Electroslag welding
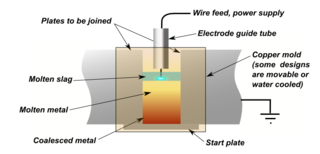
Electroslag welding (ESW) is a highly productive, single pass welding process for thick (greater than 25 mm up to about 300 mm) materials in a vertical or close to vertical position. (ESW) is similar to electrogas welding, but the main difference is the arc starts in a different location. An electric arc is initially struck by wire that is fed into the desired weld location and then flux is added. Additional flux is added until the molten slag, reaching the tip of the electrode, extinguishes the arc. The wire is then continuously fed through a consumable guide tube (can oscillate if desired) into the surfaces of the metal workpieces and the filler metal are then melted using the electrical resistance of the molten slag to cause coalescence. The wire and tube then move up along the workpiece while a copper retaining shoe that was put into place before starting (can be water-cooled if desired) is used to keep the weld between the plates that are being welded. Electroslag welding is used mainly to join low carbon steel plates and/or sections that are very thick. It can also be used on structural steel if certain precautions are observed, and for large cross-section aluminium busbars.[1] This process uses a direct current (DC) voltage usually ranging from about 600 A and 40-50 V, higher currents are needed for thicker materials. Because the arc is extinguished, this is not an arc process.
History
[edit]The process was patented by Robert K Hopkins in the United States in February 1940 (patent 2191481) and developed and refined at the Paton Institute, Kiev, USSR during the 1940s. The Paton method was released to the west at the Bruxelles Trade Fair of 1950.[2] The first widespread use in the U.S. was in 1959, by General Motors Electromotive Division, Chicago, for the fabrication of traction motor frames. In 1968 Hobart Brothers of Troy, Ohio, released a range of machines for use in the shipbuilding, bridge construction and large structural fabrication industries. Between the late 1960s and late 1980s, it is estimated that in California alone over a million stiffeners were welded with the electroslag welding process. Two of the tallest buildings in California were welded, using the electroslag welding process - The Bank of America building in San Francisco, and the twin tower Security Pacific buildings in Los Angeles. The Northridge earthquake and the Loma Prieta earthquakes provided a "real world" test to compare all of the welding processes. After the Northridge earthquake, one billion dollars were needed to repair weld cracks propagated in welds made with the gasless flux cored wire process, while no failures or crack propagations were initiated in any of the hundreds of thousands of welds made on continuity plates welded with the Electroslag welding process.[3]
However the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) monitored the new process and found that electroslag welding, because of the very large amounts of confined heat used, produced a coarse-grained and brittle weld and in 1977 banned the use of the process for many applications.[4] The FHWA commissioned research from universities and industry and Narrow Gap Improved Electro Slag Welding (NGI-ESW) was developed as a replacement. The FHWA moratorium was rescinded in 2000.[5]
Benefits
[edit]Benefits of the process include its high metal deposition rates—it can lay metal at a rate between 15 and 20 kg per hour (35 and 45 lb/h) per electrode—and its ability to weld thick materials. Many welding processes require more than one pass for welding thick workpieces, but often a single pass is sufficient for electroslag welding. The process is also very efficient, since joint preparation and materials handling are minimized while filler metal utilization is high. The process is also safe and clean, with no arc flash and low weld splatter or distortion. Electroslag welding easily lends itself to mechanization, thus reducing the requirement for skilled manual welders.
One electrode is commonly used to make welds on materials with a thickness of 25 to 75 mm (1 to 3 in), and thicker pieces generally require more electrodes. The maximum workpiece thickness that has ever been successfully welded was a 0.91 m (36 in) piece that required the simultaneous use of six electrodes to complete.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^ Leroux, Bertrand (2015). "ELECTROSLAG WELDING (ESW): A New Option for Smelters to Weld Aluminum Bus Bars". Light Metals 2015. The Minerals, Metals, and Materials Society. pp. 837–842. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-48248-4_141. ISBN 978-3-319-48610-9.
- ^ Pires, J Roberto; Loureiro, Altino; Bolmsjö, Gunnar (2005). Welding Robots: Technology, System Issues and Application. New York: Springer. p. 11. ISBN 1-85233-953-5.
- ^ Eskandari, Amir (February 2009). "The history of electroslag welding for high rise buildingsbildings and bridges". CorTech Industries/Arcmatic. Archived from the original on 2009-02-09. Retrieved 2009-06-16.
- ^ Lindberg, H. A. (February 1977). "Notice: Electro-Slag Welding". Federal Highway Administration. Retrieved 2008-04-21.
- ^ Densmore, David (2000). "Narrow-Gap Electroslag Welding for Bridges". Bridge Technology. Federal Highway Administration. Retrieved 2008-04-21.
Further reading
[edit]- Cary, Howard B. and Scott C. Helzer (2005). Modern Welding Technology. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Pearson Education. ISBN 0-13-113029-3.
- Serope Kalpakjan and Steven R. Schmid. Manufacturing Engineering and Technology. Fifth Edition. Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. ISBN 0-13-148965-8
- <Practical Welding Letter>[1]</Issue #007>. Feb 29, 2004.
