Cordycepin
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
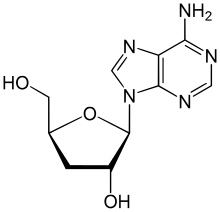
| IUPAC name
3′-Deoxyadenosine
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S,3R,5S)-2-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-ol | |
| Other names
Cordycepine
9-(3-Deoxy-β-D-ribofuranosyl)adenine 3-dA | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.720 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H13N5O3 | |
| Molar mass | 251.246 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 225.5 °C (437.9 °F; 498.6 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cordycepin, or 3'-deoxyadenosine, is a derivative of the nucleoside adenosine, differing from the latter by the replacement of the hydroxy group in the 3' position with a hydrogen. It was initially extracted from the fungus Cordyceps militaris,[1] but can now be produced synthetically.[2] It is also found in other Cordyceps species as well as Ophiocordyceps sinensis.[3]
Biological activity
[edit]Cordyceps fungi produce cordycepin as a means of infecting insect populations, due to its biological activity.[4] Because cordycepin is similar to adenosine, some enzymes cannot discriminate between the two. It can therefore participate in certain biochemical reactions (for example, 3-dA can trigger the premature termination of mRNA synthesis).[5][6] By acting as an adenosine analog, cordycepin is the most potent molecular circadian clock resetter out of several screened compounds.[7]
Cordycepin has displayed cytotoxicity against some leukemic cell lines in vitro.[8][9][10] Additionally, cordycepin displays an effect in cancers, such as lung,[11] renal,[12] colon,[13] and breast cancer.[14] Cordycepin reduces viable A549 lung cancer cell populations by 50%.[11]
Cordycepin produces rapid, robust imipramine-like antidepressant effects in animal models of depression, and these effects, similarly to those of imipramine, are dependent on enhancement of AMPA receptor signaling.[15]
Cordycepin has anti-inflammatory qualities,[16] as well as the ability to defend against injury from cerebral ischemia in mice.[17]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Cunningham, K. G., Manson, W., Spring, F. S., Hutchinson, S. A. (1950). "Cordycepin, a Metabolic Product isolated from Cultures of Cordyceps militaris (Linn.) Link". Nature. 166 (4231): 949. Bibcode:1950Natur.166..949C. doi:10.1038/166949a0. PMID 14796634.
- ^ Huang S, Liu H, Sun Y, Chen J, Li X, Xu J, Hu Y, Li Y, Deng Z, Zhong S (2018-01-01). "An effective and convenient synthesis of cordycepin from adenosine". Chemical Papers. 72 (1): 149–160. doi:10.1007/s11696-017-0266-9. ISSN 1336-9075. S2CID 90915876.
- ^ Zhou X, Luo L, Dressel W, Shadier G, Krumbiegel D, Schmidtke P, Zepp F, Meyer CU (2008). "Cordycepin is an immunoregulatory active ingredient of Cordyceps sinensis". The American Journal of Chinese Medicine. 36 (5): 967–80. doi:10.1142/S0192415X08006387. PMID 19051361.
- ^ Raethong N, Wang H, Nielsen J, Vongsangnak W (2020). "Optimizing cultivation of Cordyceps militaris for fast growth and cordycepin overproduction using rational design of synthetic media". Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal. 18: 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2019.11.003. PMC 6926140. PMID 31890138.
- ^ Siev, M., Weinberg, R., Penman, S. (1969). "The selective interruption of nucleolar RNA synthesis in HeLa cells by cordycepin". J. Cell Biol. 41 (2): 510–520. doi:10.1083/jcb.41.2.510. PMC 2107749. PMID 5783871.
- ^ Kondrashov A, Meijer HA, Barthet-Barateig A, Parker HN, Khurshid A, Tessier S, et al. (2012). "Inhibition of polyadenylation reduces inflammatory gene induction". RNA. 18 (12): 2236–50. doi:10.1261/rna.032391.112. PMC 3504674. PMID 23118416.
- ^ Ju D, Zhang W, Yan J, Zhao H, Li W, Wang J, Liao M, Xu Z, Wang Z, Zhou G, Mei L, Hou N, Ying S, Cai T, Chen S, Xie X, Lai L, Tang C, Park N, Takahashi JS, Huang N, Qi X, Zhang EE (6 May 2020). "Chemical perturbations reveal that RUVBL2 regulates the circadian phase in mammals". Science Translational Medicine. 12 (542): eaba0769. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aba0769. PMID 32376767. S2CID 218533423.
- ^ National Cancer Institute (2011-02-02). "Definition of cordycepin". NCI Drug Dictionary. Retrieved 21 December 2015.
- ^ Kodama E, McCaffrey R, Yusa K, Mitsuya H (February 2000). "Antileukemic activity and mechanism of action of cordycepin against terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-positive (TdT+) leukemic cells". Biochemical Pharmacology. 59 (3): 273–281. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(99)00325-1. PMID 10609556.
- ^ Chou S, Lai W, Hong T, Lai J, Tsai S, Chen Y, Yu S, Kao C, Chu R, Ding S, Li T, Shen T (October 2014). "Synergistic property of cordycepin in cultivated Cordyceps militaris-mediated apoptosis in human leukemia cells". Phytomedicine. 21 (12): 1516–1524. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2014.07.014. PMID 25442260.
- ^ a b Tuli HS, Kumar G, Sandhu SS, Sharma AK, Kashyap D (2015). "Apoptotic effect of cordycepin on A549 human lung cancer cell line". Turkish Journal of Biology. 39: 306–311. doi:10.3906/biy-1408-14.
- ^ Hwang IH, Oh SY, Jang HJ, Jo E, Joo JC, Lee KB, Yoo HS, Lee MY, Park SJ, Jang IS (2017-10-18). Ahmad A (ed.). "Cordycepin promotes apoptosis in renal carcinoma cells by activating the MKK7-JNK signaling pathway through inhibition of c-FLIPL expression". PLOS ONE. 12 (10): e0186489. Bibcode:2017PLoSO..1286489H. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0186489. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5646797. PMID 29045468.
- ^ Lee SY, Debnath T, Kim SK, Lim BO (October 2013). "Anti-cancer effect and apoptosis induction of cordycepin through DR3 pathway in the human colonic cancer cell HT-29". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 60: 439–447. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2013.07.068. PMID 23941773.
- ^ Lee D, Lee WY, Jung K, Kwon Y, Kim D, Hwang G, Kim CE, Lee S, Kang K (2019-08-26). "The Inhibitory Effect of Cordycepin on the Proliferation of MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells, and Its Mechanism: An Investigation Using Network Pharmacology-Based Analysis". Biomolecules. 9 (9): 414. doi:10.3390/biom9090414. ISSN 2218-273X. PMC 6770402. PMID 31454995.
- ^ Li B, Hou Y, Zhu M, Bao H, Nie J, Zhang GY, Shan L, Yao Y, Du K, Yang H, Li M, Zheng B, Xu X, Xiao C, Du J (2016). "3'-Deoxyadenosine (Cordycepin) Produces a Rapid and Robust Antidepressant Effect via Enhancing Prefrontal AMPA Receptor Signaling Pathway". International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 19 (4): pyv112. doi:10.1093/ijnp/pyv112. ISSN 1461-1457. PMC 4851261. PMID 26443809.
- ^ Tan L, Song X, Ren Y, Wang M, Guo C, Guo D, Gu Y, Li Y, Cao Z, Deng Y (March 2021). "Anti-inflammatory effects of cordycepin: A review". Phytotherapy Research. 35 (3): 1284–1297. doi:10.1002/ptr.6890. ISSN 0951-418X. PMID 33090621. S2CID 224828245.
- ^ Cheng Z, He W, Zhou X, Lv Q, Xu X, Yang S, Zhao C, Guo L (2011-08-16). "Cordycepin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo and in vitro". European Journal of Pharmacology. 664 (1): 20–28. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.04.052. PMID 21554870.
