Cangiante

Cangiante (Italian: [kanˈdʒante]) is a painting technique where, when using relatively pure colors, one changes to a different, darker color to show shading, instead of dulling the original color by mixing it with a different one. According to the theory of the art historian Marcia B. Hall,[1] which has gained considerable acceptance,[2] this is one of the canonical painting modes of the Renaissance; i.e. one of the four modes of painting colours available to Italian High Renaissance painters, along with sfumato, chiaroscuro and unione.[3] The word itself is the present participle of the Italian verb cangiare ("to change").
Cangiante is characterized by a change in color necessitated by an original color's darkness or lightness limitation. For example, when painting shadows on a yellow object, the artist may use a red color simply because the yellow paint cannot be made dark enough. There are other methods of rendering shadows or highlights (for example, mixing the original hue with black or brown), but these can render the shadow color dull and impure. During the Renaissance, the variety and availability of paint colors were severely limited.
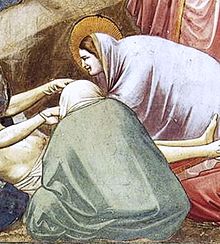
The greatest practitioner of the cangiante technique was Michelangelo,[4] especially in many parts of the Sistine Chapel ceiling. For example, in the image of the prophet Daniel, a transition from green to yellow is evident in the subject's robes. After Michelangelo's time, the technique found widespread acceptance and is now a standard painting technique.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Hall, Marcia B. (1994). Color and Meaning: Practice and Theory in Renaissance Painting. New York, N.Y.: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-45733-0.
- ^ "Four Canonical Painting Modes by APA".. Retrieved June 18, 2015.
- ^ Hall, Marcia B., Rome (series "Artistic Centers of the Italian Renaissance"), pp.148-150, 2005, Cambridge University Press, 2005, ISBN 0521624452, 9780521624459, google books
- ^ Hall, Marcia B., Rome (series "Artistic Centers of the Italian Renaissance"), pp.148-150, 2005, Cambridge University Press, 2005, ISBN 0521624452, 9780521624459, google books
