HD 50235
Appearance
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Puppis |
| Right ascension | 06h 50m 52.35242s[1] |
| Declination | −34° 22′ 02.3427″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.99[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K5III[3] |
| U−B color index | +1.56[4] |
| B−V color index | +1.38[5] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +30.30[6] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +4.26[1] mas/yr Dec.: +1.26[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 4.00 ± 0.25 mas[1] |
| Distance | 820 ± 50 ly (250 ± 20 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | -1.99[2] |
| Details | |
| Luminosity | 1,185[2] L☉ |
| Temperature | 4,420[7] K |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 2.8[8] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
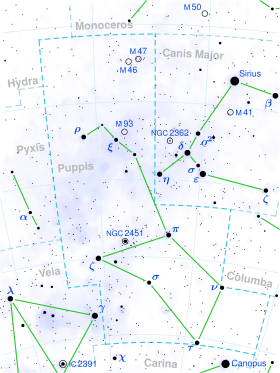
HD 50235 is a class K5III[3] (orange giant) star located approximately 811 light years away,[1] in the constellation Puppis. Its apparent magnitude is 4.99.[2] HD 50235 made its closest approach to the Sun 7.8 million years ago, at the distance of 137 light years, during which it had an apparent magnitude of 1.13.[9][citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. S2CID 18759600. Vizier catalog entry
- ^ a b c d Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters. 38 (5): 331. arXiv:1108.4971. Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. S2CID 119257644. Vizier catalog entry
- ^ a b Hoffleit, D.; Warren, W. H. (1995). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Bright Star Catalogue, 5th Revised Ed. (Hoffleit+, 1991)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: V/50. Originally Published in: 1964BS....C......0H. 5050. Bibcode:1995yCat.5050....0H.
- ^ Mermilliod, J. C. (2006). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Homogeneous Means in the UBV System (Mermilliod 1991)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: II/168. Originally Published in: Institut d'Astronomie. 2168. Bibcode:2006yCat.2168....0M.Vizier catalog entry
- ^ Mallama, A. (2014). "Sloan Magnitudes for the Brightest Stars". The Journal of the American Association of Variable Star Observers. 42 (2): 443. Bibcode:2014JAVSO..42..443M.Vizier catalog entry
- ^ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters. 32 (11): 759–771. arXiv:1606.08053. Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. S2CID 119231169.
- ^ McDonald, I.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Boyer, M. L. (2012). "Fundamental parameters and infrared excesses of Hipparcos stars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 427 (1): 343–357. arXiv:1208.2037. Bibcode:2012MNRAS.427..343M. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x. S2CID 118665352. Vizier catalog entry
- ^ De Medeiros, J. R.; Alves, S.; Udry, S.; Andersen, J.; Nordström, B.; Mayor, M. (2014). "A catalog of rotational and radial velocities for evolved stars". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 561: A126. arXiv:1312.3474. Bibcode:2014A&A...561A.126D. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201220762. S2CID 54046583. Vizier catalog entry
- ^ "VizieR Detailed Page". Retrieved 2012-07-13.