Korgantas culture
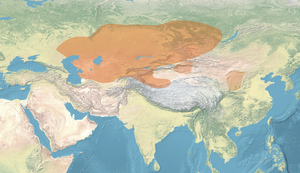
| Geographical range | South Central Siberia |
|---|---|
| Period | Iron Age |
| Dates | ca. 400–113 BCE |
| Preceded by | Tasmola culture |
| Followed by | Xiongnu Empire |
The Korgantas culture (c. 400-113 BCE) replaced the Tasmola culture in Central Kazakhstan.[2][3][4] It is used sometimes termed as the "Korgantas period" of the Tasmola culture.[3]
The tombs of the Korgantas period differ significantly from those of the earlier Tasmola, lacking dromos passageways, and being smaller, with animal sacrifices arranged near the head.[3] The burials are often covered with a chaotic assemblage of stones, and the dead were oriented to the East or the Northeast.[4] Many characteristics of these burials, especially the heads of sacrificed animals, are similar to those of early Hunnic burials.[4] In a recent study, various Korgantas period graves were carbon-dated to between 400 and circa 100 BCE cal.[4]
Genetically, the Korgantas period seems to mark an influx of Ancient Northeast Asians (Devils_Cave_N profile) in Central Asia.[5] Of four Korgantas individuals analysed in a recent study, three had about 50% Ancient Northeast Asians (Devils_Cave_N) ancestry combined with about 50% Central Saka ancestry (Tasmola_Pazyryk), while only one had a traditional Central Saka profile.[6] The Korgantas people may have resulted from immigrations from the eastern regions of Central Asia, and may have come from the Ordos region of northern China.[7]
The end of the Korgantas period is marked by the expansion of the Xiongnu. The Korgantas period is sometimes presented as the "later Korgantas phase of the early Hun period".[4]
References
[edit]- ^ Ivanov, Sergei Sergeevich (2023). "Asia, Steppe, East: Early Iron Age Pastoralist Cultures". Reference Module in Social Sciences: Fig.1. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-90799-6.00253-6. ISBN 978-0-443-15785-1.
- ^ Gnecchi-Ruscone et al. 2021, "Korgantas culture that replaced the Tasmola in central Kazakhstan.".
- ^ a b c Chang, Claudia (16 August 2017). Rethinking Prehistoric Central Asia: Shepherds, Farmers, and Nomads. Routledge. p. 52. ISBN 978-1-351-70158-7.
Korgantas phase dates between 397 and 113 BC cal BC (2 sigma). These burials lack the dromos passageway of Tasmola burials, are usually smaller in size...
- ^ a b c d e Beisenov et al. 2016.
- ^ Gnecchi-Ruscone et al. 2021, Fitting models for the main IA groups using LBA sources, the major genetic shift with the “new” East Asian influx (DevilsCave_N-like) observed in the Middle IA outliers and Korgantas. (...) From the second half of the first millennium BCE, we detect a major genetic shift in a number of outliers that are interestingly linked with the emergence of the Korgantas culture that replaced the Tasmola in central Kazakhstan..
- ^ Gnecchi-Ruscone et al. 2021.
Sources
[edit]- Gnecchi-Ruscone, Guido Alberto; Khussainova, Elmira; Kahbatkyzy, Nurzhibek; Musralina, Lyazzat; Spyrou, Maria A.; Bianco, Raffaela A.; Radzeviciute, Rita; Martins, Nuno Filipe Gomes; Freund, Caecilia; Iksan, Olzhas; Garshin, Alexander; Zhaniyazov, Zhassulan; Bekmanov, Bakhytzhan; Kitov, Egor; Samashev, Zainolla; Beisenov, Arman; Berezina, Natalia; Berezin, Yakov; Bíró, András Zsolt; Évinger, Sándor; Bissembaev, Arman; Akhatov, Gaziz; Mamedov, Aslan; Onggaruly, Akhan; Voyakin, Dmitriy; Chotbayev, Aidos; Kariyev, Yeldos; Buzhilova, Alexandra; Djansugurova, Leyla; Jeong, Choongwon; Krause, Johannes (26 March 2021). "Ancient genomic time transect from the Central Asian Steppe unravels the history of the Scythians". Science Advances. 7 (13): eabe4414. Bibcode:2021SciA....7.4414G. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abe4414. ISSN 2375-2548. PMC 7997506. PMID 33771866.
- Beisenov, Arman Z; Svyatko, Svetlana V; Kassenalin, Aibar Е; Zhambulatov, Kairat А; Duisenbai, Daniyar; Reimer, Paula J (March 2016). "First Radiocarbon Chronology for the Early Iron Age Sites of Central Kazakhstan (Tasmola Culture and Korgantas Period)" (PDF). Radiocarbon. 58 (1): 179–191. Bibcode:2016Radcb..58..179B. doi:10.1017/RDC.2015.18. S2CID 130995035.