Ipswich River
| Ipswich River | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Burlington, Massachusetts |
| • coordinates | 42°33′14″N 71°08′38″W / 42.5539828°N 71.1439441°W |
| Mouth | |
• location | Ipswich Bay, Massachusetts |
• coordinates | 42°41′38″N 70°47′23″W / 42.6939825°N 70.7897712°W |
• elevation | 0 ft |
| Length | 35 mi (56 km) |
| Basin size | 155 sq mi (400 km2) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Skug River, Boston Brook |
| • right | Miles River, Salem Beverly Waterway Canal |
Ipswich River is a small river in northeastern Massachusetts, United States. It held significant importance in early colonial migrations inland from the ocean port of Ipswich. The river provided safe harborage at offshore Plum Island Sound to early Massachusetts subsistence farmers, who were also fishermen. A part of the river forms town boundaries and divides Essex County, Massachusetts on the coast from the more inland Middlesex County.[1] It is 35 miles (56 km) long,[2] and its watershed is approximately 155 square miles (401 km2), with an estimated population in the area of 160,000 people.[3]
Historically, the settlement of Essex County began at the oldest community there, the tiny seaport of Agawam (later renamed Ipswich, and not to be confused with present-day Agawam in Hampden County), and typically proceeded westward and northward along the Ipswich or its tributary creeks. When Middlesex County was formed in the Massachusetts Bay Colony, only Salem and Charlestown across the Charles River mouth and Boston harbor's inner estuary from Boston's much smaller hill dominated peninsula were older settlements.
The upper river runs through and drains at least parts of Burlington, the lower river forms part of the borders between the towns of:
- North Reading and Lynnfield
- Middleton and the city of Peabody
- Middleton and Danvers, and
- Boxford and Topsfield.
The wide swamps along the river made it impossible to ford the stream anywhere east of Wilmington in colonial times. The only route north out of Boston to the northeast (today called the North Shore) was via the Andover Road, an often muddy track, later made a wagon road which forded the stream just below the confluence of Lubbers and Maple Meadow brooks.
Geology
[edit]The topography of eastern Massachusetts was determined most by the fact that, at the maximum glaciation of the Pleistocene Era, it was the site of the edge of the last glaciation, at approximately 18,000 BC. This glacier had planed the land under it nearly flat. Gravel- and boulder-lined streams ran along its surface. From 18,000 to about 10,000 BC, the glacier receded, dropping its stony contents as eskers and moraines, the dominant features of the region. The glacier's recession created ridges, deposited sand and gravel, the dominant material of the riverbed, over which mud has been deposited.[4] Low-gradient drainage created the meandering streams, which typically drop no more than 30–40 feet.
Usage
[edit]The first written record about the Ipswich River is from 1638 when John Winthrop bought from Chief Masconomet and the Agawam tribe the lands along the river and exclusive fishing rights for 20 pounds sterling.
Most of the land along the river is privately owned but in certain recreational areas non-motorized boats, fishing, and swimming are allowed. It is attractive to canoeists and birders. In the swampy and wetland areas a wide variety of birds and smaller wildlife species can be seen.
Drinking water for many communities is provided from Ipswich River. It is estimated that source of public drinking water for approximately 350,000 people comes from the river's watershed although most of these people live outside the area. There are some concerns about the quality of the water as the river dries up and some places become a dumping ground for tires.[5]
Geography
[edit]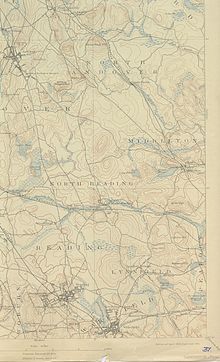
The river begins in the northeastern part of Burlington in northcentral Middlesex County Massachusetts and heading generally southeasterly, it passes through the towns of Wilmington (where once the important Middlesex Canal passed over it on an aqueduct), Reading, thence to North Reading, where it is joined by the left bank tributary Skug River — which originates in North Andover and Andover southwest of Boston Hill in a large Beaver Pond and marshland, situated north of Gray Road-jct.-Gray Street (very near the townlines of the two towns) where it crosses via culvert south of Rt. MA 125 and west of Rt. MA 114 (historically, and by street name, the Salem Turnpike), and thence, about a mile south, gains volume draining all of Harold Parker State Forest in the tri-town corner of Andover, North Andover, and Middleton — excepting the few acres draining to Ipswich tributary, Boston Brook along the other side of MA 114.
Both tributary creeks enter and mingle with the Ipswich proper in Middleton, proceed south into northern Peabody, then loop northwards through the municipalities of Danvers, Topsfield (crossing US Route 1 just south of the Topsfield Fairground, entering from the west turns northerly and runs the greater length of Teal Pond southwest to north, the east bank of which forms a part of the western border of Hamilton, and exits the lake turning easterly staying south of Ipswich Road to head through and between the Willowdale State Forest and Bradley Palmer State Park, then opens a gap from Ipswich road diverging southeasterly from the road and the south edge of the Turner Hill Golf Club to turn north and form the west border of the Julia Bird Reservation thence meanders north through settled Ipswich neighborhoods and directly through town center passing under MA 133 (County Road, aka. South Main Street) where it gradually begins widening until a mile beyond main Street it passes Nichols Field and the salt marsh floodplain begins. From Nichols it traverses a bit over 2.5 miles (4.0 km)[6] joins with Plum Island Sound in connecting with the Atlantic Ocean at Ipswich Bay.[7] There is always some flow from the river into the bay. However, the lower Ipswich and Plum Island Sound, as well as the lower four other rivers flowing into it, and the much larger Merrimack River to the north, are all tidal estuaries, so the water is brackish from mixing ocean born saltwater inland during flood tides, and the lands immediately along the banks, where not inundated some of the time, are nonetheless saturated by brackish water and support only hearty plants capable of tolerating the waters such as salt marsh hay. High tides cover all of Great Marsh and the flood plains of the lower rivers. Low tides uncover the mud flats, reducing the deep channels to small streams some often small enough one can hop across to fish elsewhere.
The river is navigable upstream to nearly Ipswich center by small craft. There a sharper drop in elevation over some rocky areas upstream characteristic of Northeastern US streams in general and which prevents further navigation without portaging light boats. The river and riverlands currently suffer from diminished flow due to extensive withdrawals from the ground water in urban areas upstream.[citation needed] The upper third of the river may become a dry bed in the summer. Wetland reservations, for wildlife have been created along much of the lower river and the mean water level therein has been prevented from falling precipitously by Willowdale Mill Dam, a remnant of a 19th-century mill system. It is currently privately owned by a canoe-rental concession.

in Ipswich Bay, July 2010
The combined Ipswich River/Plum Island Sound exits through a relatively narrow, shallow channel that passes under Castle Hill and along Crane's Beach to the south. On the north, Sandy Point at the tip of Plum Island juts into the flow. In the days of sail, Bar Head, Bar Head Rocks, and Emerson Rocks posed some threat to sailing vessels trying to tack into or out of the estuary. The shallow waters often stranded vessels in storms, which would then be dismantled by severe breakers. The combination was inevitably tragic to vessels caught there in a northeaster, or violent winter storm of near-hurricane-force winds. Despite these difficulties, the sound and the mouth of the Ipswich were mooring places of ocean-going cargo vessels and fishing and whaling boats, before the opening of Newburyport Harbor, then blocked by a sandbar. The now abandoned shores of the region give little hint of its former importance to commerce and prosperity.
See also
[edit]- Bradley Palmer State Park
- Choate Bridge
- Ipswich River Wildlife Sanctuary
- Salem Beverly Waterway Canal
References
[edit]- ^ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Ipswich River
- ^ "The National Map - National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flow line data". viewer.nationalmap.gov. United States Geological Survey. Archived from the original on 2012-03-29. Retrieved 1 Apr 2011.
- ^ "Ipswich River Watershed". mass.gov. Massachusetts Executive Office of Environmental Affairs. Archived from the original on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 8 Jan 2017.
- ^ "About the River and Watershed". ipswichriver.org. Ipswich River Watershed Association. Archived from the original on 7 February 2010. Retrieved 8 Jan 2017 – via web.archive.org.
- ^ Kirk, Bill. "Water shortage hits home upstream". Salem Evening News. Archived from the original on 26 November 2006. Retrieved 8 Jan 2017 – via net1plus.com by way of web.archive.org.
- ^ 2.5 mile measurement and previous like descriptions are approximate satellite generated data using the google.com/maps/place ruler tool with google maps in terrain mode zoomed way in to show watercourses.
- ^ "About the Ipswich River". naturecompass.org. Archived from the original on 27 May 2010. Retrieved 8 Jan 2017 – via web.archive.org.
External links
[edit]![]() Media related to Ipswich River at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ipswich River at Wikimedia Commons
