Frederik de Wit
Frederik de Wit | |
|---|---|
| Born | Frederik Hendriksz c.1629 Gouda, province of Holland, Netherlands |
| Died | July 1706 (aged 76–77) |
| Nationality | Dutch |
| Occupation | cartographer |
| Known for | "Witte Pascaert" shop |
| Notable work | several atlases |
| Spouse |
Maria van der Way (m. 1661) |
| Children | 7 |
| Parents |
|
Frederik de Wit (born Frederik Hendriksz; c. 1629 – July 1706) was a Dutch cartographer and artist.[1]
Early years
[edit]Frederik de Wit was born Frederik Hendriksz. He was born to a Protestant family in about 1629, in Gouda, a small city in the province of Holland, one of the seven united provinces of the Netherlands. His father Hendrik Fredericsz (1608 – 29 July 1668)[2] was a hechtmaecker (knife handle maker) from Amsterdam,[3] and his mother Neeltij Joosten (d. before 1658) was the daughter of a merchant in Gouda. Frederik was married on 29 August 1661, to Maria van der Way (1632–1711), the daughter of a wealthy Catholic merchant in Amsterdam.[4] From about 1648 until his death at the end of July 1706, De Wit lived and worked in Amsterdam. Frederik and Maria had seven children, but only one Franciscus Xaverius (1666–1727) survived them.[5]
By 1648, during the height of the Dutch Golden Age, De Wit had moved from Gouda to Amsterdam. As early as 1654, he had opened a printing office and shop under the name "De Drie Crabben" (the Three Crabs) which was also the name of his house on the Kalverstraat.[6] In 1655, De Wit changed the name of his shop to the "Witte Pascaert" (the White Chart). Under this name De Wit and his firm became internationally known.[7]
Cartography
[edit]The first cartographic images that De Wit engraved were a plan of Haarlem that has been dated to 1648,[8] and sometime before 1649, De Wit engraved the city views – city maps for the cities of Rijsel and Doornik that appeared in the richly illustrated Flandria Illustrata by the Flemish historian, Antonius Sanderus.[9]


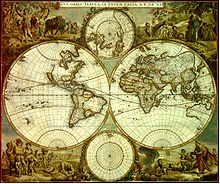
The first charts engraved by De Wit were published in 1654 under the "De Drie Crabben" address.[10][11] The first map that was both engraved and dated by De Wit was that of Denmark: "Regni Daniæ Accuratissima delineatio Perfeckte Kaerte van 't Conjnckryck Denemarcken" in 1659. His first world maps, "Nova Totius Terrarum Orbis Tabula Auctore F. De Wit" (approx. 43 × 55 cm) and Nova Totius Terrarum Orbis Tabula (a wall map approx. 140 × 190 cm) appeared around 1660.
His Atlas began to appear around 1662 and by 1671 included anywhere from 17 to 151 maps each. In the 1690s, he began to use a new title page "Atlas Maior" but continued to use his old title page.[12] His atlas of the Low Countries first published in 1667,[13] was named Nieuw Kaertboeck van de XVII Nederlandse Provinciën and contained 14 to 25 maps.[14] De Wit quickly expanded upon his first small folio atlas which contained mostly maps printed from plates that he had acquired, to an atlas with 27 maps engraved by or for him.
By 1671, he was publishing a large folio atlas with as many as 100 maps. Smaller atlases of 17 or 27 or 51 maps could still be purchased and by the mid-1670s an atlas of as many as 151 maps and charts could be purchased from his shop. His atlases cost between 7 and 20 Guilders depending on the number of maps, color and the quality of binding (€47 or $70 to €160 or $240 today). In about 1675, De Wit released a new nautical atlas. The charts in this atlas replaced the earlier charts from 1664 that are known today in only four bound examples and a few loose copies.[15] De Wit's new charts were sold in a chart book and as part of his atlases. De Wit published no fewer than 158 land maps and 43 charts on separate folio sheets.[16]
In 1695, De Wit began to publish a town atlas of the Netherlands after he acquired a large number of city plans at the auction of the famous Willem Blaeu publishing firm's printing plates. Dating De Wit's atlases is considered difficult because usually no dates were recorded on the maps and their dates of publication extended over many years.
Social standing
[edit]Through his marriage to Maria van der Way in 1661 he obtained, in 1662, the rights of Amsterdam citizenship[17] and was able to become a member of the Guild of Saint Luke in 1664.[18] In 1689, De Wit requested and received a 15-year privilege from the states of Holland and West Friesland that protected his right to publish and sell his maps.[19][20] Then in 1694, he was named a good citizen of the city of Amsterdam.[21]
Legacy
[edit]After De Wit's death in 1706, his wife Maria continued the business for four years printing and editing De Wit's maps until 1710. However, as De Wit's son Franciscus was already a prosperous stockfish merchant by this time and had little interest in his father's business, he did not take over the publishing house.[22] In 1710, Maria sold the firm at auction.[23]
At the auction most of the atlas plates and some of the wall map were sold to Pieter Mortier (1661–1711), a geographer, copper engraver, printer and publisher from Amsterdam.[24] After Mortier's death, his firm eventually passed to the ownership of his son, Cornelis Mortier and Johannes Covens I who together founded Covens & Mortier on 20 November 1721. Covens & Mortier grew to become one of the largest cartography publishing houses of the 18th century. The 27 chart plates from his 1675 sea atlas were sold at the 1710 auction, to the Amsterdam print seller Luis Renard, who published them under his own name in 1715, and then sold them to Rennier and Joshua Ottens who continued to publish them until the mid-1700s.
Most special collections libraries, rare map libraries, and private collections hold copies of De Wit's atlases and maps. To date over 121 and thousands of loose maps have been identified. Libraries that hold significant numbers are: The Amsterdam University Library, Utrecht University Library, Leiden University Library, Bibliothèque Royale Brussels, The Osher Map Library, Harvard Map Collection, Yale University Beinecke Library, The Library of Congress, Bayersche Staatsbibliothek, Staatsbibliothek zu Berlin, Österreichische Nationalbibliothek, Herzog August Bibliothek Wolfenbüttel, Sächsische Landesbibliothek-Staats-und Universitätsbibliothek Dresden, Hungarian National Library, and the collection bequeathed by William Dixson to the State Library of New South Wales. The museum at the Palazzo Rossi Poggi Marsili in Bologna has a map originally by Frederik de Wit (Nova totvs terrarvm orbis tabvla), engraved locally by Carlo Scotti (engraver).
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Isabella H van Eeghen, Frederick de Wit, Amsterdams uitgever, in A. H. Sijmons' Jacob Aertsz. Colom's Kaart van Holland 1681, (Alphen aan den Rijn: Canaletto, 1990) p. 12.
- ^ Streekarchief Midden-Holland, Gouda: inventarissen: 8. Sociale zorg; vakorganisaties (1)
- ^ Gemeente Amsterdam Stadsarcief: Archief van de Burgerlijke Stand; Doop-, trouw- en begraafboeken van Amsterdam: Book 2476, fish 764 p. 50.
- ^ Gemeente Amsterdam Stadsarcief: Archief van de Burgerlijke Stand; Doop-, trouw- en begraafboeken van Amsterdam: Bestanddeel: 685. p. 78.
- ^ Gemeente Amsterdam Stadsarcief – Begraafregister
- ^ Van Eeghen 1990, p. 12.
- ^ Johann Gottfried Gregorii, Curieuse Gedancken von den vornehmsten und accuratesten alt- und neuen Land-Charten nach ihrem ersten Ursprunge, Erfindung, Auctoribus und Sculptoribus, Gebrauch und Nutzen enworffen ...(Frankfurt, Leipzig, [Erfurt]: Ritschel, 1713) p. 75.
- ^ Max Eder, Der Annenkirchplatz in Haarlem, in Oud Holland vol 31 (1913) pp. 145, 148.
- ^ G. Caullet, De gegraveerde, onuitgegeven en verloren geraakte teekeningen voor Sanderus' 'Flandria illustrata', in Tijdschrift voor Boek- en Bibliotheekwezen VI, (Amsterdam, Emmanuel de Bom et al, 1908), pp. 3, 53, 101, 162.
- ^ George Carhart, Dissertation: "Frederick de Wit and the first 'Concise Reference Atlas': A reexamination of the Amsterdam map, print and art seller's life, work and contribution to the distribution of cartographic knowledge during the second half of the 17th and early 18th centuries". (University of Passau, 02/2011) p. 58.
- ^ Amsterdam University Library Map Collection, Harvard Map Collection, National Maritime Museum, Greenwich.
- ^ Carhart 2011
- ^ Micro film copy of the Oprechte Haerlemse Courant from 14, June 1667: Koninglijke Bibliotheek, Den Haag.
- ^ Ruud Paesie, 'Het Nieut Kaert-boeck vande XVII Nederlandse Provincie': New insights into two late 17th-century atlases, in Caert-Thresoor: Tijdschrift voor de Geschiedenis van de Cartografie 26 (3). (Middelburg: Barent Langenesstichting, 2007) p. 77.
- ^ Carhart 2011
- ^ Carhart 2011
- ^ Amsterdam City Archive, Poorterboek No. 2. p. 181.
- ^ Amsterdam Archive, Guild of St. Lucas, No. 366/365.
- ^ Frederik D. O. Obreen, Archief voor Nederlandsche Kunstgeschiedenis: Verzameling van Neerendeels Onutgegeven Berichten en Mededeelinge (Rotterdam: W. J. Hengel, 1888–1890.) Vol. 7.
- ^ National archive, The Hague, inventory of the archives of the States Holland and West-Friesland 1572–1795: Archive: 3.01.04.01, # 1640
- ^ Van Eeghen (1990)
- ^ Carhart 2011
- ^ Peter van der Krogt, Advertenties voor kaarten, atlassen, globes e.d. in Amsterdamse kranten 1621–1811, (Utrecht: HES, 1985) pp. 75–76.
- ^ Marco van Egmond, Covens & Mortier: A Map Publishing House in Amsterdam 1685–1866, (Houten, Netherlands: Hes & De Graaf, 2009) p. 125.
