Borean languages
This article may present fringe theories, without giving appropriate weight to the mainstream view and explaining the responses to the fringe theories. (August 2024) |
| Borean | |
|---|---|
| (widely rejected) | |
| Geographic distribution | Eurasia, sometimes the Americas |
| Linguistic classification | Proposed language family |
| Subdivisions |
|
| Language codes | |
| Glottolog | None |
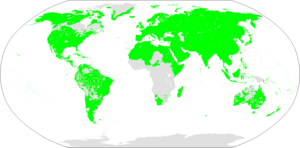 Borean macro-family according to Sergei Starostin | |
Borean (also Boreal or Boralean)[1] is a hypothetical (i.e. proposed) linguistic macrofamily that encompasses almost all language families worldwide except those native to the Americas, Africa, Oceania, and the Andaman Islands. Its supporters propose that the various languages spoken in Eurasia and adjacent regions have a genealogical relationship, and ultimately descend from languages spoken during the Upper Paleolithic in the millennia following the Last Glacial Maximum. The name Borean is based on the Greek βορέας, and means "northern". This reflects the fact that the group is held to include most language families that are native to the northern hemisphere. Two distinct models of Borean exist: that of Harold C. Fleming and that of Sergei Starostin.
Fleming's model
[edit]The concept is due to Harold C. Fleming (1987), who proposed such a "mega-super-phylum" for the languages of Eurasia, termed Borean or Boreal in Fleming (1991) and later publications. In Fleming's model, Borean includes ten different groups: Afrasian (his term for Afroasiatic), Kartvelian, Dravidian, a group comprising Sumerian, Elamitic, and some other extinct languages of the ancient Near East, Eurasiatic (a proposal of Joseph Greenberg that includes Indo-European, Uralic, Altaic, and several other language families), Macro-Caucasian (a proposal of John Bengtson that includes Basque and Burushaski), Yeniseian, Sino-Tibetan, Na-Dene, and Amerind.[2]
In 2002, Fleming argued that there were not a two large super-phyla distinction between a Nostratic and a Dené–Caucasian taxon among Borean languages, and that the language kinship between its branches is possibly more complex than a Nostratic versus a Dené–Caucasian super-phyla.[2]
However, in 2013, Fleming had changed his view about this issue in a joint article with Stephen L. Zegura, James B. Harrod, John D. Bengtson and Shomarka O.Y. Keita – "The Early Dispersions of Homo Sapiens sapiens and proto-Human from Africa." in Mother Tongue, issue XVIII, p. 143–188, 2013, where he argues that Nostratic and Dene-Caucasian as language phyla within Borean is a hypothesis that is well grounded and convincing.
Fleming writes that his work on Borean is inspired by Joseph Greenberg's exploration of Eurasiatic, and is oriented towards the concept of "valid taxon". He rejects Nostratic, a proposed macrofamily somewhat broader than Eurasiatic, and withholds judgment on Dené–Caucasian, a proposal that would encompass Sino-Tibetan, Yeniseian, Basque, and several other language families and isolates. Fleming calls Borean a "phyletic chain" rather than a super-phylum. He notes that his model of Borean is similar to Morris Swadesh's Vasco-Dene proposal, although he also sees similarities between Vasco-Dene and Dené–Caucasian. He sees Borean as closely associated with the appearance of the Upper Paleolithic in the Levant, Europe, and western Eurasia from 50 thousand to 45 thousand years ago, and observes that it is primarily associated with human populations of Caucasoid and Northern Mongoloid physical appearance, the exceptions being southern India, southern China, southwestern Ethiopia, northern Nigeria, and the Chad Republic.[2]
The phylogenetic composition of Borean (noncommital about higher linkages within the whole) according to Fleming, Bengtson, Zegura, Harrod, and Keita (2013)[3] is as follows:
- "Borean" (Phyletic Chain)[4]
- (1)
- c) (2) (strongly different languages between themselves and aberrant in its relationship to the other Borean phyla and language families)[6]
- a) (3)
- b) (4)
- d) (5)
- e) (6)
- Vasco-Caucasic (Vasco-Caucasian) (based on a John Bengtson proposal)
- f) (7)
- g) (8)
- h) (9)
- i) (10)
- Amerind (outlined by Joseph Greenberg) (a valid taxon with large contrasts among sub-taxa)
- Austric (not included in Borean) (Fleming et al.[3] are not sure if it is or not more closely related to Borean, that is, if Borean and Austric have an Austric-Borean common ancestor or if Austric is not closer to Borean than to other major language super-phyla)
Starostin's model
[edit]
As envisaged by Sergei Starostin (2002), Borean is divided into two groups, Nostratic (sensu lato, consisting of Eurasiatic and Afroasiatic) and Dene–Daic, the latter consisting of the Dené–Caucasian and Austric macrofamilies.[8] Starostin tentatively dates the Borean proto-language to the Upper Paleolithic, approximately 16 thousand years ago. Starostin's model of Borean would thus include most languages of Eurasia, as well as the Afroasiatic languages of North Africa and the Horn of Africa, and the Eskimo–Aleut and the Na-Dene languages of the New World.
Murray Gell-Mann, Ilia Peiros, and Georgiy Starostin maintain that the comparative method has provided strong evidence for some linguistic superfamilies (Dené-Caucasian and Eurasiatic), but not so far for others (Afroasiatic and Austric). Their view is that since some of these families have not yet been reconstructed and others still require improvement, it is impossible to apply the strict comparative method to even older and larger groups. However, they consider this only a technical rather than a theoretical problem, and reject the idea that linguistic relationships further back in time than 10,000 years before the present cannot be reconstructed, since the "main objects of research in this case are not modern languages, but reconstructed proto-languages which turn out to be more similar to one another than their modern day descendants".[1] They believe that good reconstructions of superfamilies such as Eurasiatic will eventually help in investigating still deeper linguistic relationships. While such 'ultra-deep' relationships can currently be discussed only on a speculative level, they maintain that the numerous morphemic similarities between language families of Eurasia, many of which Sergei Starostin compiled into a special database that he later supplemented by his own findings, are unlikely to be due to chance, making it possible to formulate a Borean super-superfamily hypothesis.[9]
They have also suggested possible links between 'Borean' and other families. In their view comparisons with 'Borean' data suggest that Khoisan cannot be included within it but that more distant connections on an even deeper level might be possible, that how the African superfamilies Niger–Congo, East Sudanic, Central Sudanic and Kordofanian are related to Borean remains to be investigated, that the situation with the native languages of the Americas remains unresolved, and that while there are some lexical similarities between Borean and the Trans–New Guinea languages, these remain too scarce to establish a firm connection. They comment that while preliminary data indicates possible connections between Borean and some superfamilies from Africa, the Americas, and the Indo-Pacific region further research is needed to determine whether these additional superfamilies are related to Borean or unidentified branches of it.[9] Gell-Mann et al. note that their proposed model of Borean differs significantly from that of Fleming.[9]
Sergei Starostin died prematurely in 2005 and his hypothesis remains in a preliminary form, with much of the material he collected available online.[10][11]
The phylogenetic composition of Borean according to Starostin is as follows:
- "Borean"
- Nostratic (speculative, Holger Pedersen 1903)
- Eurasiatic (speculative, Joseph Greenberg 2000)
- Indo-European (widely recognized family)
- Altaic (widely rejected; Roy Andrew Miller 1971, Gustaf John Ramstedt 1952, Matthias Castrén 1844)
- Uralic (widely recognized family)
- Yukaghir (language isolate)
- Paleosiberian (phylogenetic unity widely rejected)
- Eskimo–Aleut (widely recognized family)
- Chukotko-Kamchatkan (widely recognized family)
- Sumerian (language isolate)
- Elamite (language isolate)
- Kartvelian (widely recognized family)
- Dravidian (widely recognized family)
- Afroasiatic (widely recognized family)
- Eurasiatic (speculative, Joseph Greenberg 2000)
- Dene–Daic (speculative, Starostin 2005)
- Dené–Caucasian (speculative, Nikolayev 1991; expanded by Bengtson 1997), cf. Dené–Yeniseian (Edward Vajda 2008)
- Yeniseian (widely recognized family)
- Na-Dené (widely recognized family)
- Iberian (language isolate)
- Basque (language isolate)
- Sino-Caucasian (speculative, Starostin 2006)
- Sino-Tibetan (widely recognized family)
- Burushaski (language isolate)
- North Caucasian (widely rejected; Nikolayev & Starostin 1994)
- Northeast Caucasian (widely recognized family)
- Northwest Caucasian (widely recognized family)
- Hattic (language isolate)
- Hurro-Urartian (widely recognized family)
- Austric (speculative, Wilhelm Schmidt 1906)
- Austro-Tai (speculative, Paul Benedict 1942)
- Austronesian (widely recognized family)
- Tai–Kadai (widely recognized family)
- Hmong–Mien (widely recognized family)
- Austroasiatic (widely recognized family)
- Austro-Tai (speculative, Paul Benedict 1942)
- Dené–Caucasian (speculative, Nikolayev 1991; expanded by Bengtson 1997), cf. Dené–Yeniseian (Edward Vajda 2008)
- Nostratic (speculative, Holger Pedersen 1903)
Jäger (2015)
[edit]A computational phylogenetic analysis by Jäger (2015) did not support the Borean macrophylum in its entirety, but provided the following phylogeny of language families in Eurasia:[12]
Other languages
[edit]Sumerian
[edit]Allan Bomhard argues that Sumerian did not descend from a daughter language of Proto-Nostratic but from a sister language of it. In other words, Sumerian descended from an older common ancestor language with Proto-Nostratic and did not descend directly from it; that is, Sumerian was closer to Nostratic but not a member of it.[13]
Kartvelian
[edit]Bomhard argues that Kartvelian is closer to Eurasiatic than to other language families within Nostratic and that the differences are due to the fact that Kartvelian became separated from Eurasiatic at a very early date.[13]
Status of the hypothesis
[edit]Linguist Asya Pereltsvaig states in Languages of the World: An Introduction that both versions of the Borean hypothesis are "controversial and tentative".[14]
See also
[edit]- Proto-Human language
- List of proto-languages
- Origin of language-Theories of how languages are formed
References
[edit]- ^ a b "«Evolution of Human Languages»: current state of affairs (03.2014)" (PDF). ehl.santafe.edu. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ^ a b c "Harold Fleming (2002) "Afrasian and Its Closest Relatives: the Borean Hypothesis", Global Perspectives on Human Language". Archived from the original on 9 June 2007. Retrieved 2 July 2006.
- ^ a b Harold C. Fleming, Stephen L. Zegura, James B. Harrod, John D. Bengtson and Shomarka O.Y. Keita – "The Early Dispersions of Homo Sapiens sapiens and proto-Human from Africa." in Mother Tongue (journal), issue XVIII, pp. 143–188, 2013
- ^ "It is clear that the Borean hypothesis involves a super-phylum some of whose sub-taxa are themselves super-phyla. The term phyletic chain is introduced as a better label," in name="Greenberg conference">Harold Fleming (2002) "Afrasian and Its Closest Relatives: the Borean Hypothesis", Global Perspectives on Human Language Archived 9 June 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "The basic hypothesis is that Afrasian is related to the following groups of languages before it is related to any others." in Harold Fleming (2002) "Afrasian and Its Closest Relatives: the Borean Hypothesis", Global Perspectives on Human Language.
- ^ "The Nostratic hypothesis is explicitly rejected here because it is not a valid taxon, Afrasian being coordinate to the rest and group c being aberrant in its relationship to the others." in name="Greenberg conference">Harold Fleming (2002) "Afrasian and Its Closest Relatives: the Borean Hypothesis", Global Perspectives on Human Language Archived 9 June 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Ainu is still controversial, being classified as a branch of Eurasiatic by some and as a branch of Austric by others." (p.165) in Harold C. Fleming, Stephen L. Zegura, James B. Harrod, John D. Bengtson and Shomarka O.Y. Keita – "The Early Dispersions of Homo Sapiens sapiens and proto-Human from Africa." in Mother Tongue (journal), issue XVIII, p. 143–188, 2013
- ^ Driem, George van (2006). "Sino-Austronesian vs. Sino-Caucasian, Sino-Bodic vs. Sino-Tibetan, and Tibeto-Burman as Default Theory" (PDF). Contemporary Issues in Nepalese Linguistics. Kathmandu: Linguistic Society of Nepal. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 July 2011.
- ^ a b c Murray Gell-Mann et al. (2009) "Distant Language Relationship:The Current Perspective", Journal of Language Relationship·Вопросы языкового родства
- ^ Alicia Sanchez-Mazas (ed.), Past human migrations in East Asia: matching archaeology, linguistics and genetics, volume 5 of Routledge studies in the early history of Asia, Taylor & Francis, 2008, ISBN 978-0-415-39923-4, obituary, p. xxvi.
- ^ Starostin's site includes a tree diagram with a hypothesized branching chronology for Borean, Sergei Starostin. "Borean tree diagram"., a database of proposed etymologies, "Description of database of suggested Borean etymologies"., "Online query of database of long-range etymologies".
- ^ Jäger, Gerhard (2015). "Statistical support for linguistic macrofamilies". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 112 (41): 12752–12757. Bibcode:2015PNAS..11212752J. doi:10.1073/pnas.1500331112. PMC 4611657. PMID 26403857.
- ^ a b BOMHARD, Allan. (2018). A Comprehensive Introduction to Nostratic Comparative Linguistics, p. 7
- ^ Pereltsvaig, Asya (9 February 2012). Languages of the World: An Introduction. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781107002784.
Further reading
[edit]- H. C. Fleming, 'A New Taxonomic Hypothesis: Borean or Boralean', Mother Tongue 14 (1991).
- H. C. Fleming, 'Proto-Gongan Consonant Phonemes: Stage One', in Mukarovsky (ed.) FS Reinisch (1987), 141–159.
