Broadback River
| Broadback River | |
|---|---|
 Tupatukasi Waterfall, Broadback River | |
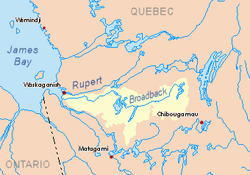 Broadback River basin in yellow | |
| Location | |
| Country | Canada |
| Province | Quebec |
| Region | Jamésie |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Lac Frotet |
| • location | 95 km north of Chibougamau, Nord-du-Québec |
| • coordinates | 50°46′0″N 74°39′20″W / 50.76667°N 74.65556°W |
| • elevation | 380 m (1,250 ft) |
| Mouth | Rupert Bay off James Bay |
• location | 17 km south of Waskaganish, Nord-du-Québec |
• coordinates | 51°21′20″N 78°52′00″W / 51.35556°N 78.86667°W |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 450 km (280 mi)[1] |
| Basin size | 20,800 km2 (8,000 sq mi)[1] |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 350 m3/s (12,000 cu ft/s)[1] |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left |
|
| • right |
|
The Broadback River (French: Rivière Broadback) (In Cree: Chistamiskau Sipi[2]) is a river in northern Quebec, Canada. It drains into Rupert Bay (a smaller bay at the south end of James Bay), just south of the Rupert River and Cree community Waskaganish. The major lake on the river's course is Lake Evans.
The river is a popular canoe-tripping destination.[3]
Geography
[edit]The hydrographic basins adjacent to the Broadback River are:
- north side: Rupert River, Nemiscau Lake, Nemiscau River;
- east side: Frotet Lake, Troilus Lake, La Marte River;
- south side: Nottaway River;
- west side: Nottaway River, Rupert Bay.
The Broadback River originates at Frotet Lake, located 28.1 kilometres (17.5 mi) west of grand Mistassini Lake. From the mouth of Frotet Lake (located north of the lake), this river winds the Jamésie on 451 kilometers to finally reach the Rupert Bay close to the mouth of the Nottaway River.
In its course, the river crosses several lakes, including: Troilus Lake, Quenonisca Lake, Evans Lake (the largest) and Giffard Lake. It flows between the Rupert River rivers to the north and the Nottaway River to the south.
At the end of the route, the river crosses marsh areas for 29.2 kilometres (18.1 mi) to the west.
History
[edit]The Broadback, together with the Nottaway and Rupert rivers, was initially considered to be dammed and diverted as part of the James Bay Project. However, in 1972 hydro-electric development began on the more northerly La Grande and Eastmain Rivers, and the NBR Project was shelved. With the decision to divert the Rupert River to the La Grande, it is not likely that the Broadback will be developed in the foreseeable future.
Tributaries
[edit]Since the Broadback River flows relatively close to the northern edge of its basin, most of its major tributaries are left tributaries. Major tributaries in downstream order include:
Tributaries above Lake Evans:
Tributaries below Lake Evans:
- Ouasouagami River
- Colomb River
- Kaminahikuschit River
- Natouacamisie River
- Machisipi River
- Lepallier River

See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Atlas of Canada Archived February 2, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Banque de noms de lieux du Québec: Reference number 8435". toponymie.gouv.qc.ca (in French). Commission de toponymie du Québec.
- ^ Lester Kovac. "Broadback 2005".
External links
[edit]![]() Media related to Rivière Broadback at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Rivière Broadback at Wikimedia Commons
