Fluorosulfonate
 Fluorosulfate ion
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| FO3S− | |
| Molar mass | 99.06 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Chlorosulfate |
Related compounds
|
Fluorine fluorosulfonate, Sulfuryl fluoride, Trifluorosulfate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Fluorosulfonate, in organic chemistry, is a functional group that has the chemical formula F-SO2-R, and typically is a very good leaving group. In organic chemistry, fluorosulfonate is different than fluorosulfate. In fluorosulfonates, sulfur atom is directly bonded to a non-oxygen atom such as carbon. In inorganic chemistry, fluorosulfonate is another term for fluorosulfate, the anion F-SO2-O−, the conjugate base of fluorosulfonic acid. They form a series of salts with metal and organic cations called fluorosulfates.
Organic (alkyl) fluorosulfonates are usually strong alkylation agents, similar to triflate esters (F3C-SO2-OR).[1] But unlike the triflate group, the fluorosulfonate group is not stable against hydrolysis. Therefore, fluorosulfonate esters are less frequently used as alkylation agents than triflate esters.
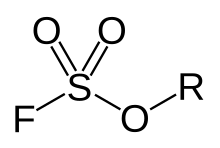
General chemical structure of a fluorosulfate ester. In Fluorosulfonates, sulfur atom is directly bonded to a non-oxygen atom such as carbon.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Revathi, Lekkala; Ravindar, Lekkala; Leng, Jing; Rakesh, Kadalipura Puttaswamy; Qin, Hua-Li (2018). "Synthesis and Chemical Transformations of Fluorosulfates". Asian Journal of Organic Chemistry. 7 (4): 662–682. doi:10.1002/ajoc.201700591.

