and extends over the Idsteiner Becken to the Rhine. It is characterized by a roughly 60 percent forested low mountain landscape, which falls away steeply toward the water gap of the Rhine Gorge. | 
| |
| Rhine-Westerwald | 1962 | 446 | The park is part of the Niederwesterwald, which in turn is part of the Rhenish Massif. The river Wied crosses the nature park in a valley that is broad in some places and gorge-like in others. Some 45 percent is forested. | 
| |
| Rhineland[8] | 1978 | 1052 | The park is characterized by a diverse landscape and lies between the plain of the Rhine at the edge of the Cologne Bay and the Erft. The Ville mountain ridge crosses the park parallel to the Rhine. | 
| |
| Rothaar Mountains | 1963 | 1355 | The park includes the Rothaar Mountains (Rothaargebirge) and is roughly 65 percent spruce and beech forest. The region ist distinguished by a diverse hilly mountain landscape between Upper Ruhr and Lahn rivers. The park is bordered to the west and northwest by Naturpark Ebbegebirge and Naturpark Homert, to the north by Naturpark Diemelsee and to the southeast by Naturpark Lahn-Dill-Bergland. | 
| |
| Saale-Unstrut-Triasland | 1991 | 710 | The park includes part of the middle Saale valley and the lower Unstrut valley as well as the adjoining plateaus. It is characterized by gentle hills and mostly open landscape with viticulture and orchards. | 
| |
| Saar-Hunsrück | 1980 | 1938 | The park includes the Hunsrück, its Schwarzwälder Hochwald and the Osburger Hochwald. The region is characterized by a low mountain landscape with deeply incised valleys, forested mountain ridges, meadows and rocks. | 
| |
| Schlaube Valley | 1995 | 228 | The park includes in its north the heath habitat Reicherskreuzer Heide, and is characterized by ground and terminal moraines as well as thrust moraines, sandur plains and inland dunes. The region contains numerous meltwater channel systems generated in the last glacial period, notably the Schlaube, Dorche, Oelse and Demnitz. | 
| |
| Schönbuch | 1972 | 156 | The park includes the Schönbuch and forms the largest contiguous forested area in the Stuttgart region. To the south it is confined by Ammer- and Neckar valleys. The eastern border is the Filder plateau and in the west the plain of the Gäu. | 
| |
| Swabian-Franconian Forest | 1979 | 904 | The park is divided into five small regions: Welzheim Forest, Murrhardt Forest, Mainhardt Forest, Waldenburg Hills and Löwenstein Hills. The region is characterized by bizarre rock formations and steep slopes in the Keuper group. | 
| |
| Siebengebirge | 1959 | 48 | The park includes the Siebengebirge and it is the only nature park in Germany that is designated in its entirety as a nature preserve. The region is characterized by a unique rocky landscape of volcanic origin, showing the results of erosion of volcanic rocks and exposure of intrusive rocks. | 
| |
| Solling-Vogler | 1966 | 527 | The park includes both the low mountain ranges Solling and Vogler and the mountain ridge of the Burgberge that lies between them. On the west it borders on the Weser falley. The park is characterized by narrow crests, steep slopes, deeply incised valleys and large forested areas. | 
| |
| Soonwald-Nahe | 2005 | 736 | The park features a diverse landscape in a small area. It comprises the Hunsrück plateaus, the quartzite crests of the Soonwald showing deeply incised streams and the Nahe river valley. The region is characterized by extensive deciduous forests. | 
| |
| Southern Black Forest | 1999 | 3940[9] | The Southern Black Forest Nature Park is Germany's biggest nature park (as of 2018).[10] Two thirds of the park is covered by forest and deeply incised by valleys of the Black Forest. In the west and south it comes close to the Rhine, in the east to the Swabian Alb - Wutach area and in the north to the Middle Black Forest. | 
| |
| Stechlin-Ruppiner Land | 2001 | 683 | The park is up to 62 percent forested, and borders the Naturpark Uckermärkische Seen. The region is characterized by long chain of lakes, some of them with very clear water, a rare feature in Middle Europe. The large beech forests are ecologically important. | 
| |
| Steigerwald | 1971 | 1280 | The park is characterized by a gentle low mountain landscape, covered with beech and partly with bright oak groves. The northern border is formed by a big loop of the Main and the southern limit by the river Aisch. | 
| |
| Steinhuder Meer | 1974 | 310 | The park includes the largest inland lake in northwestern Germany, the Steinhuder Meer, and is mostly bare of trees. The region is characterized by moorland, which takes up roughly a quarter of the park. The region was formed as a huge glacial ice-parallel meltwater channel (Urstromtal) during the Wolstonian Stage. | 
| |
| Steinwald | 1970 | 246 | The park includes the Steinwald and is embedded between Fichtel Mountains and Upper Palatinate Forest. It shows a multitude of different landscapes. The western portion is characterized by a landscape of basalt domes with stone runs and bizarre rock formations resembling castles. | 
| |
| Sternberg Lake District | 2005 | 540 | The park includes the middle Warnow valley and the Sternberg lakes. The region is characterized by forested sandur plains, the glacial meltwater valleys (Urstromtäler) of the Warnow and Mildenitz rivers, glacial lakes and terminal moraines. | 
| |
| Stromberg-Heuchelberg | 1980 | 328 | The park includes the Stromberg hills and the Heuchelberg mountain ridge. It is characterized by a well wooded hilly landscape. Geologically, it belongs to the Keuper mountains. The north slopes are mostly forested, the south slopes are used by viticulture. | 
| |
| Südheide | 1963 | 500 | The park lies in the southern Lüneburg Heath and is characterized by large forest and heath areas. The landscape dates from the ice age and is characterized by undulating to gentle hilly terrain and large contiguous forested area. | 
| |
| Stettin Lagoon | 2005 | 537 | The park extends south from lagoons by the Baltic Sea to the mountains of the Brohmer Berge, and is characterized by the partly flat and partly hilly terminal moraine landscape, a coast with lagoons. It comprises vast and contiguous forests of Ueckermünder Heide. | 
| |
| Taunus Nature Park formerly Hochtaunus Nature Park | 1962 | 1202 | The park includes the main range of the Taunus proper, an undulating to craggy, forested low mountain range with the river Lahn to the North. The Hochtaunus is dominated by coniferous trees, the Hintertaunus by deciduous forest. | 
| |
| TERRA.vita[11] | 1962 | 1140 | The park includes parts of the Teutoburg Forest, the Wiehen Hills and the Weser hills. The park is characterized by a rich and varied low mountain landscape, crossed by many valleys. | 
| |
| Teutoburg Forest / Egge Hills | 1965 | 2711 | The park includes the mountain ranges of the southern Teutoburg Forest and Egge Hills. The landscape is characterized by a rich and varied low mountainous landscape and densely forested. | 
| |
| Thuringian Highlands/ Upper Saale |
1990 | 873 | The park is characterized by deeply incised valleys, above all the Saale, which winds through its valleys among the mountain ridges. The undulating plateaus are partly covered with dense spruce forests. | 
| |
| Thuringian Forest | 1990 | 2082 | The Nature Park compices almost the entire Thuringian Forest and the Thuringian Highland. The region is mostly forested and characterized by deeply incised valleys. The Rennsteig wends its walkway along the crest. | 
| |
| Uckermark | 1997 | 897 | The landscape of the park was shaped in the ice age; it is more than half forested. Terminal moraine hills and lakes alternate in a small area. Apart from rubble, the ice of the Wolstonian stage left sandur plain with many moors and small elongated lakes in glacial valleys. | 
| |
| Upper Bavarian Forest | 1965 | 1738 | The park includes the northwestern Bavarian Forest and extends from the crest line to the Falkensteiner Vorwald. The landscape is characterized by wide and gently rolling mountain ridges with their valleys and villages. | 
| |
| Upper Danube | 1980 | 857 | The park includes the highest areas of the Swabian Jura between Lake Constance and the Black Forest. The Jura plateau is covered by extensive woodland and descends gently to the south. The region's thick limestone layers are cut by the deeply incised Danube. | 
| |
| Upper Palatinate Forest | 1971 | 724 | The park is nearly half forested and characterized by a vast undulating to hilly landscape with many small rivers and brooks. Essentially it includes the Upper and Lower Upper Palatinate Forest. | 
| |
| Usedom | 1999 | 632 | The park includes the island of Usedom, the water between Usedom and the mainland, and a small strip of mainland. Roughly 30 percent of the region is forested. The park has a great variety of landscaoe forms in a small area. | 
| |
| Weser Uplands-Schaumburg-Hamelin | 1975 | 1116 | The park lies in the transition area from the low mountains to the North German plain and is divided by the river Weser. A gentle slope, covered by large, contiguous forests, alternate with small valleys. | 
| |
| Westensee | 1969 | 260 | The park includes domelike hills as well as the Westensee, which dates from the end of the last glacial period and is crossed by the river Eider. The landscape is characterized by gentle hills and valleys, forests, lakes and moors. | 
| |
| Westhavelland | 1998 | 1315 | The park includes the largest contiguous wetland in inland Europe and is of international significance. Large portions of the region consist of inland dunes and sandur plains. The region is crossed by the river Havel and its tributaries. | 
| |
| Wildeshausen Geest | 1984 | 1554 | The park includes the lowlands on both sides of the river Hunte. The thinly forested region is characterized by part of the northwest German Geest ridge and quiet river valleys and heath plains. The region gained its current geological configuration during the Wolstonian Stage. | 
| |
| Zittau Mountains | 2007 | 133 | The park includes the Zittau Mountains (the German side of the Lusatian Mountains), and lies in the tripoint with Poland and the Czech Republic. This smallest of German low mountain ranges is characterized by variously shaped mountains of sandstone, rock formations, volcanic peaks and incised valleys. | 
|
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Verband Deutscher Naturparke
- ^ "Protected Planet | Germany". Protected Planet. Retrieved 1 February 2022.
- ^ "About us". EUROPARC Federation. Retrieved 2020-09-01.
- ^ "Lüneburg Heath Nature Park - The largest interconnected heath areas in central Europe - Lüneburg Heath Nature Park - Home". naturpark-lueneburger-heide.de. Retrieved 2020-09-01.
- ^ "Naturparks in Deutschland nach Größe". Statista (in German). Retrieved 2020-09-01.
- ^ "BfN: Naturparke". www.bfn.de (in German). Retrieved 2020-09-01.
- ^ "Naturpark Schwarzwald Mitte/Nord". Nationale Naturlandschaften (in German). Retrieved 2020-09-01.
- ^ Until 12 December 2005 Naturpark Kottenforst-Ville.
- ^ "Naturpark Südschwarzwald - Allgemeines". www.naturpark-suedschwarzwald.de. Retrieved 2020-09-01.
- ^ "Naturparks in Deutschland nach Größe". Statista (in German). Retrieved 2020-09-01.
- ^ The park was previously called Nördlicher Teutoburger Wald-Wiehengebirge.
Further reading
[edit]- Karl-Heinz Bochow, Klaus Bötig, et al.: Der große ADAC-Freizeitführer – Die letzten Paradiese – Unsere schönsten Natur- und Nationalparks in Deutschland. ADAC Verlag GmbH, München und Verlag Das Beste GmbH, Stuttgart, 1995. ISBN 3-87003-661-3.
