Indigetes
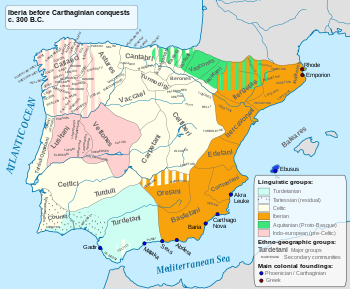
The Indigetes (Latin: indigetes or indigetae or Indiketes, Iberian: untikesken) were an ancient Iberian (Pre-Roman) people of the eastern side of the Iberian Peninsula (the Roman Hispania). They are believed to have spoken the Iberian language.
Location
[edit]They occupied the far north east area of the Iberian Peninsula known as Hispania Tarraconensis,[1] in the gulf of Empúries and Rhoda, stretching up into the Pyrenees though the regions of Empordà, Selva and perhaps as far as Gironès, where the Ausetani could be found who were related ethnically.
They were divided into four tribes,[1] and the main towns they centered on were: Indika (Untika) (only mentioned by Stephanus of Byzantium, still unidentified, but he was possibly referring to Empúries or Ullastret),[2] Empodrae (Empúries, where there was an extremely important Greek, Phocaean and Massaliotan[note 1] colony,[3] which had their corresponding commercial "emporio"), Rhoda (Roses), Juncaria (La Jonquera), Cinniana (Cervià) and Deciana (close to La Jonquera).[1] This land was watered by the Clodianus (Fluvià), the Sambrocas (Muga) and the Tichis (Ter). This district in the Gulf of Empúrias was known as Juncaris Campus.
Culture
[edit]The Indigetes minted their own coins which bore the inscription undikesken in northeastern Iberian script that is interpreted in Iberian language as a self-reference to the ethnic name of that people: from the Indigetes or from those of undika.
The main archaeological sites related to the Indigetes are in Ullastret (Baix Empordà), Castell de la Fosca (Palamós, Baix Empordà) and Puig Castellet (Lloret de Mar, Selva).
History
[edit]In 218 BC they were conquered by Rome during the Roman conquest of Hispania. In 195 BC they rebelled; the consul Marcus Porcius Cato quashed the rebellion.[4]
Gallery
[edit]-
Wall foundations in Puig Castellet near Lloret
-
Inscribed lead plate from the Ullastret Iberian archaeological site
-
Cistern at the Ullastret site
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ Information taken from the Spanish Version of this article, seems to relate to other, possibly Iberian, Peoples of the area.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Smith, William, ed. (1857). Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography. Vol. 2. Walton and Maberly. p. 52.
- ^ Sanmartí, J. & Santacana, J. ELS IBERS DEL NORD. Rafael Dalmau, Ed., Barcelona, 2005. (ISBN 84-232-0691-2)
- ^ Boardman, John; Hammond, N. G. L., eds. (1982). The Expansion of the Greek World, Eighth to Sixth Centuries B.C. The Cambridge Ancient History. Vol. 3: Part 3 (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 141–142. ISBN 0-521-23447-6.
- ^ Varga, Daniel (2015). The Roman Wars in Spain: The Military Confrontation with Guerrilla Warfare. Pen and Sword. pp. 51–52. ISBN 9781473860957.
Bibliography
[edit]- Ángel Montenegro et alii, Historia de España 2 - colonizaciones y formación de los pueblos prerromanos (1200-218 a.C), Editorial Gredos, Madrid (1989) ISBN 84-249-1386-8
External links
[edit]



