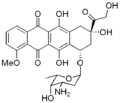
Daunosamine
Appearance
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC names
Linear:(3S,4S,5S)-3-amino-4,5-dihydroxyhexanal
Pyranose: (3S,4S,5S)-4-amino-6-methyl-tetrahydropyran-2,5-diol | |||
| Other names
3-Amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-L-lyxo-hexose
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H13NO3 | |||
| Molar mass | 147.174 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Daunosamine is a deoxy sugar and amino sugar of the hexosamine class.[1]
Daunosamine is a component of the anthracycline class of antineoplastics, linked to a derivative of naphthacene. It is a component of birch juice.
The compound is soluble in water and responds with polymers like cellulose and lignin if it is in excess, so collection of birch juice is very helpful for the birch tree.
The dnrQ gene is required for the synthesis of daunosamine.[2]
References
[edit]- ^ Grethe, Guenter; Mitt, Toomas; Williams, Thomas H; Uskokovic, Milan R (1983). "Synthesis of daunosamine". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 48 (26): 5309–5315. doi:10.1021/jo00174a028.
- ^ Otten, S. L; Liu, X; Ferguson, J; Hutchinson, C. R (1995). "Cloning and characterization of the Streptomyces peucetius dnrQS genes encoding a daunosamine biosynthesis enzyme and a glycosyl transferase involved in daunorubicin biosynthesis". Journal of Bacteriology. 177 (22): 6688–92. doi:10.1128/jb.177.22.6688-6692.1995. PMC 177529. PMID 7592454.
External links
[edit]- Daunosamine at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)