Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations
| Statutory Instrument | |
 | |
| Citation | SI 1996/341 |
|---|---|
| Territorial extent | Great Britain |
| Dates | |
| Made | 18 February 1996 |
| Laid before Parliament | 23 February 1996 |
| Commencement | 1 April 1996 |
| Other legislation | |
| Repeals/revokes | Safety Signs Regulations 1980 |
| Transposes | Directive 92/58/EEC |
Status: Current legislation | |
| Text of statute as originally enacted | |
| Text of the Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations as in force today (including any amendments) within the United Kingdom, from legislation.gov.uk. | |

The Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations 1996 specify the safety signs within Great Britain,[1] Northern Ireland has a similar law.[2] It was issued as a transposition of the European directive 92/58/EEC and replaced The Safety Signs Regulations 1980.[1] They consist of "traditional safety signs", such as prohibitory and warning signs, hand signals, spoken and acoustic signals and hazard marking.[3]
Application
[edit]The regulations applies to the occupational health and safety within the territorial borders of Great Britain, also on offshore installations.[4][5][6] It does not apply to the marking of dangerous goods and substances itself, only its storage or pipes, nor the regulation of road, rail, inland waterway, sea or air traffic, nor to signs used aboard of sea-going ships.[1] For internal road traffic, traffic signs should be used.[4][7]
The Regulations do not require the usage of safety signs and signals for third parties. However, it neither prohibits the usage for this purpose.[8]
The Regulations require safety signage to be uniform and, as far as appropriate, without words, in order to be easily and fast understandable, without knowing the language.[8]
Safety signs should only be used, if other measures of avoiding hazards failed.[3][5] Also, if there is no risk, no safety signage should be used.[7] Employees should regularly be instructed about the meaning of safety signs and signals.[9][10] Employers are obligated to maintain the safety signage.[10]
Relationship between the Regulations and BS EN ISO 7010
[edit]Minor differences between the prescribed signs and the installed signs are allowed, as long as the convey the same message.[1][4] The Health and Safety Executive specifically allows the usage of BS EN ISO 7010 safety signs.[4]
Structure
[edit]The Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations 1996 consists of 8 articles and 3 schedules.[1]
Schedule 1
[edit]Part I
[edit]As required in Annex I of the European directive 92/58/EEC, Schedule 1, Part I of the Reguations lays down a basic safety colour concept:[1][6]
| Colour | Meaning or purpose | Instructions and information |
|---|---|---|
| Red | Prohibition sign | Dangerous behaviour |
| Danger alarm | Stop, shutdown, emergency cut out devices, Evacuate | |
| Fire-fighting equipment | Identification and location | |
| Yellow or Amber | Warning sign | Be careful, take precautions |
| Examine | ||
| Blue | Mandatory sign | Specific behaviour or action |
| Wear personal protective equipment | ||
| Green | Emergency escape, first aid sign | Doors, exits, routes, equipment, facilities |
| No danger | Return to normal |
Part II
[edit]Schedule 1, Part II defines five types of signboards, as shown below.[1] They are also covered by BS 5378, Part 1 and 3 from 1980 and 1982,[5][11][12] which have been superseded by BS EN ISO 7010.[13][14][15] Safety signs must contain only symbols, not text.[5][10] However, supplementary text plates may be used.[10] For fire exits, the running man symbol should be used.[16] Fire safety signs in use before the Regulations were in place could be used until 24 December 1998.[9]
Prohibitory signs
[edit]-
No smoking
-
Smoking and naked flames forbidden
-
No access for pedestrians
-
Do not extinguish with water
-
Not drinkable
-
No access for unauthorised persons
-
No access for industrial vehicles
-
Do not touch
Warning signs
[edit]-
Flammable material or high temperature
-
Explosive material
-
Toxic material
-
Corrosive material
-
Radioactive material
-
Overhead load
-
Industrial vehicles
-
Danger: electricity
-
General danger
-
Laser beam (Version 1996)
-
Laser beam (Version 2009)
-
Oxidant material
-
Non-ionizing radiation
-
Strong magnetic field
-
Obstacles
-
Drop
-
Biological risk
-
Low temperature
-
Harmful or irritant material (withdrawn)
Mandatory signs
[edit]-
Eye protection must be worn
-
Safety helmet must be worn
-
Ear protection must be worn
-
Respiratory equipment must be worn
-
Safety boots must be worn
-
Safety gloves must be worn
-
Safety overalls must be worn
-
Face protection must be worn
-
Safety harness must be worn
-
Pedestrians must use this route
-
General mandatory sign (to be accompanied where necessary by another sign)
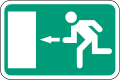
Emergency escape or first-aid signs
[edit]-
Emergency exit/escape route
-
Emergency exit/escape route
-
Emergency exit/escape route
-
Emergency exit/escape route
-
Emergency exit/escape route
-
This way (supplementary information sign)
-
This way (supplementary information sign)
-
This way (supplementary information sign)
-
This way (supplementary information sign)
-
First-aid post
-
Stretcher
-
Safety shower
-
Eyewash
-
Emergency telephone for first-aid or escape
Fire-fighting signs
[edit]-
Fire hose
-
Ladder
-
Fire extinguisher (Version 1996)
-
Fire extinguisher (Version 2009)
-
Emergency fire telephone
-
This way (supplementary information sign)
-
This way (supplementary information sign)
-
This way (supplementary information sign)
-
This way (supplementary information sign)
Part III
[edit]This part, Minimum requirements governing signs on containers and pipes, defines the marking for the transport or storage of dangerous material by pipes and in containers, originally within the scope of the European directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, which are both replaced by Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008, the CLP Regulation.[1] For marking, the warning signs of Part II should be used.[5]
Part IV
[edit]The Minimum requirements for the identification and location of fire-fighting equipment specifies, that, additionally to the Fire-fighting signs of Part II, the equipment for fire-fighting and its location has to be marked red.[1]
Part V
[edit]In this part, the Minimum requirements governing signs used for osbstacles and dangerous locations, and for marking traffic routes, requires hazardous places to be marked with either black and yellow or red and white markings. It also states that ways used for traffic have to be marked with either white or yellow stripes.[1]
Part VI
[edit]Part VI, Minimum requirements for illuminated signs, requires illuminated signs to be single-coloured or to contain a symbol. If the latter is the case, it should comply with Part II. If a flashing light and a sound are used together, they have to be synchronized.[1]
Part VII
[edit]This part, the Minimum requirements for acoustic signals, requires acoustic signals to be understandable and not harmful. If the acoustic signal is an fire alarm, it has to be continuing.[1]
Part VIII
[edit]The Minimum requirements for verbal communication defines the use of language for safety purposes. It also defines coded words:[1]
| Meaning | |
|---|---|
| start | to indicate the start of a command |
| stop | to interrupt or end a movement |
| end | to stop the operation |
| raise | to have a load raised |
| lower | to have a load lowered |
| forwards | to be co-ordinated with the corresponding hand signals |
| backwards | |
| right | |
| left | |
| danger | for an emergency stop |
| quickly | to speed up a movement for safety reasons |
Part IX
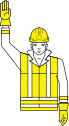
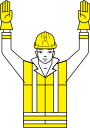
[edit]Hand signals should only be given by one instructor.[6] Other hand signals are also allowed, as specified in Schedule 2.[1]
See also
[edit]- Traffic Signs Regulations and General Directions, a similar Regulations for traffic signs
- Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n "The Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations 1996". legislation.gov.uk. Retrieved 1 September 2023.
- ^ "Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations (Northern Ireland) 1996". legislation.gov.uk. Retrieved 1 September 2023.
- ^ a b "Safety Signs L6" (PDF). Northumberland County Council. February 2014. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- ^ a b c d Safety signs and signals. The Health and Safety Regulations 1996. Guidance on Regulations (3rd ed.). Health and Safety Executive. 2015. ISBN 9780717665983.
- ^ a b c d e Stranks, Jeremy W. (2005). Health and Safety Law (5th ed.). Harlow: Pearson Education. p. 221. ISBN 9780131976467.
- ^ a b c Ridley, John (2013). Health and Safety In Brief (2nd ed.). Routledge. pp. 82–85. ISBN 9781136399619.
- ^ a b "Safety Signage". Queen Mary University of London. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- ^ a b St John Holt, Allan; Allen, Jim (2015). Principles of Health and Safety at Work (8th ed.). Routledge. ISBN 9781317341260.
- ^ a b Rowland, Edward; Day, Bob (2007). Health, Safety and Environment Legislation: A Pocket Guide. Royal Society of Chemistry. pp. 125–126. ISBN 9781847551047.
- ^ a b c d Hughes MBE, Phil; Ferrett, Ed (2020). Introduction to Health and Safety at Work: for the NEBOSH National General Certificate in Occupational Health and Safety (7th ed.). Routledge. pp. 505–507. ISBN 9781000214215.
- ^ BS 5378-1:1980 Safety signs and colours - Specification for colour and design. London: British Standards Institution. 1980.
- ^ BS 5378-3:1982 Safety signs and colours - Specification for additional signs to those given in BS 5378:Part 1. London: British Standards Institution. 1982.
- ^ BS EN ISO 7010:2020+A6:2023 Graphical symbols. Safety colours and safety signs. Registered safety signs. London: British Standards Institution. 2023.
- ^ "BS 5378-1:1980 Safety signs and colours - Specification for colour and design". British Standards Institution. 22 September 2023. Retrieved 22 September 2023.
- ^ "BS 5378-3:1982 Safety signs and colours - Specification for additional signs to those given in BS 5378:Part 1". British Standards Institution. 22 September 2023. Retrieved 22 September 2023.
- ^ Hunt, Garry (2018). Health and Safety Pocket Book (2nd ed.). Abingdon, Oxon: Routledge. p. 112. ISBN 9781138091450.
External links
[edit] Media related to The Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations 1996 (UK) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to The Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations 1996 (UK) at Wikimedia Commons The full text of The Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations 1996 at Wikisource
The full text of The Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations 1996 at Wikisource