Cycas
| Cycas Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
| A large cycas under development | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Gymnospermae |
| Division: | Cycadophyta |
| Class: | Cycadopsida |
| Order: | Cycadales |
| Suborder: | Cycadineae |
| Family: | Cycadaceae Pers.[2] |
| Genus: | Cycas L.[1] |
| Type species | |
| C. circinalis[1] L.[1]
| |
| |
| Synonyms[3] | |
| |
Cycas is a genus of cycad, and the only genus in the family Cycadaceae with all other genera of cycad being divided between the Stangeriaceae and Zamiaceae families. Cycas circinalis, a species endemic to India, was the first cycad species to be described in western literature, and is the type species of the genus.[4][5]
As of April 2024, there are 119 accepted species within the genus Cycas, all of which are native to Asia, Oceania, and eastern Africa and the Indian ocean region, with the largest number of species native to Australia, China and Vietnam.[6][7][8]
In horticulture, the most widely grown and perhaps best-known Cycas species is Cycas revoluta, which is commercially grown in large numbers for sale as houseplants or to be used in landscaping.[8][9][10]
The majority of Cycas species are highly endangered. Many are threatened by the illegal trade of wild collected plants for plant collectors, and through the conversion of land for urban development or agricultural use.[8]
Range
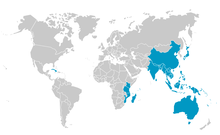
[edit]The genus Cycas is native to parts of Asia, eastern Africa and Oceania.[8] Cycas has the widest distribution of any genus of cycad.[11]
In Asia, Cycas (and therefore, the family Cycadaceae) represent the only cycads native to Asia. Within Asia, Cycas species are native from India and Sri Lanka in the west, through China to Japan in the north east and through south east Asia (including the Philippines) to Indonesia in the south. Globally, the northernmost species ( Cycas revoluta) is found at 31°N in southern Japan.[8][9]
As of April 2024, the largest number of currently accepted species of Cycas in Asia are found in Vietnam (27 species), China (23 species), India (14 species), Thailand (12 species), Philippines (12 species) and Indonesia (10 species).[7] The distribution of Cycas species in Myanmar, Laos, and Cambodia is not well known, but as of April 2024, no accepted cycad species is known to be endemic to any of these three countries.[7][8]
In Africa, cycads belonging to all three cycad families are found making it a major center of diversity for cycads in general, but only one Cycas species (Cycas thouarsii) is native and it is restricted to eastern Africa and nearby island nations. C. thouarsii grows in a comparatively wide area including coastal regions of Mozambique, Tanzania, and Kenya in mainland Africa, extending to the Seychelles, Madagascar and Comoros islands in the Indian Ocean.[8][12]
In Oceania, Cycas species are native to Australia, Papua New Guinea, and the island nations of the Pacific Ocean region, but are absent from New Zealand. As in Asia, Cycas is the only genus of cycad found across the region, with the exception for Australia, where cycads native to all three families of cycads are found. Despite this, Australia also has the largest number of Cycas species globally with 34 native Cycas species accepted (as of April 2024), including the southernmost species globally (Cycas megacarpa) found at 26°S in southeast Queensland.[7][8][13] At least 7 Cycas species are found in Papua New Guinea, some of which are also found in parts of neighbouring Indonesia.[7] In the broader region, Cycas seemannii is found in Melanesia and western Polynesia and Cycas micronesica is found across Micronesia.[8][14][15]
Globally, some Cycas species are considered to be relatively widespread, for example Cycas thouarsii is native to a large area of mainland Africa and islands of the Indian Ocean, and Cycas pectinata and Cycas clivicola are both native to large areas of Asia; however, most Cycas species have restricted distributions, with some restricted to very small areas. In Asia, for example, more than 75% of species occur in no more than one country. For some countries, even though the number of species may not be high, the level of species-specific genetic variation can be very high meaning that so that even countries with few species, it may contain distinct gene pools of widespread species.[8][16]
Evolution
[edit]
Cycas (and the Cycadaceae family) is considered as being an early offshoot that diverged early from all other living cycads (which belong to the family Zamiaceae). Estimates of the timing of the split ranging from the Jurassic[17] to the Carboniferous.[18] The earliest fossils assignable to Cycas are known from the Paleogene of East Asia, such as Cycas fushunensis from the Eocene (around 47.5 million years ago) of Northeast China with East Asia likely representing the ancestral homeland of the genus.[19] The presence of Cycas in Australasia and eastern Africa is relatively new, but the major evolutionary events behind the genesis of new species have taken place in Indochina and Australia, where the majority of living species are native.[8]
Fossil seeds from the Middle Jurassic of England and British Columbia were suggested in a 2017 study to be more closely related to Cycas than other cycads and were assigned to the same family, Cycadaceae.[20] A later study suggested that these seeds could not be assigned to the stem-group of Cycas with confidence due to lacking the double vascular system that characterises the seeds of all living cycads.[21] The leaf fossil genus Paracycas known from the Jurassic and Cretaceous of Europe has been suggested to be early representatives of the Cycas lineage by cladistic analysis.[18]
Morphology
[edit]
The plants are dioecious, and the family Cycadaceae is unique among the cycads in not forming seed cones on female plants, but rather a group of leaf-like structures called megasporophylls each with seeds on the lower margins, and pollen cones or strobilus on male individuals.
The caudex is cylindrical, surrounded by the persistent petiole bases. Most species form distinct branched or unbranched trunks but in some species the main trunk can be subterranean with the leaf crown appearing to arise directly from the ground. There are two types of leaves - foliage leaves and scaly leaves. The foliage leaves are pinnate (or more rarely bipinnate) and arranged spirally, with thick and hard keratinose.[clarification needed] They are not permanent and fall off leaving back leaf-bases. The leaflets are articulated, have midrib but lack secondary veins. The scaly leaves are persistent, brown in colour and protective in function. Megasporophylls are not gathered in cones. Pollination takes place by air.
Reproduction
[edit]
Cycas take about 10 years to reach sexual maturity, after years of exclusive vegetative growth, which occurs by bulbils arising at the base of the trunk.[citation needed]
Conservation status
[edit]Cycas species are threatened worldwide and almost all the species are listed in the IUCN Red List. Cycas beddomei is the only species of the genus Cycas listed in Appendix I of CITES. All other members of Cycadaceae are listed under Appendix II.[22] Cycas rumphii and Cycas pectinata have the most widespread distribution.
Phylogeny
[edit]


| Phylogeny of Cycas[23] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Other species:
- Cycas aenigma Hill & Lindström
- Cycas apoa Hill
- Cycas arnhemica Hill
- Cycas badensis Hill
- Cycas bglswamyi Pant ex Agrawal, Akhtar & R.C.Srivast.
- Cycas brunnea Hill
- Cycas campestris Hill
- Cycas candida Hill
- Cycas cantafolia Jutta, Chew & Saw
- Cycas changjiangensis Liu
- Cycas chenii Gong & Zhou
- Cycas collina Hill, Nguyên & Lôc
- Cycas cupida Forster
- Cycas darshii Srivastava & Jana
- Cycas desolata Forster
- Cycas dharmrajii Singh
- Cycas distans P.I.Forst. & B.Gray
- Cycas divyadarshanii Khuraijam & Rita Singh
- Cycas elephantipes Lindström & Hill
- Cycas falcata Hill
- Cycas flabellata Agoo, Madulid & Callado
- Cycas fugax Hill, Nguyên & Lôc
- Cycas furfuracea W.Fitzg.
- Cycas glauca Miquel
- Cycas hoabinhensis Lôc & Nguyên
- Cycas inermis Oudem.
- Cycas javana (Miquel) de Laubenfels
- Cycas lacrimans Lindström & Hill
- Cycas lane-poolei
- Cycas laotica Nguyên & Nguyên
- Cycas litoralis Hill
- Cycas mindanaensis Agoo, Madulid & Callado
- Cycas miquelii Warburg
- Cycas montana Lindström & Hill
- Cycas nayagarhensis Rita Singh, Radha & Khuraijam
- Cycas nathorstii Schuster
- Cycas orixensis (Haines) Rita Singh & Khuraijam
- Cycas pachypoda Hill
- Cycas panzhihuaensis Zhou & Yang
- Cycas papuana von Mueller
- Cycas pectinata
- Cycas pranburiensis Yang et al.
- Cycas pruinosa Maconochie
- Cycas sainathii Srivastava
- Cycas sancti-lasallei Agoo & Madulid
- Cycas saxatilis Hill & Lindström
- Cycas scratchleyana von Mueller
- Cycas seemannii A.Braun
- Cycas seshachalamensis Rao et al.
- Cycas sexseminifera Wei
- Cycas shanyaensis Fu
- Cycas sundaica Miquel ex Lindström & Hill
- Cycas terryana Forster
- Cycas tuckeri Hill
- Cycas xipholepis Hill
- Cycas yorkiana Hill
- Cycas yunnanensis Cheng, Fu & Cheng
- Cycas zambalensis Madulid & Agoo
- Cycas zeylanica (Schuster) Lindström & Hill
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Hill, Ken; Leonie Stanberg; Dennis Stevenson. "The Cycad Pages". Genus Cycas. Royal Botanic Gardens Sydney. Archived from the original on 2021-03-01. Retrieved 6 September 2013.
- ^ Johnson, L. A. S.; Wilson, K. L. (1990). "Cycadaceae". Pteridophytes and Gymnosperms. p. 370. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-02604-90.0. ISBN 978-3-642-08080-7.
- ^ "Cycas L." Plants of the World Online. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Retrieved 28 March 2023.
- ^ Linnaeus, Carl (1753). Palmae Pennatifoliae. Cycas [Cycas circinalis protologue]. pp. Sp. Pl. 2 : 1188.
- ^ Type Location(s): LT:t. 19, in Rheede, Hort. Malab, 3 (1682) Cycas circinalis at The World List of Cycads (cycadlist.org)
- ^ 119 accepted species, with 6 infraspecific taxa, as of April 21, 2024.
- ^ a b c d e The World List of Cycads (WLoC), a comprehensive taxonomic reference for cycad taxonomy, nomenclature, biology, and literature. The WLoC is produced under the auspices of the IUCN/SSC Cycad Specialist Group (CSG). The online edition is hosted and sponsored by Montgomery Botanical Center. Calonje M, Stevenson DW, Osborne R. The World List of Cycads, online edition [Internet]. 2013-2024. [cited 2024 Apr 21]. Available from: http://www.cycadlist.org.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Donaldson, J.S.; Dehgan, B.; Vovides, A.P.; Tang, W. (2003). "Cycads in trade and sustainable use of cycad populations" (PDF). Cycads Status Survey and Conservation Action Plan. IUCN The World Conservation Union Gland, Switzerland.
- ^ a b "Cycas revoluta". cycadlist.org. Retrieved 2024-04-21.
- ^ Marler, Thomas E.; Moore, Aubrey (May 2010). "Cryptic Scale Infestations on Cycas revoluta Facilitate Scale Invasions". HortScience. 45 (5): 837–839. doi:10.21273/HORTSCI.45.5.837.
- ^ Hill, K. D. (2004). Character evolution, species recognition and classification concepts in the Cycadaceae In Walters T., & Osborne R. (Eds.), Cycad classification, concepts and recommendations (pp. 23–44). Wallingford: CABI Publishing.Available as a PDF online at: cabidigitallibrary.org
- ^ "Cycas thouarsii". cycadlist.org. Retrieved 2024-04-21.
- ^ "Cycas megacarpa". cycadlist.org. Retrieved 2024-04-21.
- ^ "Cycas seemannii". cycadlist.org. Retrieved 2024-04-21.
- ^ "Cycas micronesica". cycadlist.org. Retrieved 2024-04-21.
- ^ Xiao, Siyue; Ji, Yunheng; Liu, Jian; Gong, Xun (February 2020). "Genetic characterization of the entire range of Cycas panzhihuaensis (Cycadaceae)". Plant Diversity. 42 (1): 7–18. doi:10.1016/j.pld.2019.10.001. PMC 7046506. PMID 32140633.
- ^ Nagalingum, N. S.; Marshall, C. R.; Quental, T. B.; Rai, H. S.; Little, D. P.; Mathews, S. (11 November 2011). "Recent Synchronous Radiation of a Living Fossil". Science. 334 (6057): 796–799. Bibcode:2011Sci...334..796N. doi:10.1126/science.1209926. PMID 22021670. S2CID 206535984.
- ^ a b Coiro, Mario; Allio, Rémi; Mazet, Nathan; Seyfullah, Leyla J.; Condamine, Fabien L. (2023-06-11). "Reconciling fossils with phylogenies reveals the origin and macroevolutionary processes explaining the global cycad biodiversity". New Phytologist. 240 (4): 1616–1635. doi:10.1111/nph.19010. ISSN 0028-646X. PMC 10953041. PMID 37302411. S2CID 259137975.
- ^ Liu, Jian; Lindstrom, Anders J; Marler, Thomas E; Gong, Xun (28 January 2022). "Not that young: combining plastid phylogenomic, plate tectonic and fossil evidence indicates a Palaeogene diversification of Cycadaceae". Annals of Botany. 129 (2): 217–230. doi:10.1093/aob/mcab118. PMC 8796677. PMID 34520529.
- ^ Spencer, Alan R. T.; Garwood, Russell J.; Rees, Andrew R.; Raine, Robert J.; Rothwell, Gar W.; Hollingworth, Neville T. J.; Hilton, Jason (2017-08-28). "New insights into Mesozoic cycad evolution: an exploration of anatomically preserved Cycadaceae seeds from the Jurassic Oxford Clay biota". PeerJ. 5: e3723. doi:10.7717/peerj.3723. ISSN 2167-8359. PMC 5578371. PMID 28875075.
- ^ Rothwell, Gar W.; Stockey, Ruth A.; Stevenson, Dennis W.; Zumajo-Cardona, Cecilia (October 2022). "Large Permineralized Seeds in the Jurassic of Haida Gwaii, Western Canada: Exploring the Mode and Tempo of Cycad Evolution". International Journal of Plant Sciences. 183 (8): 674–690. doi:10.1086/721710. hdl:2434/975729.
- ^ "Appendices I, II and III". Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora. 21 May 2023. Retrieved 22 August 2023.
- ^ Stull, Gregory W.; Qu, Xiao-Jian; Parins-Fukuchi, Caroline; Yang, Ying-Ying; Yang, Jun-Bo; Yang, Zhi-Yun; Hu, Yi; Ma, Hong; Soltis, Pamela S.; Soltis, Douglas E.; Li, De-Zhu; Smith, Stephen A.; Yi, Ting-Shuang (19 July 2021). "Gene duplications and phylogenomic conflict underlie major pulses of phenotypic evolution in gymnosperms". Nature Plants. 7 (8): 1015–1025. Bibcode:2021NatPl...7.1015S. doi:10.1038/s41477-021-00964-4. PMID 34282286.
External links
[edit]- de Laubenfels, D.J.; Adema, F. (1998). "A taxonomic revision of the genera Cycas and Epicycas Gen. Nov. (Cycadaceae)". Blumea. 43: 351–400.
- Hill, K.D.(1998–2004) The Cycad Pages, Royal Botanic Gardens Sydney. http://plantnet.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/PlantNet/cycad/index.html Archived 2021-03-29 at the Wayback Machine
- Virtual Cycad Encyclopedia edited by the Palm & Cycad Societies of Florida
- David, J. de Laubenfels, Cycas Taxonomy
- Hill, K.D.; Stevenson, Dennis W.; Osborne, Roy (2004). "The World List of Cycads". The Botanical Review. 70 (2): 274–298. doi:10.1663/0006-8101(2004)070[0274:TWLOC]2.0.CO;2. S2CID 36921733.
- Lindstrom, Anders J.; Hill, Ken D. (2007). "The genus Cycas (Cycadaceae) in India". Telopea. 11 (4): 463–488. doi:10.7751/telopea20075745.
- Singh, R & JS Khuraijam (2013-) Cycads of India. http://www.cycadsofindia.in/ Archived 2021-01-18 at the Wayback Machine
- Singh, R.; Radha, P.; Khuraijam, J.S. (2015). "A new species, a new combination and a new subsection of Cycas from Odisha, northern Eastern Ghats of India". Asian Journal of Conservation Biology. 4 (1): 3–14.
- Singh, R.; Radha, P. (2006). "Cycas annaikalensis, A new species of Cycas from the Malabar Coast, Western Ghats, India". Brittonia. 58 (2): 119–123. doi:10.1663/0007-196x(2006)58[119:ansocf]2.0.co;2. S2CID 32241023.
- Terrence Walters & Roy Osborne (eds.) (2004), Cycad Classification: Concepts and Recommendations, CABI publishing, ISBN 0-85199-741-4


