Bokode
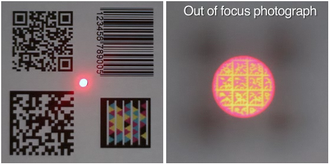
A bokode is a type of data tag which holds much more information than a barcode over the same area. They were developed by a team led by Ramesh Raskar at the MIT Media Lab.[1] Bokodes are intended to be read by any standard[vague] digital camera, focusing at infinity. With this optical setup, the tiny code appears large enough to read. Bokodes are readable from different angles and from 4 metres (13 ft) away.[2]
The bokode pattern is a tiled series of Data Matrix codes. The name is a portmanteau of the words bokeh—a photographic term for defocus—and barcode. Rewritable bokodes are called bocodes. Bokodes are circular with a diameter of 3 millimetres (0.12 in). A bokode consists of an LED covered with a photomask and a lens. Powered bokodes are relatively expensive because of the LED and the power it requires. However, prototypes have been developed which function passively with reflected light like a typical barcode.[3]
Bokodes convey a privacy advantage compared to radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags: bokodes can be covered up with anything opaque, whereas RFID tags must be masked by material opaque to radio frequencies, such as the sleeve provided by the New York State Department of Motor Vehicles when issuing their enhanced state IDs.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ Barcode replacement shown off, BBC News, 27 July 2009.
- ^ Mohan, A., Woo, G, Hiura, S, Smithwick, Q, Raskar, R. Bokode: Imperceptible Visual Tags for Camera Based Interaction from a Distance Archived July 30, 2009, at the Wayback Machine. ACM SIGGRAPH 2009.
- ^ a b Ankit Mohan, Grace Woo, Shinsaku Hiura, Quinn Smithwick, Ramesh Raskar: Bokode: Imperceptible Visual Tags for Camera Based Interaction from a Distance Archived 30 July 2009 at the Wayback Machine, Camera Culture Group, MIT Media Lab.
External links
[edit]- MIT Media Lab — Bokode: Imperceptible Visual Tags for Camera-Based Interaction from a Distance at the Wayback Machine (archived 23 March 2016)
- Camera Culture Group, MIT Media Lab — Bokode Research Paper at the Wayback Machine (archived 10 June 2013)
- Camera Culture Group
- Didactic article on Bokode "The Future of Barcodes"
- Bokode FAQ


