Semi-presidential republic
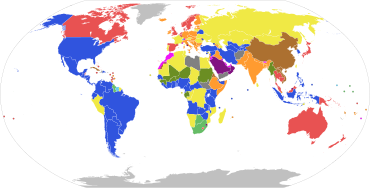
Parliamentary systems: Head of government is elected or nominated by and accountable to the legislature
Presidential system: Head of government (president) is popularly elected and independent of the legislature
Hybrid systems:
Other systems:
Note: this chart represents the de jure systems of government, not the de facto degree of democracy.
| Part of the Politics series |
| Politics |
|---|
|
|
| Part of the Politics series on |
| Executive government |
|---|
| Head of state |
| Government |
|
| Systems |
| Lists |
| Politics portal |
A semi-presidential republic, or dual executive republic, is a republic in which a president exists alongside a prime minister and a cabinet, with the latter two being responsible to the legislature of the state. It differs from a parliamentary republic in that it has an executive president independent of the legislature; and from the presidential system in that the cabinet, although named by the president, is responsible to the legislature, which may force the cabinet to resign through a motion of no confidence.[1][2][3][4]
While the Weimar Republic (1919–1933) and Finland (from 1919 to 2000) exemplified early semi-presidential systems, the term "semi-presidential" was first introduced in 1959 in an article by journalist Hubert Beuve-Méry,[5] and popularized by a 1978 work written by political scientist Maurice Duverger,[6] both of whom intended to describe the French Fifth Republic (established in 1958).[1][2][3][4]
Definition
[edit]Maurice Duverger's original definition of semi-presidentialism stated that the president had to be elected, possess significant power, and serve for a fixed term.[7] Modern definitions merely declare that the head of state has to be elected, and that a separate prime minister that is dependent on parliamentary confidence has to lead the legislative.[7]
Subtypes
[edit]There are two distinct subtypes of semi-presidentialism: premier-presidentialism and president-parliamentarism.
Under the premier-presidential system, the prime minister and cabinet are exclusively accountable to parliament. The president may choose the prime minister and cabinet, but only the parliament may approve them and remove them from office with a vote of no confidence. This system is much closer to pure parliamentarism. This subtype is used in: Burkina Faso, Cape Verde,[8] East Timor,[8][9] France, Lithuania, Madagascar, Mali, Mongolia, Niger, Georgia (2013–2018), Poland (de facto, however, according to the Constitution, Poland is a parliamentary republic),[10][11][12] Portugal, Romania, São Tomé and Príncipe,[8] Sri Lanka, Turkey (de facto between 2014 and 2018, until the constitutional amendment to switch the government to presidential from parliamentary), and Ukraine (since 2014; previously, between 2006 and 2010).[13][14]
Under the president-parliamentary system, the prime minister and cabinet are dually accountable to the president and to the parliament. The president chooses the prime minister and the cabinet, but must have the support of a parliamentary majority for his choice. In order to remove a prime minister, or the whole cabinet, from power, the president can either dismiss them, or the parliament can remove them through a vote of no confidence. This form of semi-presidentialism is much closer to pure presidentialism. It is used in: Guinea-Bissau,[8] Mozambique, Russia, and Taiwan. It was also used in Ukraine (first between 1996 and 2005; then from 2010 to 2014), Georgia (from 2004 to 2013), South Korea under the Fourth and Fifth republics, and in Germany during the Weimar Republic.[13][14]
Cohabitation
[edit]In a semi-presidential system, the president and the prime minister may sometimes be from different political parties. This is called "cohabitation", a term which originated in France after the situation first arose in the 1980s. Cohabitation can create either an effective system of checks and balances, or a period of bitter and tense stonewalling, depending on the attitudes of the two leaders, the ideologies of themselves/their parties, and the demands of their supporters.[15]
Division of powers
[edit]The distribution of power between the president and the prime minister can vary greatly between countries.
In France, for example, in the case of cohabitation, the president oversees foreign policy and defense policy (these are generally called les prérogatives présidentielles, presidential prerogatives) and the prime minister is in charge of domestic policy and economic policy.[16] In this case, the division of responsibilities between the prime minister and the president is not explicitly stated in the constitution, but has evolved as a political convention based on the constitutional principle that the prime minister is appointed (with the subsequent approval of a parliament majority) and dismissed by the president.[17] On the other hand, whenever the president and the prime minister represent the same political party, which leads the cabinet, they tend to exercise de facto control over all fields of policy via the prime minister. However, it is up to the president to decide how much autonomy is left to said prime minister.
In most cases, cohabitation results from a system in which the two executives are not elected at the same time or for the same term. For example, in 1981, France elected both a Socialist president and legislature, which yielded a Socialist premier. But while the president's term of office was for seven years, the National Assembly only served for five. When, in the 1986 legislative election, the French people elected a right-of-centre assembly, Socialist president François Mitterrand was forced into cohabitation with right-wing premier Jacques Chirac.[15]
However, in 2000, amendments to the French constitution reduced the length of the French president's term to five years. This has significantly lowered the chances of cohabitation occurring, as parliamentary and presidential elections may now be conducted within a shorter span of each other.
Advantages and disadvantages
[edit]The incorporation of elements from both presidential and parliamentary republics can bring certain advantageous elements; however, it also creates disadvantages, often related to the confusion produced by mixed authority patterns.[18][19] It can be argued that a semi-presidential republic is more likely to engage in democratic backsliding and power struggles,[20] especially ones with a president-parliamentary system.[21][22]
Advantages
- Parliament has the ability to remove an unpopular prime minister, therefore maintaining stability throughout the president's fixed term.
- In most semi-presidential systems, important segments of bureaucracy are taken away from the president, creating additional checks and balances where the running of the day-to-day government and its issues are separate from the head of state, and as such, its issues tend to be looked at on their own merits, with their ebbs and flows and not necessarily tied to who the head of state is.
- Having a separate head of government who needs to command the confidence of the parliament is seen as being more in tune to the political and economic development of the country. Because the head of government is elected from the parliament, there is little potential for political gridlock to occur, since the parliament has the power to remove the head of government if needed.
Disadvantages
- The system provides cover for the president, as unpopular policies could be blamed on the prime minister, who runs the day-to-day operations of the government.
- It creates a sense of confusion towards accountability, as there is no relatively clear sense of who is responsible for policy successes and failures.
- It creates both confusion and inefficiency in the legislative process, since the capacity of votes of confidence makes the prime minister respond to the parliament.
Republics with a semi-presidential system of government
[edit]Premier-presidential systems
[edit]In a premier-presidential system, the prime minister and cabinet are exclusively accountable to the legislature.[23]
Non-UN members or observers are in italics.
President-parliamentary systems
[edit]In a president-parliamentary system, the prime minister and cabinet are dually accountable to the president and the legislature.[23]
Non-UN members or observers are in italics.Former semi-presidential republics
[edit] Armenia (2008–2018)[c]
Armenia (2008–2018)[c] Croatia (1990–2000)
Croatia (1990–2000) Cuba (1940–1976)
Cuba (1940–1976) Finland (1919–2000)
Finland (1919–2000) Georgia (1991–1995, 2004–2005, 2011–2019)[d]
Georgia (1991–1995, 2004–2005, 2011–2019)[d] Germany (1919–1933)[e]
Germany (1919–1933)[e] Greece (1973–1974)[f]
Greece (1973–1974)[f] Kyrgyzstan (1993–2021)[g]
Kyrgyzstan (1993–2021)[g] Mali (1991–2023)
Mali (1991–2023) Moldova (1990–2001)
Moldova (1990–2001) North Macedonia (1991–2001)[35][36]
North Macedonia (1991–2001)[35][36] Philippines (1978–1986)[h]
Philippines (1978–1986)[h] Russian SFSR (1991)[i]
Russian SFSR (1991)[i] Somalia (1960–1969)
Somalia (1960–1969) Soviet Union (1990–1991)[j]
Soviet Union (1990–1991)[j] South Korea (1972–1988)[k]
South Korea (1972–1988)[k]
See also
[edit]- List of countries by system of government
- Parliamentary system
- Presidential system
- Semi-parliamentary system
Notes
[edit]- ^ The Republic of Austria is de jure semi-presidential according to the country's Constitution, however behaves more like a parliamentary republic in practice by constitutional convention, with the Chancellor being the country's leading political figure despite nominally being ranked third according to the Constitution.
- ^ Nominally a parliamentary republic; the semi-presidential system is based on temporary additional articles. According to the Constitution of the Republic of China, the National Assembly indirectly elects the President of the Republic, which is the ceremonial figurehead of the state. Executive power rested with the President of the Executive Yuan, who is nominated and appointed by the president, with the consent of the Legislative Yuan. The additional articles made the President directly elected by the citizens of the free area and replaced Legislative Yuan confirmation for Premieral appointments with a conventional vote of no confidence, superseding the ordinary constitutional provisions. A sunset clause in the additional articles will terminate them in the event of a hypothetical resumption of ROC rule in Mainland China.
- ^ One-party parliamentary republic as a Soviet member-state in 1990–1991, and after independence it was a presidential republic in 1991–2008, a semi-presidential republic in 2008–2018 and has been a parliamentary republic since 2018.
- ^ As the Georgian SSR and after independence, parliamentary in 1990–1991, semi-presidential in 1991–1995, presidential in 1995–2004, semi-presidential in 2004–2005 and presidential 2005–2011. Semi-presidential in 2011–2019 and parliamentary since 2019.
- ^ For more information, see Weimar Republic.
- ^ The Greek Constitution of 1973, enacted in the waning days of the Greek Junta, provided for a powerful directly-elected president and for a government dependent on Parliamentary confidence. Neither of these provisions were implemented, as the regime collapsed eight month's after the Constitution's promulgation.
- ^ One-party parliamentary republic as a Soviet member-state in 1936–1990, a presidential republic in 1990–1993, a semi-presidential republic in 1993–2010 and a de facto semi-presidential republic; de jure a parliamentary republic in 2010–2021.
- ^ For more information, see Fourth Philippine Republic.
- ^ One-party parliamentary republic as a Soviet member-state in 1918–1991 and semi-presidential republic in 1991
- ^ A parliamentary system in which the leader of the state-sponsored party was supreme in 1918–1990 and a semi-presidential republic in 1990–1991.
- ^ All South Korean constitutions since 1963 provided for a strong executive presidency; in addition, the formally-authoritarian Yushin Constitution of the Fourth Republic established a presidential power to dissolve the National Assembly, nominally counterbalanced by a binding vote of no confidence. Both of these provisions were retained during the Fifth Republic but repealed upon the transition to democracy and the establishment of the presidential Sixth Republic.
References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ a b Duverger (1980). "A New Political System Model: Semi-Presidential Government". European Journal of Political Research (quarterly). 8 (2): 165–187. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6765.1980.tb00569.x.
The concept of a semi-presidential form of government, as used here, is defined only by the content of the constitution. A political regime is considered as semi-presidential if the constitution which established it, combines three elements: (1) the president of the republic is elected by universal suffrage, (2) he possesses quite considerable powers; (3) he has opposite him, however, a prime minister and ministers who possess executive and governmental power and can stay in office only if the parliament does not show its opposition to them.
- ^ a b Veser, Ernst [in German] (1997). "Semi-Presidentialism-Duverger's concept: A New Political System Model" (PDF). Journal for Humanities and Social Sciences. 11 (1): 39–60. Retrieved 21 August 2016.
- ^ a b Duverger, Maurice (September 1996). "Les monarchies républicaines" [The Republican Monarchies] (PDF). Pouvoirs, revue française d'études constitutionnelles et politiques (in French). No. 78. Paris: Éditions du Seuil. pp. 107–120. ISBN 2-02-030123-7. ISSN 0152-0768. OCLC 909782158. Retrieved 10 September 2016.
- ^ a b Bahro, Horst; Bayerlein, Bernhard H.; Veser, Ernst [in German] (October 1998). "Duverger's concept: Semi-presidential government revisited". European Journal of Political Research (quarterly). 34 (2): 201–224. doi:10.1111/1475-6765.00405. S2CID 153349701.
The conventional analysis of government in democratic countries by political science and constitutional law starts from the traditional types of presidentialism and parliamentarism. There is, however, a general consensus that governments in the various countries work quite differently. This is why some authors have inserted distinctive features into their analytical approaches, at the same time maintaining the general dichotomy. Maurice Duverger, trying to explain the French Fifth Republic, found that this dichotomy was not adequate for this purpose. He therefore resorted to the concept of 'semi-presidential government': The characteristics of the concept are (Duverger 1974: 122, 1978: 28, 1980: 166):
1. the president of the republic is elected by universal suffrage,
2. he possesses quite considerable powers and
3. he has opposite him a prime minister who possesses executive and governmental powers and can stay in office only if parliament does not express its opposition to him. - ^ Le Monde, 8 January 1959.
- ^ Duverger, Maurice (1978). Échec au roi. Paris: A. Michel. ISBN 9782226005809.
- ^ a b Elgie, Robert (2 January 2013). "Presidentialism, Parliamentarism and Semi-Presidentialism: Bringing Parties Back In" (PDF). Government and Opposition. 46 (3): 392–409. doi:10.1111/j.1477-7053.2011.01345.x. S2CID 145748468.
- ^ a b c d Neto, Octávio Amorim; Lobo, Marina Costa (2010). "Between Constitutional Diffusion and Local Politics: Semi-Presidentialism in Portuguese-Speaking Countries" (PDF). APSA 2010 Annual Meeting Paper. SSRN 1644026. Retrieved 18 August 2017.
- ^ Beuman, Lydia M. (2016). Political Institutions in East Timor: Semi-Presidentialism and Democratisation. Abingdon, Oxon: Routledge. ISBN 978-1317362128. LCCN 2015036590. OCLC 983148216. Retrieved 18 August 2017 – via Google Books.
- ^ McMenamin, Iain. "Semi-Presidentialism and Democratisation in Poland" (PDF). School of Law and Government, Dublin City University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 February 2012. Retrieved 11 December 2017.
- ^ "Poland 1997 (rev. 2009) Constitution". Constitute. Retrieved 9 October 2021.
- ^ "Poland". The World Factbook. CIA. 22 September 2021. Retrieved 8 October 2021.
- ^ a b Shugart, Matthew Søberg (September 2005). "Semi-Presidential Systems: Dual Executive and Mixed Authority Patterns" (PDF). Graduate School of International Relations and Pacific Studies. United States: University of California, San Diego. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 August 2008. Retrieved 12 October 2017.
- ^ a b Shugart, Matthew Søberg (December 2005). "Semi-Presidential Systems: Dual Executive And Mixed Authority Patterns" (PDF). Graduate School of International Relations and Pacific Studies, University of California, San Diego. French Politics. 3 (3): 323–351. doi:10.1057/palgrave.fp.8200087. ISSN 1476-3427. OCLC 6895745903. Retrieved 12 October 2017.
- ^ a b Poulard JV (Summer 1990). "The French Double Executive and the Experience of Cohabitation" (PDF). Political Science Quarterly (quarterly). 105 (2): 243–267. doi:10.2307/2151025. ISSN 0032-3195. JSTOR 2151025. OCLC 4951242513. Retrieved 7 October 2017.
- ^ See article 5, title II, of the French Constitution of 1958. Jean Massot, Quelle place la Constitution de 1958 accorde-t-elle au Président de la République?, Constitutional Council of France website (in French).
- ^ Le Petit Larousse 2013 p. 880
- ^ Barrington, Lowell (1 January 2012). Comparative Politics: Structures and Choices. Cengage Learning. ISBN 978-1111341930 – via Google Books.
- ^ Barrington, Lowell; Bosia, Michael J.; Bruhn, Kathleen; Giaimo, Susan; McHenry, Jr., Dean E. (2012) [2009]. Comparative Politics: Structures and Choices (2nd ed.). Boston, MA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning. pp. 169–170. ISBN 9781111341930. LCCN 2011942386. Retrieved 9 September 2017 – via Google Books.
- ^ McAfee, Connor (2023-05-18). "Semi-Presidentialism: A Pathway to Democratic Backslide". Penn State Journal of Law & International Affairs. 11 (2). ISSN 2168-7951. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ Elgie, Robert (2011). Semi-presidentialism: sub-types and democratic performance. Comparative Politics. Oxford, UK ; New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-958598-4. OCLC 713182510.
- ^ Elgie, Robert; Mcmenamin, Iain (2008-12-01). "Semi-presidentialism and Democratic Performance". Japanese Journal of Political Science. 9 (3): 323–340. doi:10.1017/S1468109908003162. ISSN 1468-1099.
- ^ a b Shugart, Matthew Søberg (December 2005). "Semi-Presidential Systems: Dual Executive And Mixed Authority Patterns". French Politics. 3 (3): 323–351. doi:10.1057/palgrave.fp.8200087.
- ^ "Poland 1997 (rev. 2009)". www.constituteproject.org. Retrieved 9 October 2021.
- ^ Veser, Ernst [in German] (23 September 1997). "Semi-Presidentialism-Duverger's Concept — A New Political System Model" (PDF). Department of Education, School of Education, University of Cologne, zh. pp. 39–60. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
Duhamel has developed the approach further: He stresses that the French construction does not correspond to either parliamentary or the presidential form of government, and then develops the distinction of 'système politique' and 'régime constitutionnel'. While the former comprises the exercise of power that results from the dominant institutional practice, the latter is the totality of the rules for the dominant institutional practice of power. In this way, France appears as 'presidentialist system' endowed with a 'semi-presidential regime' (1983: 587). By this standard, he recognizes Duverger's pléiade as semi-presidential regimes, as well as Poland, Romania, Bulgaria and Lithuania (1993: 87).
- ^ Shugart, Matthew Søberg (September 2005). "Semi-Presidential Systems: Dual Executive and Mixed Authority Patterns" (PDF). Graduate School of International Relations and Pacific Studies. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 August 2008. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
- ^ Shugart, Matthew Søberg (December 2005). "Semi-Presidential Systems: Dual Executive And Mixed Authority Patterns" (PDF). French Politics. 3 (3): 323–351. doi:10.1057/palgrave.fp.8200087. Retrieved 21 August 2017.
Even if the president has no discretion in the forming of cabinets or the right to dissolve parliament, his or her constitutional authority can be regarded as 'quite considerable' in Duverger's sense if cabinet legislation approved in parliament can be blocked by the people's elected agent. Such powers are especially relevant if an extraordinary majority is required to override a veto, as in Mongolia, Poland, and Senegal. In these cases, while the government is fully accountable to Parliament, it cannot legislate without taking the potentially different policy preferences of the president into account.
- ^ McMenamin, Iain. "Semi-Presidentialism and Democratisation in Poland" (PDF). School of Law and Government, Dublin City University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 February 2012. Retrieved 11 December 2017.
- ^ [24][25][26][27][28]
- ^ Kudelia, Serhiy (4 May 2018). "Presidential activism and government termination in dual-executive Ukraine". Post-Soviet Affairs. 34 (4): 246–261. doi:10.1080/1060586X.2018.1465251. S2CID 158492144.
- ^ a b Zaznaev, Oleg (2005). "Атипичные президентские и полупрезидентские системы" [Atypical presidential and semi-presidential systems]. Uchenyye Zapiski Kazanskogo Gosudarstvennogo Universiteta (in Russian). 147 (1): 62–64. Retrieved 3 April 2021.
- ^ Constitution of Belarus, 106, 97.5 97.7.
- ^ Leubnoudji Tan Nathan (4 October 2023). "Chad's Proposed New Constitution: Between Hopes for Refoundation and an Uncertain Future". ConstitutionNet. International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance. Retrieved 12 June 2024.
- ^ https://www.venice.coe.int/webforms/documents/default.aspx?pdffile=CDL-AD(2017)010-e
- ^ Keil, S.; Stahl, B. (17 December 2014). The Foreign Policies of Post-Yugoslav States: From Yugoslavia to Europe. ISBN 9781137384133.
- ^ Shugart, Matthew Søberg (December 2005). "Semi-Presidential Systems: Dual Executive And Mixed Authority Patterns". French Politics. 3 (3): 11. doi:10.1057/palgrave.fp.8200087. ISSN 1476-3427. OCLC 6895745903.
Sources
[edit]- Bahro, Horst; Bayerlein, Bernhard H.; Veser, Ernst (October 1998). "Duverger's concept: Semi–presidential government revisited". European Journal of Political Research (quarterly). 34 (2): 201–224. doi:10.1111/1475-6765.00405. S2CID 153349701.
- Beuman, Lydia M. (2016). Political Institutions in East Timor: Semi-Presidentialism and Democratisation. Abingdon, Oxon: Routledge. ISBN 978-1317362128. LCCN 2015036590 – via Google Books.
- Canas, Vitalino (2004). "The Semi-Presidential System" (PDF). Zeitschrift für ausländisches öffentliches Recht und Völkerrecht. 64 (1): 95–124.
- Duverger, Maurice (1978). Échec au roi. Paris: A. Michel. ISBN 9782226005809.
- Duverger, Maurice (June 1980). "A New Political System Model: Semi-Presidential Government". European Journal of Political Research (quarterly). 8 (2): 165–187. doi:10.1111/j.1475-6765.1980.tb00569.x.
- Elgie, Robert (2011). Semi-Presidentialism: Sub-Types And Democratic Performance. Comparative Politics. (Oxford Scholarship Online Politics), Oxford University Press ISBN 9780199585984
- Frye, Timothy (October 1997). "A Politics of Institutional Choice: Post-Communist Presidencies" (PDF). Comparative Political Studies. 30 (5): 523–552. doi:10.1177/0010414097030005001. S2CID 18049875.
- Goetz, Klaus H. (2006). Heywood, Paul; Jones, Erik; Rhodes, Martin; Sedelmeier (eds.). Developments in European politics. Power at the Centre: The Organization of Democratic Systems. Basingstoke England New York: Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 368. ISBN 9780230000414.
- Lijphart, Arend (1992). Parliamentary versus presidential government. Oxford New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780198780441.
- Nousiainen, Jaakko (June 2001). "From Semi-presidentialism to Parliamentary Government: Political and Constitutional Developments in Finland". Scandinavian Political Studies (quarterly). 24 (2): 95–109. doi:10.1111/1467-9477.00048. ISSN 0080-6757. OCLC 715091099.
- Passarelli, Gianluca (December 2010). "The government in two semi-presidential systems: France and Portugal in a comparative perspective" (PDF). French Politics. 8 (4): 402–428. doi:10.1057/fp.2010.21. ISSN 1476-3427. OCLC 300271555. S2CID 55204235. Archived from the original (PDF) on Oct 2, 2018.
- Rhodes, R. A. W. (1995). "From Prime Ministerial power to core executive". In Rhodes, R. A. W.; Dunleavy, Patrick (eds.). Prime minister, cabinet, and core executive. New York: St. Martin's Press. pp. 11–37. ISBN 9780333555286.
- Roper, Steven D. (April 2002). "Are All Semipresidential Regimes the Same? A Comparison of Premier-Presidential Regimes". Comparative Politics. 34 (3): 253–272. doi:10.2307/4146953. JSTOR 4146953.
- Sartori, Giovanni (1997). Comparative constitutional engineering: an inquiry into structures, incentives, and outcomes (2nd ed.). Washington Square, New York: New York University Press. ISBN 9780333675090.
- Shoesmith, Dennis (March–April 2003). "Timor-Leste: Divided Leadership in a Semi-Presidential System". Asian Survey (bimonthly). 43 (2): 231–252. doi:10.1525/as.2003.43.2.231. ISSN 0004-4687. OCLC 905451085. Archived from the original on Oct 28, 2021.
- Shugart, Matthew Søberg (December 2005). "Semi-Presidential Systems: Dual Executive And Mixed Authority Patterns" (PDF). Graduate School of International Relations and Pacific Studies, University of California, San Diego. French Politics. 3 (3): 323–351. doi:10.1057/palgrave.fp.8200087. ISSN 1476-3427. OCLC 6895745903.
- Shugart, Matthew Søberg; Carey, John M. (1992). Presidents and assemblies: constitutional design and electoral dynamics. Cambridge England New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521429900.
- Veser, Ernst (1997). "Semi-Presidentialism-Duverger's concept: A New Political System Model" (PDF). Journal for Humanities and Social Sciences. 11 (1): 39–60.
External links
[edit]- Governing Systems and Executive-Legislative Relations. (Presidential, Parliamentary and Hybrid Systems), United Nations Development Programme (n.d.). Archived 10 February 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- J. Kristiadi (April 22, 2008). "Indonesia Outlook 2007: Toward strong, democratic governance". The Jakarta Post. PT Bina Media Tenggara. Archived from the original on 21 April 2008.
- The Semi-Presidential One, blog of Robert Elgie
- Presidential Power blog with posts written by several political scientists, including Robert Elgie.
