List of motmots
Motmots are birds in the family Momotidae in the order Coraciiformes. There are currently 14 extant species of motmots recognised by the International Ornithologists' Union.[1]
Conventions
[edit]| Conservation status | |
|---|---|
| EX | Extinct (0 species) |
| EW | Extinct in the wild (0 species) |
| CR | Critically Endangered (0 species) |
| EN | Endangered (0 species) |
| VU | Vulnerable (1 species) |
| NT | Near threatened (0 species) |
| LC | Least concern (13 species) |
Conservation status codes listed follow the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species. Range maps are provided wherever possible; if a range map is not available, a description of the motmot's range is provided. Ranges are based on the IOC World Bird List for that species unless otherwise noted. Population estimates are of the number of mature individuals and are taken from the IUCN Red List.
This list follows the taxonomic treatment (designation and order of species) and nomenclature (scientific and common names) of version 13.2 of the IOC World Bird List.[1] Where the taxonomy proposed by the IOC World Bird List conflicts with the taxonomy followed by the IUCN[a] or the 2023 edition of The Clements Checklist of Birds of the World,[3] the disagreement is noted next to the species's common name (for nomenclatural disagreements) or scientific name (for taxonomic disagreements).
Classification
[edit]The International Ornithologists' Union (IOU) recognises 14 species of motmots in six genera.[1] This list does not include hybrid species, extinct prehistoric species, or putative species not yet accepted by the IOU.
Family Momotidae
- Genus Hylomanes: one species
- Genus Aspatha: one species
- Genus Momotus: seven species
- Genus Baryphthengus: two species
- Genus Electron: two species
- Genus Eumomota: one species
Motmots
[edit]| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tody motmot | H. momotula Lichtenstein, M. H. C., 1839 Three subspecies
|
Southern Mexico to northwestern Colombia
|
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blue-throated motmot | A. gularis (Lafresnaye, 1840) |
Southern Mexico to Honduras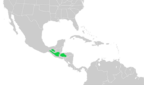
|
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Russet-crowned motmot | M. mexicanus Swainson, 1827 Four subspecies
|
Northwestern Mexico to southwestern Guatemala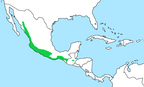
|
LC
|
| Blue-capped motmot | M. coeruliceps (Gould, 1836) |
Northeastern Mexico
|
LC
|
| Lesson's motmot | M. lessonii Lesson, R. P., 1842 Three subspecies
|
Southern Mexico to western Panama
|
LC
|
| Whooping motmot | M. subrufescens Sclater, P. L., 1853 Four subspecies
|
Central and South America
|
LC
|
| Trinidad motmot | M. bahamensis (Swainson, 1838) |
Trinidad and Tobago
|
LC
|
| Amazonian motmot | M. momota (Linnaeus, 1766) Nine subspecies
|
Amazon rainforest
|
LC
|
| Andean motmot | M. aequatorialis Gould, 1858 Two subspecies
|
Andes
|
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rufous motmot | B. martii (Spix, 1824) Two subspecies
|
Central and South America
|
LC
|
| Rufous-capped motmot | B. ruficapillus (Vieillot, 1818) |
Southeastern Brazil, eastern Paraguay and northeastern Argentina
|
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Keel-billed motmot | E. carinatum (du Bus de Gisignies, 1847) |
Southern Mexico to northern Costa Rica
|
VU
|
| Broad-billed motmot | E. platyrhynchum (Leadbeater, 1829) Six subspecies
|
Central and South America
|
LC
|
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Turquoise-browed motmot | E. superciliosa (Sandbach, 1837) Seven subspecies
|
Southern Mexico to northwestern Costa Rica
|
LC
|
Notes
[edit]- ^ The IUCN follows the taxonomy proposed by the HBW and BirdLife Taxonomic Checklist.[2]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P., eds. (July 2023). "Todies, motmots, bee-eaters". IOC World Bird List. v 13.2. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ "Handbook of the Birds of the World and BirdLife International digital checklist of the birds of the world. Version 7". HBW and BirdLife International. 2022. Archived from the original on 25 September 2019. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ Clements, James F.; Schulenberg, T. S.; Iliff, M. J.; Fredericks, T. A.; Gerbracht, J. A.; Lepage, Denis; Billerman, S. M.; Sullivan, B. L.; Wood, C. L. (2022). "The eBird/Clements checklist of Birds of the World: v2022". Clements Checklist. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ BirdLife International (2020). "Hylomanes momotula". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T22682980A152231624. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22682980A152231624.en. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ BirdLife International (2020). "Aspatha gularis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T22682983A152200542. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22682983A152200542.en. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ BirdLife International (2020). "Momotus mexicanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T22683001A163627056. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22683001A163627056.en. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ BirdLife International (2020). "Momotus coeruliceps". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T61634591A163627466. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T61634591A163627466.en. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ BirdLife International (2020). "Momotus lessonii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T61634649A163627947. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T61634649A163627947.en. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ BirdLife International (2020). "Momotus subrufescens". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T61634657A163628473. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T61634657A163628473.en. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ BirdLife International (2016). "Momotus bahamensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T61634940A95173793. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T61634940A95173793.en. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ BirdLife International (2016). "Momotus momota". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T61634607A95173087. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T61634607A95173087.en. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ BirdLife International (2016). "Momotus aequatorialis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22729189A95009151. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22729189A95009151.en. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ BirdLife International (2020). "Baryphthengus martii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T22682995A163629009. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22682995A163629009.en. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ BirdLife International (2016). "Baryphthengus ruficapillus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22682998A92972518. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22682998A92972518.en. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ BirdLife International (2020). "Electron carinatum". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T22682989A179184295. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22682989A179184295.en. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ BirdLife International (2020). "Electron platyrhynchum". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T22682986A163629547. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22682986A163629547.en. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ BirdLife International (2020). "Eumomota superciliosa". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2020: e.T22682992A163630124. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22682992A163630124.en. Retrieved 7 October 2023.














