FlmA-FlmB toxin-antitoxin system
| flmB | |
|---|---|
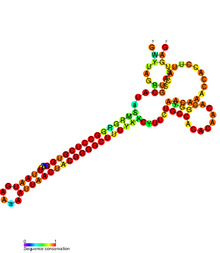 Conserved secondary structure of flmB RNA. | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | FlmB |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | antisense RNA |
| Domain(s) | E. coli, S. enterica |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
The FlmA-FlmB toxin-antitoxin system consists of FlmB RNA (F leading-region maintenance B), a family of non-coding RNAs and the protein toxin FlmA. The FlmB RNA transcript is 100 nucleotides in length and is homologous to sok RNA from the hok/sok system and fulfills the identical function as a post-segregational killing (PSK) mechanism.[1][2]
flmB is found on the F-plasmid of Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica. It is responsible for stabilising the plasmid. If the plasmid is not inherited, long-lived FlmA mRNA and protein will be highly toxic to the cell, possibly to the point of causing cell death.[2] Daughter cells which inherit the plasmid inherit the FlmB gene, coding for FlmB RNA which binds the leader sequence of FlmA mRNA and represses its translation.[1]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Loh SM, Cram DS, Skurray RA (June 1988). "Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis of a third function (Flm) involved in F-plasmid maintenance". Gene. 66 (2): 259–268. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(88)90362-9. PMID 3049248.
- ^ a b Kobayashi M, Kurusu Y, Yukawa H (February 1991). "High-expression of a target gene and high-stability of the plasmid". Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 27 (2): 145–162. doi:10.1007/BF02921523. PMID 2029184. S2CID 41601297.
Further reading
[edit]- Fozo EM, Makarova KS, Shabalina SA, Yutin N, Koonin EV, Storz G (June 2010). "Abundance of type I toxin–antitoxin systems in bacteria: searches for new candidates and discovery of novel families". Nucleic Acids Res. 38 (11): 3743–3759. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq054. PMC 2887945. PMID 20156992.
- Fozo EM, Hemm MR, Storz G (December 2008). "Small Toxic Proteins and the Antisense RNAs That Repress Them". Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 72 (4): 579–589, Table of Contents. doi:10.1128/MMBR.00025-08. PMC 2593563. PMID 19052321.
- Gerdes K, Wagner EG (April 2007). "RNA antitoxins". Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 10 (2): 117–124. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2007.03.003. PMID 17376733.
- Hayes F (September 2003). "Toxins-antitoxins: plasmid maintenance, programmed cell death, and cell cycle arrest". Science. 301 (5639): 1496–1499. doi:10.1126/science.1088157. PMID 12970556. S2CID 10028255.
