Draft:Ranks of the Royal Australian Navy
 | Draft article not currently submitted for review.
This is a draft Articles for creation (AfC) submission. It is not currently pending review. While there are no deadlines, abandoned drafts may be deleted after six months. To edit the draft click on the "Edit" tab at the top of the window. To be accepted, a draft should:
It is strongly discouraged to write about yourself, your business or employer. If you do so, you must declare it. Where to get help
How to improve a draft
You can also browse Wikipedia:Featured articles and Wikipedia:Good articles to find examples of Wikipedia's best writing on topics similar to your proposed article. Improving your odds of a speedy review To improve your odds of a faster review, tag your draft with relevant WikiProject tags using the button below. This will let reviewers know a new draft has been submitted in their area of interest. For instance, if you wrote about a female astronomer, you would want to add the Biography, Astronomy, and Women scientists tags. Editor resources
Last edited by Felix QW (talk | contribs) 5 months ago. (Update) |
The structure of the Ranks of the Royal Australian Navy have been inherited from the rank structure of the Royal Navy. The insignia used to identify these ranks are also generally similar to those used in the British navy.

Commissioned Officers
[edit]Commissioned officers of the Australian Navy have pay grades ranging from S-1 to O-11. The only O-11 position in the navy is honorary and has only ever been held by royalty, most recently being held by The Duke of Edinburgh as the Lord High Admiral of the United Kingdom.[citation needed] The highest rank achievable in the current Royal Australian Navy structure is O-10, an admiral who serves as the Chief of the Defence Force (CDF) when the position is held by a Naval Officer.
The ranks O-8 (rear admiral) to O-11 (admiral of the fleet) are referred to as flag officers, O-5 (commander) and above are referred to as senior officers, while S-1 (midshipman) to O-4 (lieutenant commander) are referred to as junior officers. All RAN Officers are issue a commission by the Governor General of Australia as Commander-in-Chief on behalf of His Majesty King Charles III, King of Australia.
Naval officers are trained at the Royal Australian Naval College (HMAS Creswell) in Jervis Bay as well as the Australian Defence Force Academy in Canberra.[1]
| NATO Code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aus/US Code | O-11 | O-10 | O-9 | O-8 | O-7 |

|

|

|

|

| |
| Rank title: | Admiral of the Fleet | Admiral | Vice Admiral | Rear Admiral | Commodore |
| Abbreviation: | AF | ADML | VADM | RADM | CDRE |
| NATO Code | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | OF(D) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aus/US Code | O-6 | O-5 | O-4 | O-3 | O-2 | O-1 | O-0 | ||||

|

|

|

|

|
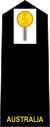
| ||||||
| Rank title | Captain | Commander | Lieutenant Commander | Lieutenant | Sub Lieutenant | Acting Sub Lieutenant | Midshipman | ||||
| Abbreviation | CAPT | CMDR | LCDR | LEUT | SBLT | ASLT | MIDN | ||||
Sailors
[edit]| NATO Code | OR-9* | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aus/US Code | E-9 | E-9 | E-8 | E-6 | E-5 | E-3 | E-2 | E-1 | |||

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
No insignia | ||||
| Rank Title: | Warrant Officer of the Navy | Warrant Officer | Chief Petty Officer | Petty Officer | Leading Seaman | Able Seaman | Seaman | Recruit | |||
| Abbreviation: | WO-N | WO | CPO | PO | LS | AB | SMN/SMN* | RCT | |||
Rate Insignia
[edit]
Royal Australian Navy Other Ranks wear "right arm rates" insignia, called "Category Insignia" to indicate specialty training qualifications.[3] This is a holdover from the Royal Navy.
Special insignia
[edit]The Warrant Officer of the Navy (WO-N) is an appointment held by the most senior sailor in the RAN and holds the rank of warrant officer (WO). However, the WO-N does not wear the WO rank insignia; instead, they wear the special insignia of the appointment.[4] The WO-N appointment has similar equivalent appointments in the other services, each holding the rank of warrant officer, each being the most senior sailor/soldier/airman in that service, and each wearing their own special insignia rather than their rank insignia. The Australian Army equivalent is the Regimental Sergeant Major of the Army (RSM-A)[5] and the Royal Australian Air Force equivalent is the Warrant Officer of the Air Force (WOFF-AF).[6]

Religious and Spiritual Officers
[edit]Chaplains in the Royal Australian Navy are commissioned officers who complete the same training as other officers in the RAN at the Royal Australian Naval College, HMAS Creswell. From July 2020, Maritime Spiritual Wellbeing Officers (MSWOs) were introduced to the Navy Chaplaincy Branch, designed to give Navy people and their families with professional, non-religious pastoral care and spiritual support.[7]
RAN regulations group RAN Chaplains and MSWOs with Commanders for purposes of protocol such as marks of respect (saluting); however, have no other rank other than the notional rank of "Chaplain" or "MSWO" respectively. From January 2021, MSWOs and all chaplains will wear the branch's new non-faith-specific rank insignia of a fouled anchor overlaying a compass rose, which represents a united team front, encompassing all faiths and purpose. Faith Chaplains will have insignia that reflect their religion on collar mounted patches (Cross for Christian, Crescent for Muslim etc.)[8] Senior Chaplains and MSWOs are grouped with captains, and Principal Chaplains and MSWOs are grouped with Commodores, but their rank slide remains the same. Principal Chaplains and MSWOs, however, have gold braid on the peak of their white service cap.[citation needed]
Historical changes to rank insgnia
[edit]The historical changes to rank insignia for enlisted personnel of the navy are listed in the table below:[9]
References
[edit]- ^ "Navy Training: Officer Training". Defence Jobs. Archived from the original on 3 September 2014. Retrieved 31 August 2014.
- ^ a b "Australian Defence Force Badges of Rank and Special Insignia" (PDF). Australian Defence Force. 20 October 2008. DPS: APR025/08. Retrieved 23 March 2023.
- ^ "Category Badges". Navy (dot) Gov. Royal Australian Navy. Archived from the original on 1 December 2022. Retrieved 1 December 2022.
- ^ "Defence Leaders: Navy". www.defence.gov.au. Archived from the original on 14 May 2015. Retrieved 10 August 2013.
- ^ "Regimental Sergeant Major – Army". www.army.gov.au. Archived from the original on 9 June 2012.
- ^ "Warrant Officer of the Air Force". www.airforce.gov.au. Archived from the original on 9 June 2012. Retrieved 21 June 2012.
- ^ Defence, Department of (2020-05-11). "New chaplaincy branch reflects secular care option". news.defence.gov.au. Archived from the original on 1 November 2021. Retrieved 2021-11-01.
- ^ Navy, corporateName=Royal Australian. "Chaplains". www.navy.gov.au. Archived from the original on 1 November 2021. Retrieved 2021-11-01.
- ^ "A History of Australian Navy Health Sailor Uniforms and Ranks (Part 3)". Retrieved 23 February 2021.















