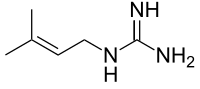
Galegine
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(3-Methylbut-2-enyl)guanidine
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H13N3 | |
| Molar mass | 127.191 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Galegine is a toxic chemical compound that has been isolated from Galega officinalis.[1] It has also been found to be the principal cause of the toxicity of poison sedge (Schoenus asperocarpus).[2]
Galegine was used in the 1920s as a pharmaceutical treatment for diabetes;[3] however, because of its toxicity, its use was soon supplanted by superior alternatives. Research on galegine eventually led to the development of metformin which is used today for treatment of type 2 diabetes.[3]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Oldham, Michelle; Ransom, Corey V.; Ralphs, Michael H.; Gardner, Dale R. (2011). "Galegine Content in Goatsrue (Galega officinalis) Varies by Plant Part and Phenological Growth Stage". Weed Science. 59 (3): 349–352. doi:10.1614/WS-D-10-00169.1.
- ^ Huxtable, C. R.; Dorling, P. R.; Colegate, S. M. (1993). "Identification of galegine, an isoprenyl guanidine, as the toxic principle of Schoenus asperocarpus (poison sedge)". Australian Veterinary Journal. 70 (5): 169–71. doi:10.1111/j.1751-0813.1993.tb06120.x. PMID 8343085.
- ^ a b Bailey, CJ; Day, C. (2004). "Metformin: Its botanical background". Practical Diabetes International. 21 (3): 115–117. doi:10.1002/pdi.606.
