Betti reaction
| Betti reaction | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Mario Betti |
| Reaction type | Coupling reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| RSC ontology ID | RXNO:0000522 |
The Betti reaction is a chemical addition reaction of aldehydes, primary aromatic amines and phenols producing α-aminobenzylphenols.
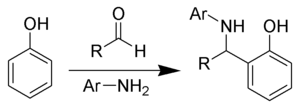
The Betti reaction is a special case of the Mannich reaction.
History
[edit]The reaction is named after the Italian chemist Mario Betti (1857-1942). Betti worked at many universities in Italy, including Florence, Cagliari, Siena, Genoa and Bologna, where he was the successor of Giacomo Ciamician. Betti's main research was focused on stereochemistry, and the resolution of racemic compounds, the relationship between molecular constitution and optical rotation, as well asymmetric synthesis using chiral auxiliaries or in the presence of polarized light.
In 1939 Mario Betti was appointed the Senator of the Kingdom of Italy.
In 1900 Betti hypothesized that 2-naphthol would be a good carbon nucleophile to the imine produced from the reaction of benzaldehyde and aniline. This led to the Betti reaction.[1]

Today, the name has grown to refer to any reaction of aldehydes, primary aromatic amines and phenols producing α-aminobenzylphenols.
Mechanism
[edit]The reaction mechanism[2] begins with an imine condensation of a primary aromatic amine and formaldehyde
Once the imine is produced, it reacts with phenol in the presence of water to yield an α-aminobenzylphenol.

First, the lone-pair on the nitrogen of the imine deprotonates the phenol, pushing the bonding electrons onto the oxygen. The carbonyl is then reformed and a double bond in the benzene ring attacks the carbon atom in the pronated imine cation. Water then acts as a base and deprotonates the α-carbon, reforming the aromatic ring and pushing electrons onto oxygen. The oxygen, which now has a negative formal charge, then attacks a hydrogen on the hydronium, resulting in an α-aminobenzylphenol, with water as the only byproduct.
Betti Base
[edit]
The product of the Betti reaction is called the Betti base. The stereochemistry of the base was resolved into two isomers by using tartaric acid.
Uses for the Betti base and its derivatives include:[1][3][4]
- Enantioselective addition of diethylzinc to aryl aldehydes.
- Enantioselective alkenylation of aldehydes.
- Preparation of stable boronate complexes, which can be alkylated to yield amino acid precursors.
- Separation of enantiomers.
References
[edit]- ^ a b Cardellicchio, C.; Capozzi, M.A.M.; Naso, F. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 2010, 21, 507-517.(doi:10.1016/j.tetasy.2010.03.020)
- ^ SynArchive. The Organic Synthesis Archive: Betti Reaction. http://www.synarchive.com/named-reactions/Betti_Reaction.
- ^ Cardellicchio, C.; Ciccarella, C.; Naso, F.; Perna, F.; Tortotrella, P. Tetrahedron. 1999, 55, 14685-14692.(doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(99)00914-X)
- ^ Cardellicchio, C.; Ciccarella, C.; Naso, F.; Schingaro,E.; Scordari, F. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 1998, 9, 3667-3675. (doi:10.1016/S0957-4166(98)00379-6)
Further reading
[edit]- Betti, M. Gazz. Chim. Ital. 1900, 30 II, 301.
- Betti, M. Gazz. Chim. Ital. 1903, 33 II, 2.
- Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 1, p.381 (1941); Vol. 9, p.60 (1929). (Article)
- Pirrone, F Gazz. Chim. Ital. 1936, 66, 518.
- Pirrone, F Gazz. Chim. Ital. 1937, 67, 529.
- Phillips, J. P. Chem. Rev. 1956, 56, 286.
- Phillips, J. P.; Barrall, E. M. J. Org. Chem. 1956, 21, 692.
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Gupta, M. K. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 12, 1582-1584.
