James Gregory Telescope
 The James Gregory telescope | |
| Named after | James Gregory |
|---|---|
| Location(s) | St Andrews, Fife, Scotland |
| Coordinates | 56°20′14″N 2°48′59″W / 56.33715°N 2.8165°W |
| Organization | University of St Andrews |
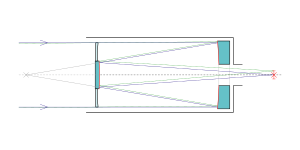
| Telescope style | optical telescope Schmidt–Cassegrain telescope |
| Diameter | 0.94 m (3 ft 1 in) |
| Website | observatory |
| | |
The James Gregory Telescope was constructed in 1962 by the University of St Andrews. It is of a Schmidt-Cassegrain design and is fitted with a CCD camera.[1] The telescope has very large field of view, compared even to regular 'wide field' designs, and can view 5 square degrees.[2]
The James Gregory Telescope is the largest working optical telescope in the UK and is still used by the School of Physics and Astronomy for research in collaborative projects such as SuperWASP and the study of super massive black holes and their impact on galaxy structure.[3]
The James Gregory Telescope is named after the Scottish mathematician, astronomer and University academic James Gregory, who invented the design Gregorian telescope.[4] This was the first design for a reflecting telescope, and pre-dates Newton's design; however Newton is better known as he actually produced a functioning example. (see Newton's reflector)
As of 2018, this telescope is recognized as the largest telescope in operation in the United Kingdom. It is also recognized as the largest Schmidt-Cassegrain. This design was developed by Baker and Linfoot, and a half-scale model was also made during its development. It was estimated that the telescope cost about £1 million to manufacture, in early 21st-century currency.[2]
The telescope uses both a mirror and corrector, and is capable up to 16 degrees but was adjusted after it came online in 1962.[2]
The telescope has an aperture of 37 inches, but in the current setup about 33 inches of aperture are used.[5]
See also
[edit]- List of largest optical telescopes in the 20th century
- Gregor telescope at the Teide Observatory.
- Gregorian telescope is a type of telescope.
- James Gregory is the inventor of the Gregorian telescope.
- Greenwich 28 inch refractor (At RGO)
- List of largest optical telescopes in the British Isles
References
[edit]- ^ Tim Lister. "James Gregory Telescope". Tim Lister. Archived from the original on 23 December 2012. Retrieved 4 May 2009.
- ^ a b c Dvinsky, Dalcash (5 April 2018). "A short history of Scotland's largest telescope". Medium. Retrieved 27 October 2019.
- ^ Anon. "St Andrews Observatory". University of St Andrews School of Physics and Astronomy. Archived from the original on 26 December 2008. Retrieved 4 May 2009.
- ^ J J O'Connor and E F Robertson. "James Gregory". University of St Andrews School of Mathematics and Statistics. Retrieved 4 May 2009.
- ^ "JGT".