Henry Vaughan (art collector)
Henry Vaughan | |
|---|---|
| Born | 17 April 1809. |
| Died | 26 November 1899 (aged 90) |
| Resting place | Highgate Cemetery |
| Nationality | British |
| Occupation | Art collector |
| Known for | Bequests to Art Galleries |
Henry Vaughan (17 April 1809 – 26 November 1899) was a British art collector. He is best known for his many generous gifts and bequests to British and Irish public collections.
Early life
[edit]Henry Vaughan, who was born in Southwark, London on 17 April 1809, was the son of a successful hat manufacturer, George Vaughan, and his wife Elizabeth Andrews.[1] Henry and his elder brother and sister, George and Mary, were brought up as Quakers. He attended a school at Higham Hill, Walthamstow, run by Eliezer Cogan, where a fellow pupil was Benjamin Disraeli.[2] On the death of his father in 1828, Henry inherited a large fortune and thereafter lead what could be thought of as a rather self-indulgent life, but he went on to become one of the most discerning art collectors and generous philanthropists of his time.[3]
Art collector
[edit]In 1834 he bought a lease on a large house, number 28 Cumberland Terrace, on one of the grandest of John Nash's developments in the newly fashionable Regent's Park, which would be his home for the rest of his long life. He spent much of his time travelling extensively, becoming a cultivated, enthusiastic, and eclectic collector of works of art, especially of prints and drawings by J. M. W. Turner, with whom he was personally acquainted.[1] He was elected a fellow of the Society of Antiquaries in 1879, was a founder member of the Burlington Fine Arts Club and was also a member of the Athaeneum.[1] His collecting interests were varied and eclectic; visitors to the house, which he shared with his sister Mary, would have seen rooms richly decorated with sculptures, bronzes, ivories, Spanish clocks, medieval stained glass, frames from Siena and Venice and Rembrandt etchings.[3] However the house had few visitors as Vaughan was known as something of a recluse,[1] preferring his collection to be shown in public galleries. He bought drawings by Michelangelo, Raphael and Rubens, but it was eighteenth and nineteenth century British art which was his main area of interest, acquiring works by Reynolds, Gainsborough, Flaxman, Millais and Leighton, among others.[3] Unusually for the time, Vaughan was particularly interested in artists' ideas and working methods, acquiring many informal, preparatory drawings and sketches including fifteen of John Constable's oil sketches.[3]
The artist he admired above all was J.M.W. Turner, whom he probably first met in the 1840s.[3] By the time of Vaughan's death he owned more than one hundred watercolours and drawings by Turner and as many prints. His collection included examples of almost every type of work on paper the artist produced, from early topographical drawings and atmospheric landscape watercolours, to brilliant colour studies, literary vignette illustrations and spectacular exhibition pieces. It was an unparalleled collection that comprehensively represented the diversity, imagination and technical inventiveness of Turner's work throughout his sixty-year career.[3]
Benefactor
[edit]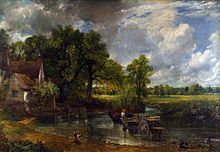
Arguably the jewel in Vaughan's collection was Constable's The Hay Wain, later to become one of the greatest and most popular British paintings,[4] which he bought in the 1860s[1] and enjoyed in his home for twenty years before presenting it to the National Gallery in 1886. He had hoped to keep the gift confidential, but this proved impossible and it was announced in the House of Commons to roars of approval.[3] He had a particularly impressive collection of Turner watercolours, many of which he kept unframed and carefully stored away from the light in strong boxes, showing an awareness of conservation which was unusual at the time, even stipulating in his bequest that they should only be shown in January.[2] During his lifetime he was a generous lender to public exhibitions, museums and galleries and in 1887 he gave five important Michelangelo drawings to the British Museum. He stipulated that his loans should be ‘exhibited to the public all at one time, free of charge’, which demonstrated that he was a man ahead of his time.[5]
When he died, his will stipulated that the bulk of his money should be distributed among various medical charities and hospitals, and most of his art collections among museums and galleries:[1]
The British Museum, in addition to the gifts during his lifetime, received a further 555 artworks, including fifty-seven old master drawings, over 300 drawings by Flaxman, Thomas Lawrence, and Thomas Stothard, and, above all, nearly a hundred proofs of Turner's Liber Studiorum and twenty-three drawings connected with it.[1]
The National Gallery, had some of the above drawings transferred to it and received sculptures as well as Italian and British paintings (the latter now in the Tate collection).[1]
The Victoria and Albert Museum was bequeathed collections of stained glass and carved panels, six Turner watercolours, and the full-scale studies for Constable's The Hay Wain and The Leaping Horse, which had been on loan to that museum since 1862.[1]
University College, London was the recipient of the remainder of his Liber Studiorum prints, his collection of Constable mezzotints, his Rembrandt etchings and other prints, and a number of English drawings.[1]
The National Gallery of Scotland received a representative selection of thirty-nine drawings as well as 38 Turner watercolours.[1][3]
The National Gallery of Ireland received a similar group of drawings and 31 Turner watercolours.[1][5]

Death
[edit]Vaughan died on 26 November 1899 at his house in Cumberland Terrace and his estate was valued for probate at £230,000.[1] He is buried with his sister in a family vault on the western side of Highgate Cemetery, opposite the grave of George Wombwell.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Herrmann, L. (23 September 2004). Vaughan, Henry (1809–1899), art collector. Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Retrieved 31 Mar. 2021, from https://www.oxforddnb.com/view/10.1093/ref:odnb/9780198614128.001.0001/odnb-9780198614128-e-28131
- ^ a b Barrow, Viola (Spring 1991). "Turner in the National Gallery". Dublin Historical Record. 44 (1): 6–16. JSTOR 30100861. Retrieved 31 March 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Henry Vaughan – 'A great Turner man'". www.nationalgalleries.org. Retrieved 31 March 2021.
- ^ "Turner wins 'great painting' vote". BBC News. 5 September 2005.
- ^ a b "Henry Vaughan: Bringing art to the masses who couldn't afford to travel". www.shoutoutuk.org. 5 February 2019. Retrieved 31 March 2021.
