Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary

The Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary (CCGA; French: Garde côtière auxiliaire canadienne, GCAC) is a Canada-wide volunteer marine association dedicated to marine search and rescue (SAR) and the promotion of boating safety, through association with the Canadian Coast Guard under the auspices of Canada's National Search and Rescue Program.
Mandate
[edit]Members of the CCGA are usually recreational boaters and commercial fishermen who use their vessels to assist the Canadian Coast Guard with search and rescue (SAR) as well as boating safety education. CCGA members who assist in SAR operations have their vessel insurance covered by CCG, as well as any fuel and operating costs associated with a particular tasking.
The CCGA enables the CCG to provide maritime SAR coverage in many isolated areas of Canada's coastlines without having to maintain an active base and/or vessels in those areas. The auxiliary is dedicated to providing a permanent day and night search and rescue service to cover marine requirements in Canada and prevent the loss of life and injury.
- Save lives at risk
- Reduce the number and severity of SAR incidents
- Promote marine safety
- Support the Canadian Coast Guard
- Provide a humanitarian service
- Maintain the highest professional standards
- Promote dedication and pride of membership
History
[edit]Coastal lifesaving stations manned by volunteers pre-date Canadian Confederation (1867), with some coastal services in what is now Atlantic Canada dating to the early 1800s. The country's first motorized lifeboat was established in 1907 by volunteers at Bamfield, British Columbia.
Formal responsibility for organizing and overseeing search and rescue in Canada was given to the Minister of National Defence in 1951. This responsibility mostly fell to the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) which, in coordination with the International Maritime Organization (IMO) and International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), delineated search and rescue regions (SRRs) to be overseen by rescue coordination centres (RCCs) that would manage SAR response activities.
Changes to the Canada Shipping Act in 1961 and the formation of the Canadian Coast Guard in 1962 saw the Department of Transport, which had responsibility for the CCG from 1962-1995, given responsibility for maritime search and rescue in support of the Minister of National Defence's mandate. As a result, the Minister of Transport designated "marine rescue controllers" who were CCG personnel that would work within the RCAF's rescue co-ordination centres. The RCCs were renamed joint rescue coordination centres (JRCCs) to denote the dual role of aeronautical and maritime search and rescue, as well as their joint operation by RCAF and CCG personnel.
CCG search and rescue officers (CGRO) first formally recognized volunteers in 1963. Volunteer "rescue agents" were individuals with access to seaworthy boats equipped with radios and volunteer "search masters” were individuals who served as local points of communication with CCG maritime rescue controllers operating in the RCCs and Maritime Rescue Sub-Centres. A metal sign depicting a ball and square day shape (distress) and the CCG-GCC crest was provided to identify search masters. A distinctive pennant based on the design of the CCG jack was also issued: white hoist, blue fly, single red maple leaf with the letters S and R on either side of the leaf, to identify rescue agent vessels.
By the mid 1970s, it became clear that a formal organization for training volunteer search and rescuers was necessary in order to improve the CCG's response to maritime search and rescue incidents, particularly in remote locations. This was confirmed in a 1975 study commissioned by CCG and led to the Canadian Marine Rescue Auxiliary or CMRA being formed in late 1978 as a non-profit organization in an effort to enhance search and rescue coverage and capability, and to better coordinate volunteer efforts. The CMRA was renamed the Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary or CCGA in 1997.
As of 2019 the CCG has also been partnering with a number of First Nations communities to establish the Coastal Nations Coast Guard Auxiliary (CNCGA).
Current operations
[edit]Similar to its predecessor, the CMRA, the CCGA is a non-profit organization of volunteers who provide maritime search and rescue services for the federal government upon request from one of Canada's three Joint Rescue Coordination Centres (JRCCs) and two MRSC's.
CCGA units may respond on their own or may be asked to respond with regular CCG search and rescue vessels or Royal Canadian Air Force aircraft, as determined by the JRCC in charge of coordinating the response.
Some CCGA units on the Atlantic and Pacific coasts as well as the Great Lakes and St. Lawrence River actually have dedicated rescue vessels such as rigid hull inflatable boats similar to the Zodiac Hurricane 733 or Titan 249 XL. These vessels are owned and equipped by non-profit organizations located in the communities where the vessels are home ported but are still crewed by volunteers. The organizations, their volunteers and their vessels are part of the CCGA. In some cases the coxswains of these vessels receive fast rescue craft (FRC) training from CCG; CCG Station Bamfield in British Columbia and CCG Station Sambro in Nova Scotia.
Regions
[edit]The CCGA operations are divided into five regions which reflect the way that the Canadian Coast Guard is also organized. Each region is separately incorporated and is a registered charity under the Canada Revenue Agency with the ability to issue charitable donation receipts.
- Newfoundland and Labrador
CCGA operations in Newfoundland and Labrador are grouped under Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary (Newfoundland and Labrador) Incorporated.[2]
- Maritimes
CCGA operations in New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island are grouped under Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary (Maritimes) Incorporated.[3]
- Quebec
CCGA operations in Quebec are grouped under Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary (Quebec) Incorporated.[4]
- Central and Arctic
CCGA operations in Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta, Northwest Territories and Nunavut are grouped under Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary (Central and Arctic) Incorporated. [5]
- Western
The CCGA program is supported by a federally incorporated non-profit society that is based in British Columbia called the Royal Canadian Marine Search and Rescue.
RCMSAR has its origins from the Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary (Pacific) Incorporated which re-branded itself in 2012 as RCMSAR to signify the service's non-governmental and volunteer-based status. The operations are limited to the west coast of the province of British Columbia and interior freshwater lakes and are NOT nation wide as might otherwise be implied or inferred by the use of the adjective Canadian (as used by the national RCMP, RCAF, RCN services). The change assisted the public in British Columbia to better understand the community-based nature of the service and the importance of local support in maintaining rescue vessels, recruiting and training volunteers, and equipping them with the tools they need to save lives on the water.
The title "Royal" was granted by Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II in February 2012 in recognition of the organization's long-standing service, broad geographic coverage, and philanthropic mandate. HRH The Prince of Wales is the Royal Patron.
In 2017, RCMSAR signed a memorandum of understanding with the Province of British Columbia to allow local authorities and provincial agencies to request assistance from RCMSAR directly in times of emergency specifically related to their jurisdictions, for example water ambulance mode transportation and ground search support where vessels are requested by the police.
Marine search and rescue on federal waters connected with the BC provincial domain remain RCMSAR's core operation and primary support function. In 2017, RCMSAR also signed a memorandum of understanding establishing a relationship with the 4th Canadian Ranger Patrol Group for the purpose of training and operational collaboration.
Uniforms
[edit]Although the majority of CCGA volunteers across Canada respond to incidents upon being tasked by a JRCC in civilian clothes, the service does have a uniform that can be worn on formal occasions and occasionally on operations.
These CCGA uniforms are based on Canadian Coast Guard uniforms, however, they differ by having unique CCGA badges and insignia that are silver in colour whereas regular CCG fleet personnel have gold insignia.
RCMSAR retains a distinct operational uniform that is worn as part of their crew's personal protective equipment on dedicated response vessels.
Ranks
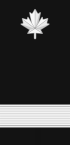
[edit]| Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary ranks and insignia[6][7][8] | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | National President | President | Vice President | Director | Alternate Director Advisor District Training Officer District Prevention Officer |
Unit Leader | Alternate Unit Leader | Unit Training Officer Unit Prevention Officer |
Employee | Member | |||||||||
| Epaulette and cuff insignia | 
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| |||||||||
| Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary Member Insignia |
|---|
| Rank | Crew | Advanced Crew | Coxswain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shoulder insignia |
nil
[edit]See also
[edit]- Royal Canadian Marine Search and Rescue (RCMSAR)
- Civil Air Search and Rescue Association (CASARA)
- Joint Rescue Coordination Centre Halifax (JRCC Halifax)
- Joint Rescue Coordination Centre Trenton (JRCC Trenton)
- Joint Rescue Coordination Centre Victoria (JRCC Victoria)
References
[edit]- ^ "Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary". Public Register of Arms, Flags and Badges of Canada. Office of the Secretary to the Governor General. Retrieved 2019-12-17.
- ^ "Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary - Newfoundland and Labrador". Retrieved 2024-03-25.
- ^ "Unknown".[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Garde côtière auxiliaire canadienne (Québec)" (in French).
- ^ "Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary Central & Arctic Region". Retrieved 2024-03-25.
- ^ "Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary 2001 Uniform Policy" (PDF). ccga-pacific.org/. Retrieved 17 May 2021.
- ^ "Canadian Coast Guard Auxiliary (CCGA)". uniforminsignia.org. Retrieved 17 May 2021.
- ^ Melanie Irwin (16 August 2017). "Sarnia-Lambton First Responders Condemn Float Down". blackburnnews.com. Retrieved 17 May 2021.
