Berthe Rakotosamimanana
Berthe Rakotosamimanana | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | 18 January 1938 |
| Died | 29 November 2005 |
| Citizenship | Madagascar |
| Education | University of Paris VII |
| Occupation(s) | Palaeontologist; Primatologist; Government Adviser |
| Employer | University of Madagascar |
Berthe Rakotosamimanana (born Berthe Rasoamialinivo, 18 January 1938, Andasibe; died on 29 November 2005, Antananarivo) was a primatologist and palaeontologist from Madagascar.
Early life
[edit]Rakotosamimanana was born in Andasibe in Moramanga District on 18 January 1938.[1] She studied at the University of Paris VII, Faculty of Sciences, for a degree in animal biology and anthropology.[1] On her return in 1967 she was employed in the Geology Department at the University of Madagascar.[1] She was married to the primatologist Philibert Rakotosamimanana.[2]
Career
[edit]Rakotosamimanana's work in the Department of Geology, from the first included supervising and teaching practical aspects of the subject.[2] After seven years, she and her colleague Professor Henri Rakotoarivelo, set up the university's first palaeontology service in 1974.[2]
In 1977 she was awarded a doctorate from University of Paris VII, entitled "La diversité anthropologique des isolats des hautes terres de l'Imerina (Madagascar). Confrontation du biologique et du social".[3] This research examined diversity of people and species and their interactions in the Imerina Highlands.[1]
In 1993, the palaeontology service became a full Department, mostly due to her initiatives, and was head of it from 1995-8.[1] She created also created three new departments: Physical Anthropology, Nutritional Anthropology, Primatology and Evolutionary Biology.[2] She was active in the department until 2003 and supervised doctoral students until her death.[1]
Throughout her career Rakotosamimanana was a member of several professional bodies, including the "Groupe d'Etude et de Recherche sur les Primate de Madagascar" (GERP).[2] Other organisations she was involved with include: Malagasy Academy, "Ranomafana National Park" project, IUCN / SSC Primate Survival Commission, the editorial Board of "International Journal of Primatology" and "Lemur News", Society of Human Biometrics, Society of Anthropology of Paris and the International Association of Anthropologists.[1]
After the financial crisis in Madagascar in the 1980s, Rakotosamimanana was one of the architects to negotiate for foreign conservation NGOs to instigate programmes, which were to be truly beneficial to the development of the country.[4] As Secretary-General of the 17th Congress of the International Primatological Society, Rakotosamimanana persuaded the government to provide significant funding for the university as preparation for the 1998 conference, which was hosted in Antananarivo.[4] From 1977-83 she was Director of Scientific Research at the Malagasy Ministry for Education and Scientific Research.[2] From 1986-92 she was a technical adviser to the same ministry.[2] She was an active agent in the creation of Madagascar's National Environmental Action Plan.[5]
Legacy
[edit]
Rakotosamimanana's research focused on Madagascar's fossil and subfossil mammalian fauna.[6]
Species named after Rakotosamimanana
[edit]Microcebus berthae
[edit]During Rakotosamimanana's lifetime, a newly described type of mouse lemur was named after her: Madame Berthe's mouse lemur. The authors of the first description paid tribute to their long-term coordination of research with the German Primate Centre in the Kirindy-Mitea National Park, the habitat of the new lemur.[7]
Microcebus berthae is the world's smallest true primate and was discovered in 1992 in the forests of Menabe.[8]
Coua berthae
[edit]In 1993, researchers named an extinct species of silk cuckoo, Coua berthae or Madame Berthe's Coua,[9] after Rakotosamimanana.[10]
First descriptions
[edit]Rakotosamimanana was part of the teams which first described:
- † Babakotia, a lemur genus that died out less than 1000 years ago.[11]
- † Ambondro mahabo, an early mammal from the Malagasy Middle Jurassic.[12]
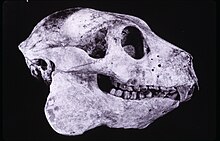
Babakotia radofilai skull 
Ambondro lingual teeth, from which both the monotypic genus and its single species A. mahabo were first described.
Palaeontology
[edit]Rakotosamimanana collaborated internationally on both palaeontological and primatological research projects and was a widely respected authority on primates from Madagascar, including their historical distributions across the island.[13] She was part of a team which used DNA sequencing to demonstrate that all Madagascan lemurs descended from a common ancestor.[14]
Madagascar's triassic fossil record is sparse and Rakotosamimanana was part of a team which identified new areas of deposits and as a result, was able to identify some of the island's earliest dinosaurs.[15] These included two new species of non-mammalian eucynodonts.[16]
Primatology
[edit]Rakotosamimanana had a keen research interest in Milne-Edwards' Sportive Lemur and studied the pair-usage of sleeping sites by them,[17] and well as infanticide in their populations.[18] She was part of a broader team which researched connections between genetic distance and geographic distribution in dwarf lemurs.[19] Her work on Pachylemur insignis with colleagues demonstrated that it was closer to the genus Variecia than Lemur.[20] She also studied lemur dermatoglyphs.[21]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g "RAKOTOSAMIMANANA Berthe". Université d'Antananarivo (in French). 2015-06-20. Retrieved 2020-02-15.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Professeur Berthe RAKOTOSAMIMANANA" (PDF). Lemur News. 11.
- ^ "Diversité anthropobiologique des isolats des Hautes-Terres (Imerina, Madagascar) : confrontations du biologique et du social : études comparatives / Berthe Rakotosamimanana née Rasoamialinivo - Sudoc". www.sudoc.fr. Retrieved 2020-02-16.
- ^ a b "Notes on the History of Ecological Studies of Malagasy Lemurs" (PDF). Lemurs. Developments in Primatology: Progress and Prospect. Boston, MA: Springer. 2007.
- ^ Hannah, Lee; Rakotosamimanana, Berthe; Ganzhorn, Jorg; Mittermeier, Russell A.; Olivieri, Silvio; Iyer, Lata; Rajaobelina, Serge; Hough, John; Andriamialisoa, Fanja; Bowles, Ian; Tilkin, Georges (1998). "Participatory planning, scientific priorities, and landscape conservation in Madagascar". Environmental Conservation. 25 (1): 30–36. doi:10.1017/S0376892998000071. ISSN 1469-4387. S2CID 84188190.
- ^ Beolens, Bo. (2009). The eponym dictionary of mammals. Watkins, Michael, 1940-, Grayson, Michael. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 41. ISBN 978-0-8018-9533-3. OCLC 593239356.
- ^ Rasolooarison, Rodin M.; Goodman, Steven M.; Ganzhorn, Jörg U. (2000). "Taxonomic Revision of Mouse Lemurs (Microcebus) in the Western Portions of Madagascar". International Journal of Primatology. 21 (6): 963–1019. doi:10.1023/A:1005511129475. S2CID 24593160.
- ^ "Smallest primate". Guinness World Records. Retrieved 2020-02-16.
- ^ Brown, Leslie, 1917-1980. (1982). The birds of Africa. Urban, Emil K., Newman, Kenneth, 1924-2006. London: Academic Press. p. 45. ISBN 0-12-137301-0. OCLC 8982298.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Steven M. Goodman and Florent Ravoavy: Identification of bird subfossils from cave surface deposits at Anjohibe, Madagascar, with a description of a new giant Coua (Cuculidae: Couinae) . In: Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington 1993, Volume 106, No. 1, pp. 24-33, digitized
- ^ Simons, Elwyn L.; Godfrey, Laurie R.; Jungers, William L.; Chatrath, Prithijit S.; Rakotosamimanana, Berthe (1992). "A New Giant Subfossil Lemur, Babakotia, and the Evolution of the Sloth Lemurs". Folia Primatologica. 58 (4): 197–203. doi:10.1159/000156629. ISSN 1421-9980.
- ^ Flynn, John J.; Parrish, J. Michael; Rakotosamimanana, Berthe; Simpson, William F.; Wyss, André R. (1999). "A Middle Jurassic mammal from Madagascar". Nature. 401 (6748): 57–60. Bibcode:1999Natur.401...57F. doi:10.1038/43420. ISSN 1476-4687. S2CID 40903258.
- ^ Godfrey, Laurie R.; Jungers, William L.; Simons, Elwyn L.; Chatrath, Prithijit S.; Rakotosamimanana, Berthe (1999), Rakotosamimanana, Berthe; Rasamimanana, Hanta; Ganzhorn, Jörg U.; Goodman, Steven M. (eds.), "Past and Present Distributions of Lemurs in Madagascar", New Directions in Lemur Studies, Springer US, pp. 19–53, doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-4705-1_2, ISBN 978-1-4615-4705-1
- ^ Karanth, K. Praveen; Delefosse, Thomas; Rakotosamimanana, Berthe; Parsons, Thomas J.; Yoder, Anne D. (2005-04-05). "Ancient DNA from giant extinct lemurs confirms single origin of Malagasy primates". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 102 (14): 5090–5095. Bibcode:2005PNAS..102.5090K. doi:10.1073/pnas.0408354102. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 555979. PMID 15784742.
- ^ Flynn, J. J. (1999-10-22). "A Triassic Fauna from Madagascar, Including Early Dinosaurs". Science. 286 (5440): 763–765. doi:10.1126/science.286.5440.763. PMID 10531059.
- ^ Flynn, John J.; Parrish, J. Michael; Rakotosamimanana, Berthe; Ranivoharimanana, Lovasoa; Simpson, William F.; Wyss, André R. (2000-09-25). "New Traversodontids (Synapsida: Eucynodontia) from the Triassic of Madagascar". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 20 (3): 422–427. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2000)020[0422:NTSEFT]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0272-4634. S2CID 130041740.
- ^ Rasoloharijaona, Solofonirina; Rakotosamimanana, Berthe; Randrianambinina, Blanchard; Zimmermann, Elke (2003). "Pair-specific usage of sleeping sites and their implications for social organization in a nocturnal Malagasy primate, the Milne Edwards' sportive lemur (Lepilemur edwardsi)". American Journal of Physical Anthropology. 122 (3): 251–258. doi:10.1002/ajpa.10281. ISSN 1096-8644. PMID 14533183.
- ^ Rasoloharijaona, Solofonirina; Rakotosamimanana, Berthe; Zimmermann, Elke (2000-02-01). "Infanticide by a Male Milne-Edwards' Sportive Lemur (Lepilemur edwardsi) in Ampijoroa, NW-Madagascar". International Journal of Primatology. 21 (1): 41–45. doi:10.1023/A:1005419528718. ISSN 1573-8604. S2CID 37545719.
- ^ Hapke, Andreas; Fietz, Joanna; Nash, Stephen D.; Rakotondravony, Daniel; Rakotosamimanana, Berthe; Ramanamanjato, Jean-Baptiste; Randria, Gisèle F. N.; Zischler, Hans (2005-08-01). "Biogeography of Dwarf Lemurs: Genetic Evidence for Unexpected Patterns in Southeastern Madagascar". International Journal of Primatology. 26 (4): 873–901. doi:10.1007/s10764-005-5327-0. ISSN 1573-8604. S2CID 38974228.
- ^ Crovella, S.; Montagnon, D.; Rakotosamimanana, B.; Rumpler, Y. (1994-10-01). "Molecular biology and systematics of an extinct Lemur:Pachylemur insignis". Primates. 35 (4): 519–522. doi:10.1007/BF02381961. ISSN 1610-7365. S2CID 31774375.
- ^ RAKOTOSAMIMANANA, B. (1970). "Etude des dermatoglyphes et des coussinets palmaires et plantaires de quelques Lemuriens Malgaches". Bull. Ass. Anat. 148: 413–510.
External links
[edit] Data related to Berthe Rakotosamimanana at Wikispecies
Data related to Berthe Rakotosamimanana at Wikispecies- Film of Madame Berthe's Mouse Lemur


