List of human endocrine organs and actions
 |
| Part of a series of lists about |
| Human anatomy |
|---|
Hypothalamic-pituitary axis
[edit]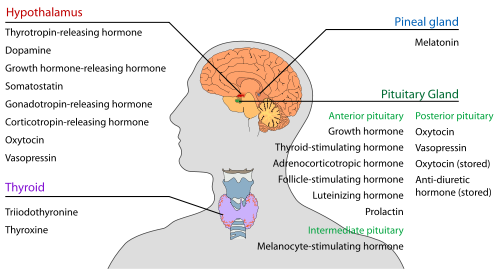
| Secreted hormone | Abbreviation | Produced by | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thyrotropin-releasing hormone | TRH | Parvocellular neurosecretory neurons | Stimulate thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) release from anterior pituitary (primarily) |
| Dopamine (Prolactin-inhibiting hormone) |
DA or PIH | Dopamine neurons of the arcuate nucleus | Inhibit prolactin released from anterior pituitary |
| Growth hormone-releasing hormone | GHRH | Neuroendocrine neurons of the Arcuate nucleus | Stimulate Growth hormone (GH) release from anterior pituitary |
| Somatostatin (growth hormone-inhibiting hormone) |
SS, GHIH, or SRIF | Neuroendocrine cells of the Periventricular nucleus | Inhibit Growth hormone release from anterior pituitary Inhibit thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) release from anterior pituitary |
| Gonadotropin-releasing hormone | GnRH or LHRH | Neuroendocrine cells of the Preoptic area | Stimulate follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) release from anterior pituitary Stimulate luteinizing hormone (LH) release from anterior pituitary |
| Corticotropin-releasing hormone | CRH or CRF | Parvocellular neurosecretory neurons of the Paraventricular nucleus | Stimulate adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) release from anterior pituitary |
| Oxytocin | OX or OXT | Magnocellular neurosecretory cells | In females: uterine contraction during birthing, lactation (letdown reflex) when nursing |
| Vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) |
ADH or AVP or VP | Parvocellular neurosecretory neurons, Magnocellular neurosecretory neurons of the Paraventricular nucleus and Supraoptic nucleus | Increases water permeability in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct of nephrons, thus promoting water reabsorption and increasing blood volume |
Pineal body (epiphysis)
[edit]| Secreted hormone | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Melatonin | Pinealocytes | Antioxidant Monitors the circadian rhythm including induction of drowsiness and lowering of the core body temperature |
Pituitary gland (hypophysis)
[edit]The pituitary gland (or hypophysis) is an endocrine gland about the size of a pea and weighing 0.5 grams (0.018 oz) in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain, and rests in a small, bony cavity (sella turcica) covered by a dural fold (diaphragma sellae). The pituitary is functionally connected to the hypothalamus by the median eminence via a small tube called the infundibular stem or pituitary stalk.[1] The anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis) is connected to the hypothalamus via the hypothalamo–hypophyseal portal vessels, which allows for quicker and more efficient communication between the hypothalamus and the pituitary.[2]
Anterior pituitary lobe (adenohypophysis)
[edit]| Secreted hormone | Abbreviation | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Growth hormone (somatotropin) |
GH | Somatotrophs | Stimulates growth and cell reproduction Stimulates Insulin-like growth factor 1 release from liver |
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone (thyrotropin) |
TSH | Thyrotropes | Stimulates thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) synthesis and release from thyroid gland Stimulates iodine absorption by thyroid gland |
| Adrenocorticotropic hormone (corticotropin) |
ACTH | Corticotrophs | Stimulates corticosteroid (glucocorticoid and mineralcorticoid) and androgen synthesis and release from adrenocortical cells |
| Beta-endorphin | – | Corticotrophs | Inhibits perception of pain |
| Follicle-stimulating hormone | FSH | Gonadotrophs | In females: Stimulates maturation of ovarian follicles in ovary In males: Stimulates maturation of seminiferous tubules In males: Stimulates spermatogenesis In males: Stimulates production of androgen-binding protein from Sertoli cells of the testes |
| Luteinizing hormone | LH | Gonadotrophs | In females: Stimulates ovulation In females: Stimulates formation of corpus luteum In males: Stimulates testosterone synthesis from Leydig cells (interstitial cells) |
| Prolactin | PRL | Lactotrophs | Stimulates milk synthesis and release from mammary glands Mediates sexual gratification |
| Melanocyte-stimulating hormone | MSH | Melanotropes in the Pars intermedia of the Anterior Pituitary | Stimulates melanin synthesis and release from skin/hair melanocytes |
Posterior pituitary lobe (neurohypophysis)
[edit]| Stored hormone | Abbreviation | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxytocin | OX or OXT | Magnocellular neurosecretory cells | In females: uterine contraction during birthing, lactation (letdown reflex) when nursing |
| Vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone) |
ADH or AVP | Parvocellular neurosecretory neurons | Increases water permeability in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct of nephrons, thus promoting water reabsorption and increasing blood volume |
Oxytocin and anti-diuretic hormone are not secreted in the posterior lobe, merely stored.
| Secreted hormone | Abbreviation | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Triiodothyronine | T3 | Thyroid epithelial cell | (More potent form of thyroid hormone) Stimulates body oxygen and energy consumption, thereby increasing the basal metabolic rate Stimulates RNA polymerase I and II, thereby promoting protein synthesis |
| Thyroxine (tetraiodothyronine) |
T4 | Thyroid epithelial cell's | (Less active form of thyroid hormone) (Acts as a prohormone to triiodothyronine) Stimulates body oxygen and energy consumption, thereby increasing the basal metabolic rate Stimulates RNA polymerase I and II, thereby promoting protein synthesis |
| Calcitonin | Parafollicular cell's | Stimulates osteoblasts and thus bone construction Inhibits Ca2+ release from bone, thereby reducing blood Ca2+ |
Digestive system
[edit]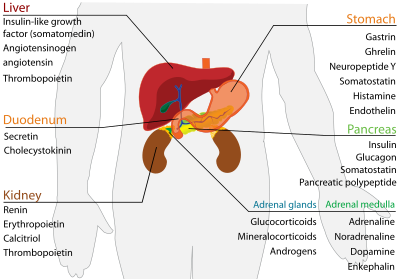
| Secreted hormone | Abbreviation | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gastrin (Primarily) | G cells | Secretion of gastric acid by parietal cells | |
| Ghrelin | P/D1 cells | Stimulate appetite. | |
| Neuropeptide Y | NPY | Increased food intake and decreased physical activity. It can be associated with obesity. | |
| Somatostatin | D cells | Suppress release of gastrin, cholecystokinin (CCK), secretin, motilin, vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP), enteroglucagon
Lowers rate of gastric emptying Reduces smooth muscle contractions and blood flow within the intestine.[3] | |
| Histamine | ECL cells | stimulate gastric acid secretion | |
| Endothelin | X cells | Smooth muscle contraction of stomach[4] |
| Secreted hormone | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Secretin | S cells | Secretion of bicarbonate from liver, pancreas and duodenal Brunner's glands
Enhances effects of cholecystokinin, stops production of gastric juice |
| Cholecystokinin | I cells | Release of digestive enzymes from pancreas
Release of bile from gallbladder, hunger suppressant |
| Secreted hormone | Abbreviation | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insulin-like growth factor (or somatomedin) (Primarily) | IGF | Hepatocytes | insulin-like effects
regulate cell growth and development |
| Angiotensinogen and angiotensin | Hepatocytes | vasoconstriction
release of aldosterone from adrenal cortex dipsogen. | |
| Thrombopoietin | THPO | Hepatocytes | stimulates megakaryocytes to produce platelets[5] |
| Hepcidin | Hepatocytes | inhibits intestinal iron absorption and iron release by macrophages |
The pancreas is a heterocrine gland as it functions both as an endocrine and as an exocrine gland.[6]
| Secreted hormone | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Insulin (Primarily) | β Islet cells | Intake of glucose, glycogenesis and glycolysis in liver and muscle from blood.
Intake of lipids and synthesis of triglycerides in adipocytes. Other anabolic effects |
| Glucagon (Also Primarily) | α Islet cells | Glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in liver.
Increases blood glucose level. |
| Somatostatin | δ Islet cells | Inhibit release of insulin[7]
Inhibit release of glucagon[7] Suppress the exocrine secretory action of pancreas. |
| Pancreatic polypeptide | PP cells | Self regulate the pancreas secretion activities and effect the hepatic glycogen levels. |
| Secreted hormone | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Renin (Primarily) | Juxtaglomerular cells | Activates the renin–angiotensin system by producing angiotensin I of angiotensinogen |
| Erythropoietin (EPO) | Extraglomerular mesangial cells | Stimulate erythrocyte production |
| Calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3) | Proximal tubule cells | Active form of vitamin D3
Increase absorption of calcium and phosphate from gastrointestinal tract and kidneys inhibit release of PTH |
| Thrombopoietin | stimulates megakaryocytes to produce platelets[5] |
| Secreted hormone | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Glucocorticoids (chiefly cortisol) | zona fasciculata and zona reticularis cells | Stimulates gluconeogenesis Stimulates fat breakdown in adipose tissue Inhibits protein synthesis Inhibits glucose uptake in muscle and adipose tissue Inhibits immunological responses (immunosuppressive) Inhibits inflammatory responses (anti-inflammatory) |
| Mineralocorticoids (chiefly aldosterone) | Zona glomerulosa cells | Stimulates active sodium reabsorption in kidneys Stimulates passive water reabsorption in kidneys, thus increasing blood volume and blood pressure Stimulates potassium and H+ secretion into nephron of kidney and subsequent excretion |
| Androgens (including DHEA and testosterone) | Zona fasciculata and Zona reticularis cells | In males: Relatively small effect compared to androgens from testes In females: masculinizing effects |
| Secreted hormone | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Adrenaline (epinephrine) (Primarily) | Chromaffin cells | Fight-or-flight response:
|
| Noradrenaline (norepinephrine) | Chromaffin cells | Fight-or-flight response:
|
| Dopamine | Chromaffin cells | Increase heart rate and blood pressure |
| Enkephalin | Chromaffin cells | Regulate pain |
Reproductive
[edit]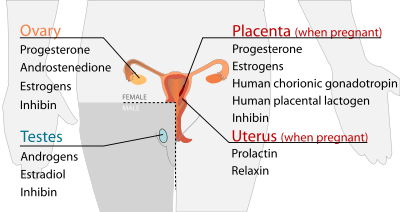
| Secreted hormone | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Androgens (chiefly testosterone) | Leydig cells | Anabolic: growth of muscle mass and strength, increased bone density, growth and strength,
Virilizing: maturation of sex organs, formation of scrotum, deepening of voice, growth of beard and axillary hair. |
| Estradiol | Sertoli cells | Prevent apoptosis of germ cells[8] |
| Inhibin | Sertoli cells | Inhibit production of FSH |
| Secreted hormone | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Progesterone | Granulosa cells, theca cells | Support pregnancy:[9]
Other:
|
| Androstenedione | Theca cells | Substrate for estrogen |
| Estrogens (mainly estradiol) | Granulosa cells | Structural:
Protein synthesis:
Fluid balance:
Gastrointestinal tract:
Melanin:
Cancer:
Lung function: |
| Inhibin | Granulosa cells | Inhibit production of FSH from anterior pituitary |
| Secreted hormone | Abbreviation | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Progesterone (Primarily) | Support pregnancy:[9]
Other effects on mother similar to ovarian follicle-progesterone | ||
| Estrogens (mainly Estriol) (Also Primarily) | Effects on mother similar to ovarian follicle estrogen | ||
| Human chorionic gonadotropin | HCG | Syncytiotrophoblast | Promote maintenance of corpus luteum during beginning of pregnancy
Inhibit immune response, towards the human embryo. |
| Human placental lactogen | HPL | Syncytiotrophoblast | Increase production of insulin and IGF-1
Increase insulin resistance and carbohydrate intolerance |
| Inhibin | Fetal Trophoblasts | Suppress FSH |
| Secreted hormone | Abbreviation | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prolactin | PRL | Decidual cells | milk production in mammary glands |
| Relaxin | Decidual cells | Unclear in humans and animals |
Calcium regulation
[edit]| Secreted hormone | Abbreviation | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parathyroid hormone | PTH | Parathyroid chief cell | Calcium:
|
| Secreted hormone | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) | Keratinocytes | Cholecalciferol is an inactive form of vitamin D3
|
Other
[edit]
| Secreted hormone | Abbreviation | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atrial natriuretic peptide | ANP | Cardiac myocytes | Reduce blood pressure by:
reducing systemic vascular resistance, reducing blood water, sodium and fats |
| Brain natriuretic peptide | BNP | Cardiac myocytes | (To a lesser degree than ANP) reduce blood pressure by:
reducing systemic vascular resistance, reducing blood water, sodium and fats |
| Secreted hormone | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Osteocalcin | osteoblasts | stimulates beta cells to produce insulin |
In 1998, skeletal muscle was identified as an endocrine organ[14] due to its now well-established role in the secretion of myokines.[14][15] The use of the term myokine to describe cytokines and other peptides produced by muscle as signalling molecules was proposed in 2003.[16]
Signalling molecules released by adipose tissue are referred to as adipokines.
| Secreted hormone | From cells | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Leptin (Primarily) | Adipocytes | decrease of appetite and increase of metabolism. |
| Adiponectin | Adipocytes | Reduces insulin resistance[17] |
| Estrogens[18] (mainly Estrone) | Adipocytes |
References
[edit]- ^ Vander A (2008). Vander's Human Physiology: the mechanisms of body function. Boston: McGraw-Hill Higher Education. pp. 345–347. ISBN 978-0-07-304962-5.
- ^ Vander, Arthur (2008). Vander's Human Physiology: the mechanisms of body function. Boston: McGraw-Hill Higher Education. pp. 332–333.
- ^ Colorado State University – Biomedical Hypertextbooks – Somatostatin
- ^ Endo K, Matsumoto T, Kobayashi T, Kasuya Y, Kamata K (2005). "Diabetes-related changes in contractile responses of stomach fundus to endothelin-1 in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats". J Smooth Muscle Res. 41 (1): 35–47. doi:10.1540/jsmr.41.35. PMID 15855738.
- ^ a b Kaushansky K (May 2006). "Lineage-specific hematopoietic growth factors". N Engl J Med. 354 (19): 2034–45. doi:10.1056/NEJMra052706. PMID 16687716.
- ^ Molnar, Charles; Gair, Jane (14 May 2015). "Endocrine glands". opentextbc. Retrieved 16 September 2019.
- ^ a b Nosek, Thomas M. "Section 5/5ch4/s5ch4_17". Essentials of Human Physiology. Archived from the original on 2016-03-24.
- ^ Pentikäinen V, Erkkilä K, Suomalainen L, Parvinen M, Dunkel L (2000). "Estradiol acts as a germinal cell survival factor in the human testis in vitro". J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 85 (5): 2057–67. doi:10.1210/jcem.85.5.6600. PMID 10843196.
- ^ a b c d Bowen, R. (August 6, 2000) Placental Hormones. Colorado State University
- ^ Nosek, Thomas M. "Section 5/5ch9/s5ch9_13". Essentials of Human Physiology. Archived from the original on 2016-03-24.
- ^ Hould F, Fried G, Fazekas A, Tremblay S, Mersereau W (1988). "Progesterone receptors regulate gallbladder motility". J Surg Res. 45 (6): 505–12. doi:10.1016/0022-4804(88)90137-0. PMID 3184927.
- ^ Hormonal Therapy
- ^ Massaro D, Massaro GD (2004). "Estrogen regulates pulmonary alveolar formation, loss, and regeneration in mice". American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 287 (6): L1154–9. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00228.2004. PMID 15298854.
- ^ a b Pedersen BK, Febbraio MA (October 2008). "Muscle as an endocrine organ: focus on muscle-derived interleukin-6". Physiological Reviews. 88 (4): 1379–406. doi:10.1152/physrev.90100.2007. PMID 18923185.
- ^ Ostrowski K, Hermann C, Bangash A, Schjerling P, Nielsen JN, Pedersen BK (December 1998). "A trauma-like elevation of plasma cytokines in humans in response to treadmill running". The Journal of Physiology. 513 (3): 889–94. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.889ba.x. PMC 2231318. PMID 9824725.
- ^ Pedersen BK, Steensberg A, Fischer C, et al. (2003). "Searching for the exercise factor: is IL-6 a candidate?". Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility. 24 (2–3): 113–9. doi:10.1023/A:1026070911202. PMID 14609022.
- ^
 This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 4.0 license. Betts, J Gordon; Desaix, Peter; Johnson, Eddie; Johnson, Jody E; Korol, Oksana; Kruse, Dean; Poe, Brandon; Wise, James; Womble, Mark D; Young, Kelly A (July 27, 2023). Anatomy & Physiology. Houston: OpenStax CNX. 17.10 Organs with Secondary Endocrine Functions. ISBN 978-1-947172-04-3.
This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 4.0 license. Betts, J Gordon; Desaix, Peter; Johnson, Eddie; Johnson, Jody E; Korol, Oksana; Kruse, Dean; Poe, Brandon; Wise, James; Womble, Mark D; Young, Kelly A (July 27, 2023). Anatomy & Physiology. Houston: OpenStax CNX. 17.10 Organs with Secondary Endocrine Functions. ISBN 978-1-947172-04-3.
- ^ Frühbeck G (July 2004). "The adipose tissue as a source of vasoactive factors". Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents. 2 (3): 197–208. doi:10.2174/1568016043356255. PMID 15320786.


