Curled octopus
| Curled octopus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Cephalopoda |
| Order: | Octopoda |
| Family: | Eledonidae |
| Genus: | Eledone |
| Species: | E. cirrhosa
|
| Binomial name | |
| Eledone cirrhosa | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
| |
The curled octopus (Eledone cirrhosa), also known as the horned octopus,[4] lesser octopus or northern octopus,[5] is a species of cephalopod found in the northeast Atlantic, ranging from Norway to the Mediterranean, including the British Isles. The total length of an adult is around 50 cm, but their arms are often tightly curled. It immobilises and eats large crustaceans by drilling a hole through their shell. It is mainly by-catch in commercial fisheries of the north eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean, where the common octopus is the preferred species.
Description
[edit]
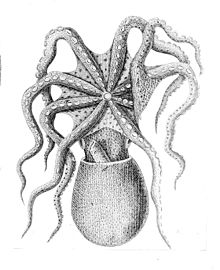
It has a broad, ovoid-shaped mantle and can reach a total length (including arms) of up to 50 cm (20 in). The head is narrower than the rest of the body with a filament over each eye. The octopus's colour is yellowish or reddish-orange to reddish-brown dorsally with diffuse rust-brown patches, and white on the underside. The skin is covered with very fine, closely set granulations, interspersed with larger warts. The relatively short arms have a single series of suckers on them and at rest are held with the tips lightly curled, hence the species's common name.[6] This species maximum weight is 1 kilogram (2.2 lb) in the more southerly parts of its distribution and 2 kilograms (4.4 lb) in the northern part.[7]
Habitat and distribution
[edit]The curled octopus is mainly found at depths between 0 and 150 m (0 and 492 ft) and may occur down to 800 m (2,600 ft). It lives in the northeast Atlantic Ocean, including the English Channel, the North Sea, and the Mediterranean Sea. In recent years the North Sea populations have increased, probably due to overfishing of large predatory fish such as Atlantic cod. This has had an effect on crab and lobster fisheries as the curled octopus readily enters pots to take the bait or the catch. In seas of Scotland, E. cirrhosa is infrequently caught when trawling over rocky substrates and are more frequently captured when fishing over sandy or muddy substrates.[8] A survey using different methods found that Eledone cirrhosa was common and widespread throughout the Scottish inshore waters covered by fishing activity, from the shoreline down to 140m, on substrates ranging through rocky, stoney, sandy and muddy. Specimens were caught throughout the year but is most common in inshore waters during the summer months and moves further offshore to the trawling grounds in October–December.[9]
Diet
[edit]The curled octopus feeds on crabs and other large crustaceans, as well as fish.[5] Serological analysis of the crop of specimens sampled in the Moray Firth and Sound of Jura revealed the main prey to be Liocarcinus spp, Nephrops norvegicus, Cancer pagurus , Crangon crangon and Carcinus maenas, although a large proportion of the samples analysed did not react in the tests suggesting they had consumed alternative prey.[10] It is cited as a significant predator of such commercially important species as Homarus gammarus (European lobster), Nephrops norvegicus (Norway lobster), and Cancer pagurus (edible crab) from traps.[9] When preying on crabs, it immobilises the crab by injecting toxins into the body of the crab through a hole created in its shell using the octopus's radula.[11] The octopus then injects saliva into the crab and the digestive enzymes contained in that saliva break down the crab's internal attachments to its shell, allowing the octopus to easily remove the carapace.[5]
Biology
[edit]The growth rate of the curled octopus is quite rapid and its life span is generally short at 1–5 years, although there may be some variation between warmer and colder areas. The curled octopus matures at around 1 year (on reaching a total length of 12–40 cm or 4.7–15.7 in for females, slightly smaller for males) and with 1,000–5,000 eggs laid on average. The females normally attain sexual maturity when they reach a body size of between 400 and 1000 g but some females weighing up to 1000–1200 g show no evidence of enlargement of the ovaries.[12] The males reach just over 600g and typically have well-developed reproductive organs from around 200g.[13] It breeds at a lower rate than the partially sympatric Octopus vulgaris (common octopus). Populations are apparently at their lowest density in the autumn, probably due to post-spawning die off as reproduction involves females laying eggs, guarding them and dying once the eggs hatch. Curled octopuses are solitary animals, generally inhabiting depths of less than 100 m (330 ft), and more common in shallow water, but they have been found down to 800 m (2,600 ft).[14]
Breeding activity of the curled octopus peaks between July and September and there are many juveniles present in October. In 2017 Storm Brian was followed by reports of many curled octopus on beaches and rock pools around the island of Anglesey and the Llyn Peninsula in north Wales. These were mostly juveniles which with their weaker suction than the adults were more affected by waves created by the storm, swept away from their hiding places among the rocks and stranded.[15]
Analysis carried out on the stomach contents of stranded Risso's dolphins demonstrates that the most important species fed on in Scottish waters is the curled octopus.[8]
Fisheries
[edit]The curled octopus is taken as bycatch in trawl fisheries for other species. It is also captured in earthenware pots in the Mediterranean, although the fishery for curled octopuses is less important than that of the common octopus. International Council for the Exploration of the Sea (ICES) catch data for both the curled octopus and common octopus, from all ICES regions (NE Atlantic) in 2006, indicated around 8,999 tonnes, but more recent estimates indicate a substantial increase to around 19,000 tonnes in 2008 (ICES WGCEPH, 2010). Nearly all landings of both species within these regions are taken by Portugal and Spain, with Spain taking the vast majority, although most of these will be of the common octopus.[16] Neither species is subject to either stock assessment or quota controls in Europe and in the case of the curled octopus there is no minimum size for landing.[17] In the Adriatic this species is caught and sold alongside Eledone moschata but is the less numerous of the two.[4] It is not regarded as a commercially viable species in Scotland and any caught are normally discarded.[8]

References
[edit]- ^ Allcock, L.; Taite, M.; Headlam, J.; Allen, G. (2018). "Eledone cirrhosa". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T163307A995942. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T163307A995942.en. Retrieved 20 November 2021.
- ^ "Eledone cirrhosa (Lamarck, 1798)". Integrated Taxonomic Information System.
- ^ S. Gofas (2004). "Eledone cirrhosa (Lamarck, 1798)". World Register of Marine Species. Retrieved 2 April 2017.
- ^ a b "Eledone cirrhosa (Lamarck, 1798)". Adriamed. FAO. Retrieved 24 December 2016.
- ^ a b c "Curled octopus (Eledone cirrhosa)". Wildscreen Arkive. Wildscreen. Archived from the original on 2016-12-24. Retrieved 24 December 2016.
- ^ Wilson, Emily (2008) "Eledone cirrhosa. Curled octopus". Marine Life Information Network: Biology and Sensitivity Key Information Sub-programme. Plymouth: Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. Retrieved 24/01/2012
- ^ SCICOM STEERING GROUP ON ECOSYSTEM FUNCTIONS (SSGEF) (2013). "Report of the Working Group on Cephalopod Fisheries and Life History (WGCEPH)" (PDF). International Council for the Exploration of the Sea. Retrieved 20 April 2018.
- ^ a b c MacLeod, C. D.; Santos, M. B.; Burns, F.; Brownlow, A.; Pierce, G. J. (March 2014). "MacLeod, C.D., Santos, M.B and Pierce, G.J. 2014. Can habitat modelling for the octopus Eledone cirrhosa help identify key areas for Risso's dolphin in Scottish waters? Scottish Natural Heritage Commissioned Report No. 530". Scottish Natural Heritage. doi:10.1007/s10750-013-1555-0. hdl:2164/5728. S2CID 1335648. Retrieved 24 December 2016.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b P.R. Boyle (1986). "A Descriptive Ecology of Eledone Cirrhosa (Mollusca: Cephalopoda) in Scottish Waters (abstract)". Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 66 (4): 855–865. doi:10.1017/s0025315400048487. S2CID 86564565.
- ^ P.R. Boyle; M. S. Grisley; G. Robertson (1986). "Crustacea in the Diet of Eledone Cirrhosa (Mollusca: Cephalopoda) determined by Serological Methods (abstract)". Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 66 (4): 867–879. doi:10.1017/s0025315400048499. S2CID 84526994.
- ^ N.W. Runham; C.J. Bailey; M. Carr; C.A. Evans; S. Malham (1997). "Hole drilling in crab and gastropod shells by Eledone cirrhosa (Lamarck, 1798)" (PDF). Scientia Marina. 61 (Supplement2): 67–76.
- ^ P.R. Boyle; Daniela Knobloch (1983). "The female reproductive cycle of the octopus, Eledone cirrhosa (abstract)". Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 63 (1): 71–83. doi:10.1017/s002531540004981x. S2CID 86778330.
- ^ P.R. Boyle (1984). "Male reproductive maturity in the octopus, Eledone cirrhosa (Cephalopoda: Octopoda) (abstract)". Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom. 64 (3): 573–579. doi:10.1017/s0025315400030265. S2CID 85572659.
- ^ "Eledone cirrhosa". www.european-marine-life.org. Bay-Nouailhat A. Retrieved 24 December 2016.
- ^ Frances Dipper (2017). "Wildlife Reports: Marine Life". British Wildlife. 29 (2): 135–137.
- ^ Curled octopus at Fish online
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-01-10. Retrieved 2012-01-24.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
External links
[edit]- Photos of Curled octopus on Sealife Collection

