Astraeus hygrometricus
| Astraeus hygrometricus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Basidiomycota |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes |
| Order: | Boletales |
| Family: | Diplocystaceae |
| Genus: | Astraeus |
| Species: | A. hygrometricus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Astraeus hygrometricus | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Lycoperdon stellatus Scop. (1772) | |
| Astraeus hygrometricus | |
|---|---|
| Glebal hymenium | |
| No distinct cap | |
| Hymenium attachment is not applicable | |
| Lacks a stipe | |
| Spore print is brown | |
| Ecology is mycorrhizal | |
| Edibility is inedible | |
Astraeus hygrometricus, commonly known as the hygroscopic earthstar, the barometer earthstar, or the false earthstar, is a species of fungus in the family Diplocystaceae. Young specimens resemble a puffball when unopened. In maturity, the mushroom displays the characteristic earthstar shape that is a result of the outer layer of fruit body tissue splitting open in a star-like manner. The false earthstar is an ectomycorrhizal species that grows in association with various trees, especially in sandy soils. A. hygrometricus was previously thought to have a cosmopolitan distribution, though it is now thought to be restricted to Southern Europe, and Astraeus are common in temperate and tropical regions.[2] Its common names refer to the fact that it is hygroscopic (water-absorbing) and can open up its rays to expose the spore sac in response to increased humidity, then close them up again in drier conditions. The rays have an irregularly cracked surface, while the spore case is pale brown and smooth with an irregular slit or tear at the top. The gleba is white initially, but turns brown and powdery when the spores mature. The spores are reddish-brown and roughly spherical with minute warts, measuring 7.5–11 micrometers in diameter.
Despite a similar overall appearance, A. hygrometricus is not related to the true earthstars of genus Geastrum, although historically, they have been taxonomically confused. The species was first described by Christiaan Hendrik Persoon in 1801 as Geastrum hygrometricus. In 1885, Andrew P. Morgan proposed that differences in microscopic characteristics warranted the creation of a new genus Astraeus distinct from Geastrum; this opinion was not universally accepted by later authorities. Several Asian populations formerly thought to be A. hygrometricus were renamed in the 2000s once phylogenetic analyses revealed they were unique Astraeus species, including A. asiaticus and A. odoratus. Similarly, in 2013, North American populations were divided into A. pteridis, A. morganii, and A. smithii on the basis of molecular phylogenetics. This research suggests that the type specimen of Astraeus hygrometricus originates in a population restricted to Europe between Southern France and Turkey, with A. telleriae found nearby in Spain and Greece.[2] Research has revealed the presence of several bioactive chemical compounds in Astraeus fruit bodies. North American field guides typically rate A. hygrometricus as inedible; while this may be accurate for the now-separate North American species, A. hygrometricus is commonly consumed in South and Southeast Asia.
Taxonomy, naming, and phylogeny
[edit]Because this species resembles the earthstar fungi of Geastrum, it was placed in that genus by early authors, starting with Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1801[3] (as Geaster, an alternate spelling of Geastrum). According to the American botanist Andrew P. Morgan, however, the species differed from those of Geastrum in not having open chambers in the young gleba, having larger and branched capillitium threads, not having a true hymenium, and having larger spores. Accordingly, Morgan set Persoon's Geaster hygrometricum as the type species of his new genus Astraeus in 1889.[4] Despite Morgan's publication, some authorities in the following decades continued to classify the species in Geastrum.[5][6] The New-Zealand based mycologist Gordon Herriot Cunningham explicitly transferred the species back to the genus Geastrum in 1944, explaining:
The treatment of this species by certain taxonomists well illustrates the pitfalls that lie in wait for those who worship at the shrine of ontogenic classification ... The only feature of those outlined in which the species differs from others of Geastrum is the somewhat primitive hymenium. In the developing plant the glebal cavities are separated by tramal plates so tenuous as to be overlooked by the uncritical worker. Each cavity is filled with basidia somewhat irregularly arranged in clusters (like those of Scleroderma) and not in the definite palisade of the species which have been studied. This difference disappears as maturity is reached, when plants resemble closely the fructification of any other member of the genus. The taxonomist is then unable to indicate any point of difference by which "Astraeus" may be separated from Geastrum, which indicates that the name should be discarded.[7]
Cunningham's treatment was not followed by later authorities, who largely considered Astraeus a distinct genus. According to the taxonomical authority MycoBank,[1] synonyms of Astraeus hygrometricus include Lycoperdon stellatus Scop. (1772);[8] Geastrum fibrillosum Schwein. (1822);[9] Geastrum stellatum (Scop.) Wettst. (1885); and Astraeus stellatus E.Fisch. (1900).[10]
Astraeus hygrometricus has been given a number of colloquial names that allude to its hygroscopic behavior, including the "hygrometer earthstar", the "hygroscopic earthstar", the "barometer earthstar", and the "water-measure earthstar".[11][12] The resemblance to Geastrum species (also known as true earthstars) accounts for the common name "false earthstar".[13] The specific name is derived from the Greek words ὑγρός (hygros) 'wet' and μέτρον (metron) 'measure'.[14] The German Mycological Society selected the species as their "Mushroom of the Year" in 2005.[15]
Studies in the 2000s showed that several species from Asian collection sites labelled under the specific epithet hygrometricus were actually considerably variable in a number of macroscopic and microscopic characteristics.[16] Molecular studies of the DNA sequences of the ITS region of the ribosomal DNA from a number of Astraeus specimens from around the world have helped to clarify phylogenetic relationships within the genus. Based on these results, two Asian "hygrometricus" populations have been described as new species: A. asiaticus[16] and A. odoratus (synonymous with Petcharat's A. thailandicus described in 2003[17]). Preliminary DNA analyses suggests that the European A. hygrometricus described by Persoon is a different species than the North American version described by Morgan, and that the European population may be divided into two distinct phylotypes, from France (A. hygrometricus) and from the Mediterranean (A. telleriae).[18][19] A follow-up analysis from 2013 named two new North American species: A. morganii from the Southern US and Mexico and A. smithii from the Central and Northern United States, and grouped western US specimens in A. pteridis.[2] A 2010 study identified a Japanese species, previously identified as A. hygrometricus, as genetically distinct; it has yet to be officially named.[19]
A form of the species found in Korea and Japan, A. hygrometricus var. koreanus, was named by V.J. Stanĕk in 1958;[20] it was later (1976) published as a distinct species—A. koreanus—by Hanns Kreisel.[21] As pointed out by Fangfuk and colleagues, clarification of the proper name for this taxon must await analysis of A. hygrometricus var. koreanus specimens from the type locality in North Korea.[19]
Description
[edit]
Young specimens of A. hygrometricus have roughly spherical fruit bodies that typically start their development partially embedded in the substrate. A smooth whitish mycelial layer covers the fruit body, and may be partially encrusted with debris. As the fruit body matures, the mycelial layer tears away, and the outer tissue layer, the exoperidium, breaks open in a star-shaped (stellate) pattern to form 4–20 irregular "rays". This simultaneously pushes the fruit body above ground to reveal a round spore case enclosed in a thin papery endoperidium. The rays open and close in response to levels of moisture in the environment, opening up in high humidity, and closing when the air is dry.[22] This is possible because the exoperidium is made of several different layers of tissue; the innermost, fibrous layer is hygroscopic, and curls or uncurls the entire ray as it loses or gains moisture from its surroundings.[23] This adaptation enables the fruit body to disperse spores at times of optimum moisture, and reduce evaporation during dry periods.[24][25] Further, dry fruit bodies with the rays curled up may be readily blown about by the wind, allowing them to scatter spores from the pore as they roll.[22]
"This veritable barometer is the most theatrical of all the earthstars. A few minutes immersion in water will open up old, dried-up specimens that seem as tightly closed as clenched fists."
The fruit body is 1–8 cm (0.5–3 in) in diameter from tip to tip when expanded.[26] The exoperidium is thick, and the rays are typically areolate (divided into small areas by cracks and crevices) on the upper surface,[27] and are dark grey to black. The spore case is sessile (lacking a stalk), light gray to tan color and 1 to 3 cm (0.4 to 1.2 in) broad with a felt-like or scurfy (coated with loose scaly crust) surface; the top of the spore case is opened by an irregular slit, tear or pore.[28] The gleba is white and solid when young, and divided into oval locules—a characteristic that helps to distinguish it from Geastrum.[29] The gleba becomes brown and powdery as the specimen matures.[30] Small dark hairlike threads (rhizomorphs) extend from the base of the fruit body into the substrate. The rhizomorphs are fragile, and often break off after maturity.[5]
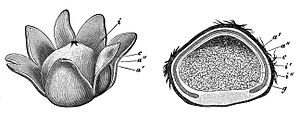
The spores are spherical or nearly so, reddish-brown, thick-walled and verrucose (covered with warts and spines). The spores' dimensions are 7–11 μm;[31] the warts are about 1 μm long.[32] The spores are non-amyloid, and will not stain with iodine from Melzer's reagent.[11] The use of scanning electron microscopy has shown that the spines are 0.90–1.45 μm long, rounded at the tip, narrow, tapered, and sometime joined at the top.[16] The capillitia (masses of thread-like sterile fibers dispersed among the spores) are branched, 3.5–6.5 μm in diameter, and hyaline (translucent).[5] The basidia (spore-bearing cells) are four- to eight-spored,[5] with very short sterigmata.[33] The basidia are arranged in long strings of clusters; individual basidia measure 11–15 by 18–24 μm. The threads of the capillitia arise from the inner surface of the peridium, and are thick-walled, long, interwoven, and branched, measuring 3–5.5 μm thick.[5] The exoperidium (the outer layer of tissue, comprising the rays) is made of four distinct layers of tissue: the mycelial layer contains branched hyphae that are 4–6 μm in diameter; the hyphae of the fibrous layer are 6–8 μm diameter and branched; the collenchyma-type layer has branched hyphae of 3–4 μm diameter; the soft layer contains hyphae that are 3–6 μm in diameter.[34]
Edibility
[edit]
North American sources list A. hygrometricus as inedible,[29] in some cases because of its toughness.[28][35][36] However, they are regularly consumed in Nepal[37] and South Bengal, where "local people consume them as delicious food".[38] They are collected from the wild and sold in the markets of India.[39][40] A. hygrometricus is also eaten in Japan, being especially popular in the Tōhoku region as a seasonal summer delicacy. The skin is washed and cooked with rice or deep fried.[41]
A study of a closely related southeast Asian Astraeus species concluded that the fungus contained an abundance of volatile eight-carbon compounds (including 1-octanol, 1-octen-3-ol, and 1-octen-3-one) that imparted a "mushroom-like, earthy, and pungent odor that was evident as an oily and moss-like smell upon opening the caps". The study's authors further noted that the fruit bodies after cooking have a "roasted, maillard, herbal, and oily flavor". Volatile compounds detected after cooking the mushroom samples included furfural, benzaldehyde, cyclohexenone, and furanyl compounds.[42] The regional differences in opinions on edibility are from sources published before it was known that North American and Asian versions of A. hygrometricus were not always the same; in some cases Asian specimens have been identified as new species, such as A. asiaticus and A. odoratus.[16][18]
Similar species
[edit]
Although A. hygrometricus bears a superficial resemblance to members of the "true earthstars" Geastrum, it may be readily differentiated from most by the hygroscopic nature of its rays. Hygroscopic earthstars include G. arenarium, G. corollinum, G. floriforme, G. recolligens, and G. kotlabae.[26] Unlike Geastrum, the young fruit bodies of A. hygrometricus do not have a columella (sterile tissue in the gleba, at the base of the spore sac).[43] Geastrum tends to have its spore sac opening surrounded by a peristome or a disc, in contrast with the single lacerate slit of A. hygrometricus. There are also several microscopic differences: in A. hygrometricus, the basidia are not arranged in parallel columns, the spores are larger, and the threads of the capillitia are branched and continuous with the hyphae of the peridium.[5][27] Despite these differences, older specimens can be difficult to distinguish from Geastrum in the field.[12] One species of Geastrum, G. mammosum, does have thick and brittle rays that are moderately hygroscopic, and could be confused with A. hygrometricus; however, its spores are smaller than A. hygrometricus, typically about 4 μm in diameter.[31]
Astraeus pteridis is larger, 5 to 15 cm (2 to 6 in) or more when expanded, and often has a more pronounced areolate pattern on the inner surface of the rays.[26] It is found in North America and the Canary Islands.[18] A. asiaticus and A. odoratus are two similar species known from throughout Asia and Southeast Asia, respectively.[18] A. odoratus is distinguished from A. hygrometricus by a smooth outer mycelial layer with few adhering soil particles, 3–9 broad rays, and a fresh odor similar to moist soil. The spore ornamentation of A. odoratus is also distinct from A. hygrometricus, with longer and narrower spines that often joined.[16] A. asiaticus has an outer peridial surface covered with small granules, and a gleba that is purplish-chestnut in color, compared to the smooth peridial surface and brownish gleba of A. hygrometricus. The upper limit of the spore size of A. asiaticus is larger than that of its more common relative, ranging from 8.75 to 15.2 μm.[18] A. koreanus (sometimes named as the variety A. hygrometricus var. koreanus; see Taxonomy) differs from the more common form in its smaller size, paler fruit body, and greater number of rays; microscopically, it has smaller spores (between 6.8 and 9 μm in diameter), and the spines on the spores differ in length and morphology.[16] It is known from Korea and Japan.[19]
Habitat, distribution, and ecology
[edit]Astraeus hygrometricus is an ectomycorrhizal fungus and grows in association with a broad range of tree species.[44] The mutualistic association between tree roots and the mycelium of the fungus helps the trees extract nutrients (particularly phosphorus) from the earth; in exchange, the fungus receives carbohydrates from photosynthesis.[38] In North America, associations with oak and pine are usual,[11] while in India, it has been noted to grow commonly with chir pine (Pinus roxburghii) and sal (Shorea robusta).[38] The false earthstar is found on the ground in open fields, often scattered or in groups, especially in nutrient-poor, sandy or loamy soils.[27][32][33] It has also been reported to grow on rocks, preferring acid substrates like slate and granite, while avoiding substrates rich in lime.[45] In Nepal, fruit bodies have been collected at elevations of 3,000 m (9,800 ft).[46] Fruit bodies typically appear in autumn, although the dry fruit bodies are persistent and may last up to several years.[31] Gelatinipulvinella astraeicola is a leotiaceous fungus with minute, gelatinous, pulvinate (cushion-shaped) apothecia, known to grow only on the inner surface of the rays of dead Astraeus species, including A. hygrometricus.[47]
The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution except for arctic, alpine and cold temperate regions;[33] it is common in temperate and tropical regions of the world.[18] It has been collected in Africa, Asia, Australia, Europe, North America,[17] and South America.[48]
Bioactive compounds
[edit]
Mushroom polysaccharides from a number of species have attracted research interest for their immunomodulatory and antitumor properties.[49] Extracts from A. hygrometricus containing the polysaccharide named AE2 were found to inhibit the growth of several tumor cell lines in laboratory tests,[50][51] and stimulated the growth of splenocytes, thymocytes, and bone marrow cells from mice. The extract also stimulated mouse cells associated with the immune system; specifically, it enhanced the activity of mouse natural killer cells, stimulated macrophages to produce nitric oxide, and enhanced production of cytokines.[39][52][53][54] The activation of macrophages by AE2 might be mediated by a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway of signal transduction.[55][56] AE2 is made of the simple sugars mannose, glucose, and fucose in a 1:2:1 ratio.[38]
In addition to the previously known steroid compounds ergosta-7,22-diene-3-ol acetate and ergosta-4,6,8-(14),22-tetraene-3-one, three unique triterpenes—derivatives of 3-hydroxy-lanostane—have been isolated from fruit bodies of A. hygrometricus. The compounds, named astrahygrol, 3-epi-astrahygrol, and astrahygrone (3-oxo-25S-lanost-8-eno-26,22-lactone), have δ-lactone (a six-membered ring) in the side chain—a chemical feature previously unknown in the basidiomycetes.[57][58] A previously unknown steryl ester (3β, 5α-dihydroxy-(22E, 24R)-ergosta-7,22-dien-6α-yl palmitate) has been isolated from mycelia grown in liquid culture. The compound has a polyhydroxylated ergostane-type nucleus.[59]
Ethanol extracts of the fruit body are high in antioxidant activity, and have been shown in laboratory tests to have anti-inflammatory activity comparable to the drug diclofenac.[60] Studies with mouse models have also demonstrated hepatoprotective (liver-protecting) ability, possibly by restoring diminished levels of the antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase and catalase caused by experimental exposure to the liver-damaging chemical carbon tetrachloride.[61]
Traditional beliefs
[edit]This earthstar has been used in traditional Chinese medicine as a hemostatic agent; the spore dust is applied externally to stop wound bleeding and reduce chilblains.[62] Two Indian forest tribes, the Baiga and the Bharia of Madhya Pradesh, have been reported to use the fruit bodies medicinally. The spore mass is blended with mustard seed oil and used as a salve against burns.[63] The Blackfoot of North America called the fungus "fallen stars", considering them to be stars fallen to the earth during supernatural events.[64]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b "Astraeus hygrometricus (Pers.) Morgan 1889". MycoBank. International Mycological Association. Retrieved 2011-08-24.
- ^ a b c Phosri C, Martín MP, Watling R (December 2013). "Astraeus: hidden dimensions". IMA Fungus. 4 (2): 347–56. doi:10.5598/imafungus.2013.04.02.13. PMC 3905946. PMID 24563840.
- ^ Persoon CH. (1801). Synopsis Methodica Fungorum (in Latin). Göttingen, Germany: Apud Henricum Dieterich. p. 135.
- ^ Morgan AP (1889). "North American fungi: the Gasteromycetes". Journal of the Cincinnati Society of Natural History. 12: 8–22.
- ^ a b c d e f Johnson MM, Coker WS, Couch JN (1974) [1928]. The Gasteromycetes of the Eastern United States and Canada. New York, New York: Dover Publications. pp. 185–8. ISBN 0-486-23033-3.
- ^ Lloyd CG (1902). The Geastrae. Bulletin of the Lloyd Library of Botany, Pharmacy and Materia Medica: Mycological Series, No. 2. Cincinnati, Ohio: J.U. & C.G. Lloyd. p. 8.
- ^ Cunningham GH (1944). The Gasteromycetes of Australia and New Zealand. Dunedin, New Zealand: John McIndoe. pp. 178–9. OCLC 551312340.
- ^ Scopoli JA (1772). Flora Carniolica (in Latin). Vol. 2 (2nd ed.). Vienna, Austria: impensis Ioannis Pauli Krauss, bibliopolae vindobonensis. p. 489.
- ^ von Schweinitz LD (1822). "Synopsis fungorum Carolinae superioris". Schriften der Naturforschenden Gesellschaft in Leipzig (in Latin). 1: 59.
- ^ Engler A, Prantl K (1900). Die natürlichen Pflanzenfamilien nebst ihren Gattungen und wichtigeren Arten insbesondere den Nutzpflanzen: I. Tl., 1. Abt.: Fungi (Eumycetes) (in German). Vol. Teil 1, Abt.1**. Leipzig, Germany: W. Engelmann. p. 341.
- ^ a b c Roody WC. (2003). Mushrooms of West Virginia and the Central Appalachians. Lexington, Kentucky: University Press of Kentucky. p. 438. ISBN 0-8131-9039-8.
- ^ a b McKnight VB, McKnight KH (1987). A Field Guide to Mushrooms, North America. Boston, Massachusetts: Houghton Mifflin. p. 358. ISBN 0-395-91090-0.
- ^ Alexopoulos CJ, Mims CW, Blackwell M (1996). Introductory Mycology. New York, New York: John Wiley and Sons. p. 551. ISBN 0-471-52229-5.
- ^ Rea C (1922). British Basidiomycetae: A Handbook to the Larger British Fungi. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. p. 51.
- ^ "2005: Astraeus hygrometricus (Pers.) Morgan, Wetterstern" (in German). Deutsche Gesellschaft Für Mycologie (German Mycological Society). Retrieved 2011-08-25.
- ^ a b c d e f Phosri C, Watling R, Martín MP, Whalley AJ (2004). "The genus Astraeus in Thailand". Mycotaxon. 89 (2): 453–63.
- ^ a b Petcharat V (2003). "Edible Astraeus (Basidiomycota) from Thailand". Nordic Journal of Botany. 23 (4): 499–503. doi:10.1111/j.1756-1051.2003.tb00423.x.
- ^ a b c d e f Phosri C, Martín MP, Sihanonth P, Whalley AJ, Watling R (2007). "Molecular study of the genus Astraeus". Mycological Research. 111 (3): 275–86. doi:10.1016/j.mycres.2007.01.004. PMID 17360168.
- ^ a b c d Fangfuk W, Petchang R, To-Aanun T, Fukuda M, Yamada A (2010). "Identification of Japanese Astraeus, based on morphological and phylogenetic analyses". Mycoscience. 51 (4): 291–9. doi:10.1007/s10267-010-0039-6. S2CID 85088635.
- ^ Stanĕk VJ (1958). "Rod Astraeus Morg.–Hvĕzdák". In Pilát A (ed.). Flora ČSR B-1: Gasteromycetes, Houby-Břichatky (Gasteromycetes-Puffballs) (in Czech). Prague: Nakladatelstvi Československé Akademie Ved. pp. 632, 819.
- ^ Kreisel H (1976). "Gasteromyzeten aus Nepal II". Feddes Repertorium (in German). 87 (1–2): 83–107. doi:10.1002/fedr.19760870106.
- ^ a b Schaechter E. (1998). In the Company of Mushrooms: A Biologist's Tale. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. pp. 51–2. ISBN 0-674-44555-4.
- ^ Gäumann EA, Dodge CW (1928). Comparative Morphology of Fungi. New York, New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company. p. 475.
- ^ Foy N, Phillips R, Kibby G (1991). Mushrooms of North America. Boston, Massachusetts: Little, Brown. p. 163. ISBN 0-316-70613-2.
- ^ Volk T. (2003). "Astraeus hygrometricus, an earth star. Tom Volk's Fungus of the Month for December 2003". University of Wisconsin-La Crosse, Department of Biology. Retrieved 2011-08-24.
- ^ a b c d Arora D (1986). Mushrooms Demystified: a Comprehensive Guide to the Fleshy Fungi. Berkeley, California: Ten Speed Press. p. 706. ISBN 0-89815-169-4.
- ^ a b c Orr DB, Orr RT (1979). Mushrooms of Western North America. Berkeley, California: University of California Press. p. 123. ISBN 0-520-03656-5.
- ^ a b Foy N, Phillips R, Kibby G (1991). Mushrooms of North America. Boston, Massachusetts: Little, Brown. ISBN 0-316-70613-2.
- ^ a b Miller HR, Miller OK (2006). North American Mushrooms: A Field Guide to Edible and Inedible Fungi. Guilford, Connecticut: FalconGuides. p. 463. ISBN 978-0-7627-3109-1.
- ^ Jordan M. (2004). The Encyclopedia of Fungi of Britain and Europe. London, UK: Frances Lincoln. p. 365. ISBN 0-7112-2378-5.
- ^ a b c Healy RA, Huffman DR, Tiffany LH, Knaphaus G (2008). Mushrooms and Other Fungi of the Midcontinental United States. Bur Oak Guide. Iowa City, Iowa: University of Iowa Press. p. 235. ISBN 978-1-58729-627-7.
- ^ a b Ellis JB, Ellis MB (1990). Fungi without Gills (Hymenomycetes and Gasteromycetes): an Identification Handbook. London, UK: Chapman and Hall. p. 220. ISBN 0-412-36970-2.
- ^ a b c Laessøe T, Pegler DN, Spooner B (1995). British Puffballs, Earthstars and Stinkhorns: an Account of the British Gasteroid Fungi. Kew, UK: Royal Botanic Gardens. pp. 40–1. ISBN 0-947643-81-8.
- ^ Baseia IG, de Galvão TC (2002). "Some interesting Gasteromycetes (Basidiomycota) in dry areas from northeastern Brazil". Acta Botanica Brasilica. 16 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1590/S0102-33062002000100002.
- ^ Wood M, Stevens F. "Astraeus hygrometricus". MykoWeb. California Fungi. Retrieved 2011-08-29.
- ^ Smith AH. (1975). A Field Guide to Western Mushrooms. Ann Arbor, Michigan: University of Michigan Press. p. 256. ISBN 0-472-85599-9.
- ^ Christensen M, Bhattarai S, Devkota S, Larsen HO (2008). "Collection and use of wild edible fungi in Nepal". Economic Botany. 62 (1): 12–23. doi:10.1007/s12231-007-9000-9. S2CID 6985365.
- ^ a b c d Maiti D, Chandra K, Mondal S, Ojha AK, Das D, Roy SK, Ghosh K, Chakraborty I, Islam SS (2008). "Isolation and characterization of a heteroglycan from the fruits of Astraeus hygrometricus". Carbohydrate Research. 343 (4): 817–24. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2007.12.003. PMID 18206864.
- ^ a b Maiti S, Bhutia SK, Mallick SK, Kumar A, Khadgi N, Maiti TK (2008). "Antiproliferative and immunostimulatory protein fraction from edible mushrooms". Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology. 26 (2): 187–91. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2008.03.009. PMID 21783909.
- ^ Harsh NS, Tiwari CK, Rai BK (1996). "Forest fungi in the aid of tribal women of Madhya Pradesh". Sustainable Forestry. 1 (1): 10–5.
- ^ Ushijima, Shuji (November 1, 2021). 牛島秀爾『道端から奥山まで採って食べて楽しむ菌活 きのこ図鑑』 [Enjoy Fungal Activities with Mushrooms: Picking and Eating from Roadsides to Deep Mountains]. Japan: Tsuribitosha. p. 82. ISBN 978-4-86447-382-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date and year (link) - ^ Kakumyan P, Matsui K (2009). "Characterization of volatile compounds in Astraeus spp". Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. 73 (12): 2742–5. doi:10.1271/bbb.90282. PMID 19966456. S2CID 44724095.
- ^ Metzler V, Metzler S (1992). Texas Mushrooms: a Field Guide. Austin, Texas: University of Texas Press. p. 298. ISBN 0-292-75125-7.
- ^ Harley JB, Smith SP, Read DJ (1997). Mycorrhizal symbiosis. Boston, Massachusetts: Academic Press. p. 172. ISBN 0-12-652840-3.
- ^ Mishra SR. (2005). Morphology of Fungi. New Delhi, India: Discovery Publishing House. p. 167. ISBN 978-81-7141-980-7.
- ^ Balfour-Browne FL (1955). "Some Himalayan fungi". Bulletin of the British Museum (Natural History). 1 (7): 187–218 (see p. 201).
- ^ Hosoya T, Otani Y (1995). "Gelatinipulvinella astraeicola gen. et sp. nov., a fungicolous Discomycete and its anamorph". Mycologia. 87 (5): 689–96. doi:10.2307/3760813. JSTOR 3760813.
- ^ Nouhra ER, Dominguez De Toledo L (1998). "The first record of Astraeus hygrometricus from Argentina". Mycologist. 12 (3): 112–3. doi:10.1016/S0269-915X(98)80009-8.
- ^ Moradali MF, Mostafavi H, Ghods S, Hedjaroude GA (2007). "Immunomodulating and anticancer agents in the realm of macromycetes fungi (macrofungi)". International Immunopharmacology. 7 (6): 701–24. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2007.01.008. PMID 17466905.
- ^ Mallick SK, Maiti S, Bhutia SK, Maiti TK (2010). "Antitumor properties of a heteroglucan isolated from Astraeus hygrometricus on Dalton's lymphoma bearing mouse". Food and Chemical Toxicology. 48 (8–9): 2115–21. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2010.05.013. PMID 20472019.
- ^ Mallick SK, Maiti S, Bhutia SK, Maiti TK (2010). "Immunostimulatory properties of a polysaccharide isolated from Astraeus hygrometricus". Journal of Medicinal Food. 13 (3): 665–72. doi:10.1089/jmf.2009.1300. PMID 20521989.
- ^ Pramanik A, Sirajul Islam S (1997). "Structural studies of a polysaccharide isolated from an edible mushroom, Astraeus hygrometricus". Trends in Carbohydrate Chemistry. 3: 57–64.
- ^ Pramanik A, Sirajul Islam S (2000). "Structural studies of a polysaccharide isolated from an edible mushroom, Astraeus hygrometricus". Indian Journal of Chemistry, Section B. 39B (7): 525–9.
- ^ Chakraborty I, Mondal S, Pramanik M, Rout D, Islam SS (2004). "Structural investigation of a water-soluble glucan from an edible mushroom, Astraeus hygrometricus". Carbohydrate Research. 339 (13): 2249–54. doi:10.1016/j.carres.2004.07.013. PMID 15337453.
- ^ Mallick SK, Bhutia SK, Maiti TK (2009). "Macrophage stimulation by polysaccharides isolated from barometer earthstar mushroom, Astraeus hygrometricus (Pers.) Morgan (Gasteromycetideae)". International Journal of Medicinal Mushrooms. 11 (3): 237–48. doi:10.1615/IntJMedMushr.v11.i3.30.
- ^ Mallick SK, Maiti S, Bhutia SK, Maiti TK (2011). "Activation of RAW 264.7 cells by Astraeus hygrometricus-derived heteroglucan through MAP kinase pathway". Cell Biology International. 35 (6): 617–21. doi:10.1042/CBI20100199. PMID 21143204. S2CID 36705550.
- ^ Takaishi Y, Murakami Y, Ohashi T, Nakano K, Murakami K, Tomimatsu T (1987). "Three triterpenes from Astraeus hygrometricus". Phytochemistry. 26 (8): 2341–4. Bibcode:1987PChem..26.2341T. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(00)84715-9.
- ^ Hill RA, Makin HL, Kirk DN, Murphy GM (1991). Dictionary of Steroids: Chemical Data, Structures, and Bibliographies. London, UK: Chapman and Hall. p. 447. ISBN 0-412-27060-9.
- ^ Shao HJ, Fang LZ, Yang WQ, Wang F, Liu JK (2007). "A new steryl ester from the culture mycelia of the Basidiomycete Astraeus hygrometricus (Astraceae)". Acta Metallurgica Sinica. 29 (3): 371–4. ISSN 0412-1961.
- ^ Biswas G, Sarkar S, Acharya K (2010). "Free radical scavenging and anti-inflammatory activities of the extracts of Astraeus hygrometricus (Pers.) Morg". Latin American Journal of Pharmacy. 29 (4): 549–53.
- ^ Biswas G, Sarkar S, Acharya K (2011). "Hepatoprotective activity of the ethanolic extract of Astraeus hygrometricus (Pers.) Morg" (PDF). Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures. 6 (2): 637–41. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-31.
- ^ Hobbs CJ (1995). Medicinal Mushrooms: An Exploration of Tradition, Healing & Culture. Portland, Oregon: Culinary Arts Ltd. p. 109. ISBN 1-884360-01-7.
- ^ Rai BK, Ayachi SS, Rai A (1993). "A note on ethno-myco-medicines from Central India". Mycologist. 7 (4): 192–3. doi:10.1016/S0269-915X(09)80397-2.
- ^ Burk W (1983). "Puffball usages among North American Indians" (PDF). Journal of Ethnobiology. 3 (1): 55–62.
External links
[edit]
