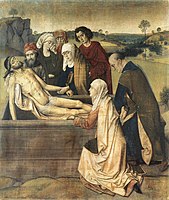
Glue-size

Glue-size is a painting technique in which pigment is bound (sized) to cloth (usually linen) with hide glue, and typically the unvarnished cloth was then fixed to the frame using the same glue. Glue-size is also known as distemper, though the term "distemper" is applied variously to different techniques. Glue-size was used because hide glue was a popular binding medium in the 15th century, particularly among artists of the Early Netherlandish period, who used it as an inexpensive alternative to oil. Although a large number of works using this medium were produced, few survive today, mainly because of the high perishability of linen cloth and the solubility of hide glue. Well-known and relatively well-preserved – though substantially damaged – the most notable examples include Quentin Matsys' Virgin and Child with Saints Barbara and Catherine (c. 1515–25)[1] and Dirk Bouts' Entombment (c. 1440–55).[2] In German the technique is known as Tüchleinfarben, meaning "small cloth colours", or Tüchlein, derived from the German word for “handkerchief” (i.e., “small cloth”).
Technique
[edit]A binding agent for pigment was made by boiling animal skin mixed with other organic tissue and applied to linen, itself prepared with a thin layer of glue.[3] The linen was ground, but sometimes treated, by both the glue and also white chalk, which allowed a surface suitable for underdrawing and a base that would not absorb the final layer's pigment.[4]
The advantage of using glue as a binder is that the colours render as matte and opaque textures suited to austere or mournful images as opposed to the translucent appearance associated with oil. Many reds and blues bound in glue would have appeared with a brilliance and intensity difficult to achieve with oil. Unfortunately the surviving examples have greatly deteriorated over time, having suffered from colour alteration due to exposure to light. Furthermore, the solubility of glue derived from animal products has meant that the accumulated layers of dirt cannot be removed without damaging the linen or dissolving the pigment.[3]
Although it allowed fine linear detail, subtle tonal transition and at times vivid colourisation, by the end of the 15th century the medium, along with egg tempera, had fallen out of favour. Oil painting had become predominant among the artists of the early Northern Renaissance, mainly due to the innovations in oil by Jan van Eyck[5] and Rogier van der Weyden.[3] It can be viewed as a transitional method between works in tempera or oils on wooden panels and oil paintings on canvas, although tüchlein co-existed with panel painting until both were supplanted by oil-on-canvas by the end of the 16th century. The technique corresponds with the Spanish sarga, where a thin gesso ground was favoured to create a smooth working surface.
Examples
[edit]Several examples by mid-16th century Dutch artist Pieter Bruegel the Elder have survived. Bruegel's Adoration of the Magi has traces of colour on the back of the canvas, demonstrating that the linen was not prepared with a traditional ground before it was painted; other examples, such as Bouts' The Entombment were simply sized with glue to prevent the paint from bleeding through. Other Netherlandish examples from approximately a century earlier include the Virgin and Child with Saints Barbara and Catherine by Quentin Matsys c. 1515–25, and The Entombment by Dieric Bouts c.1440–55 and related works by Bouts including his Annunciation (now in the J. Paul Getty Museum, California), Adoration of the Kings (now in a private collection in Germany) and Presentation (or Resurrection; now in the Norton Simon Museum, Pasadena, California) which may have formed part of a single polyptych.
-
Bruegel, The Adoration of the Magi, c.1564, Royal Museums of Fine Arts of Belgium
-
Bruegel: The Wine of Saint Martin's Day, 1565-1568, Prado
-
Bruegel, The Blind Leading the Blind, 1568, Museo di Capodimonte, Naples
-
Bruegel, The Misanthrope, 1568, Museo di Capodimonte, Naples
-
Dieric Bouts, Resurrection, Norton Simon Museum, Pasadena
Less popular in Germany, the term tüchlein is used by German Albrecht Dürer in his travel diary in the Netherlands, when he records selling a "tüchlein" image of the Virgin Mary to an innkeeper for two florins in Antwerp in 1520, and he was used for one of his portraits of Emperor Maximilian I (now in the Germanisches Nationalmuseum, Nuremberg). The surviving works by Andrea Mantegna include some tüchlein, some with and some without a prepared ground. The image of Our Lady of Guadalupe may have been painted in Mexico using a similar technique in the 1550s.
-
Albrecht Dürer, Portrait of the Emperor Maximilian I, 1519, Germanisches Nationalmuseum, Nuremberg
-
Our Lady of Guadalupe, 1531, Mexico
Notes
[edit]- ^ "The Virgin and Child with Saints Barbara and Catherine Archived 2012-05-11 at the Wayback Machine". National Gallery, London. Retrieved 7 November 2011
- ^ "The Entombment". National Gallery, London. Retrieved 7 November 2011.
- ^ a b c Jones 2011, p. 10.
- ^ Campbell 1998, p. 29.
- ^ Van Eyck is often mistakenly credited with the invention of oil painting, whereas in fact the tradition in northern Europe goes back to at least the 12th century.
Sources
[edit]- Campbell, Lorne (1998). The Fifteenth Century Netherlandish Paintings. National Gallery. ISBN 1-85709-171-X.
- Jones, Susan Frances (2011). Van Eyck to Gossaert. National Gallery. ISBN 978-1-85709-504-3.
- "Dieric Bouts's 'Annunciation'. Materials and Techniques: A Summary", Mark Leonard, Frank Preusser, Andrea Rothe and Michael Schilling, The Burlington Magazine, Vol. 130, No. 1024 (Jul., 1988), pp. 517–522.
- The Technique of a 'Tüchlein' by Quinten Massys, Ashok Roy, National Gallery Technical Bulletin Volume 12, 1988.
- The Wine of Saint Martin’s Day. Pieter Bruegel the Elder, IV. Technique and state of conservation, Museo del Prado.
- The Annunciation, J. Paul Getty Museum, California.
- Conservation of Easel Paintings, edited by Joyce Hill Stoner, Rebecca Rushfield, p. 207–8.
- LACMA Unveils Rare, Major Painting, Los Angeles Times, March 29, 1991.