Languages of Senegal
| Languages of Senegal | |
|---|---|
 French in use on an official sign in Agnam-Goly | |
| Official | French |
| National | Wolof, Balanta-Ganja, Jola-Fonyi, Mandinka, Mandjak, Mankanya, Noon, Pulaar, Serer, Soninke |
| Vernacular | Wolof |
| Minority | Bambara, Bandial, Bapeng, Bassari, Bayot, Bedik, Dyula, Gusilay, Jola-Felupe, Karon, Kasa, Kassonke, Kobiana, Laalaa, Maninka, Ndut, Palor, Safen |
| Foreign | English, Arabic, Creole |
| Signed | Francophone African Sign Language |
| Keyboard layout | |
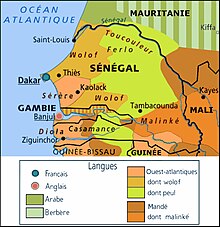
Senegal is a multilingual country: Ethnologue lists 36 languages, Wolof being the most widely spoken language.
French, is the only official language of Senegal, used mainly by the administration, the education and spoken by 26% of the total population.[1] Senegal is a member State of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie. A Senegalese, Abdou Diouf, held the position of its Executive Secretary between 2003 and 2014.
Several of the Senegalese languages have the status of "national languages": Wolof, Balanta-Ganja, Arabic, Jola-Fonyi, Mandinka, Mandjak, Mankanya, Noon (Serer-Noon), Pulaar, Serer, and Soninke.
Senegal is a Francophone country, where, as of 2024, 5,13 million (27.73%) out of 18,50 million people speak French.[2]
In terms of usage, Wolof is the lingua franca and the most widely spoken language in Senegal, as a first or second language (80%).[3]
Mande languages spoken include Soninke, and Mandinka. Jola (Diola) is a main language in the Casamance region. The Guinea Creole dialect, based on Portuguese is also spoken in that region. In 2008 Senegal, due to its historical connections to Portuguese colonisation in Casamance, was admitted as Associate Observer in the CPLP (Community of Portuguese Language Countries).
Education for the deaf in Senegal uses American Sign Language, introduced by the deaf American missionary Andrew Foster. A local language is Mbour Sign Language.
A report for the High Council of Francophonie in Paris stated in 1986 that in Senegal, 60,000 people spoke French as a first language and 700,000 spoke French as a second language. The total population of Senegal at the time was 6,500,000.[4]
Languages taught at school
[edit]French is the only official language of education in the Senegalese system, for 96% of public education, and 90% of private education.[1]
English is taught as a subject in secondary school across the country.[5][6]
Languages
[edit]- Arabic
- American Sign Language
- Badyara
- Banyum
- Balanta
- Bandial
- Bassari
- Bayot
- Bedik
- Guinea-Bissau Creole (Casamance Creole dialect)
- French
- Fula
- Gusilay
- Hassaniya Arabic
- Jola-Felupe
- Jola-Fonyi
- Kasa
- Karon
- Kassonke
- Kobiana
- Kwatay
- Laalaa
- Mandinka
- Manjak
- Maninka
- Mankanya
- Mbouti Sign Language
- Mlomp
- Ndut
- Nko
- Noon
- Palor
- Pulaar
- Pular
- Safen
- Serer
- Soninke
- Wamey
- Wolof
- Yalunka
References
[edit]- ^ a b La langue française dans le monde (2015-2018), Éditions Gallimard, Organisation internationale de la Francophonie
- ^ "Accueil-Francoscope". ODSEF (Observatoire démographique et statistique de l'espace francophone de l'Université Laval) (in French). Laval, Québec. Organisation internationale de la Francophonie.
- ^ Pariona, Amber (27 September 2017). "What Languages Are Spoken in Senegal?". WorldAtlas. Retrieved 4 October 2022.
- ^ Meisler, Stanley. "Seduction Still Works : French--a Language in Decline." Los Angeles Times. March 1, 1986. Retrieved on May 18, 2013.
- ^ "Young Senegalese Turn to English".
- ^ "The Warwick Elt". 31 December 2016.
Further reading
[edit]- Dumont, Pierre (1982). Le français et les langues africaines au Sénégal. Paris: AACT and Karthala.


