Avontuur Railway
| Avontuur Railway | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
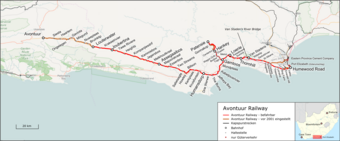 Avontuur railway map | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Avontuur Railway is a closed railway line between Gqeberha and the town of Avontuur in the Western and Eastern Cape provinces of South Africa. It is the longest 610 mm (2 ft) narrow gauge route in the world at a length of 285 kilometres (177 mi).[1] "Avontuur" is the Afrikaans and Dutch word for "adventure".
History
[edit]


The railway was built by the government of the Cape Colony between 1890 and 1906, to connect the Langkloof fruit growing industry with the new port at Port Elizabeth.[2] The section of line between Humewood Road and Humansdorp was opened for public traffic on 1 November 1905.[3]
In 1903 a request was laid before the then government in order to add a branch line to Patensie. This branch was commissioned on 3 April 1914.[4]
In 1906 a branch line was opened to the Port Elizabeth's suburb Walmer and in 1928 a twelve mile long private branch was constructed to the Eastern Province Cement Company (EPCC).[5]
Passenger traffic
[edit]Scheduled trains
[edit]Scheduled passenger trains were discontinued in the 1940s, although limited space was available on scheduled freight trains until the mid-1970s.[6]
Walmer Branch
[edit]From 1906 to 1928 a passenger only branch line, from Valley junction near Port Elizabeth, to the suburb of Walmer, serviced up to 22 trains a day between Port Elizabeth and the terminus at 14th Avenue in Walmer.[7] It was closed as a result from competition from a bus service.
Apple Express
[edit]The line was best known for its tourist train, the Apple Express, which commenced operations in 1965 to Loerie, later to Thornhill or Van Stadens River, the highest two-foot narrow-gauge railway bridge in the world. The motive power for the Apple Express was retained as steam, normally a SAR NGG16 Class Garratt. The Apple Express ceased operations in 2011.
Today, there is a new effort to restore a partial, limited, service in 2016 / 2017 from Port Elizabeth to Van Stadens Station – if not Thornhill - with two NG/G15 and one NG/G16 Garratt along with a fleet of passenger cars under restoration inside the former Humewood Road narrow Gauge diesel depot in Port Elizabeth.
From 2011 onward a volunteer team undertook the restoration of the NG15 NG119 steam locomotive, returning the locomotive to running order during 2017.[8] Restoration of the NG15 NG124 steam locomotive was started in 2016.
After running a test Apple Express train on 24 December 2017, using the restored NG15 NG119 locomotive, the Apple Express started running a summer holiday special service between King's Beach halt and a point near the Chief Dawid Stuurman International Airport.[9]
Freight traffic
[edit]Fruit and agriculture
[edit]The presence of the railway contributed significantly to the development of agriculture in the Lankloof and Gamtoos Valley, enabling farmers to transport their produce conveniently to the warehouses and harbour at Port Elizabeth.[10] Unfortunately, agricultural transport was lost due to competition from road haulage.[11]
Limestone
[edit]In the 1920s a limestone quarry was opened near Loerie to serve the Eastern Province Cement Company (EPCC) in New Brighton near Port Elizabeth via the EPCC owned private line branching off at Chelsea. The limestone traffic ceased in 2001 when the quarries were closed.[11]
Operations
[edit]The railway was operated by the South African national railway company Spoornet.
As the South African Government has deregulated the road transport industry, a large amount of traffic has moved from the railway to the roads. Spoornet has hence designated the line as "low density," and always had the threat of closure hanging over it.
After all major freight traffic ceased, only the Apple Express continued operations but finally ceased in 2010.
In 2014 a team of volunteers started working to recommence the running of the Apple Express.
After running a test Apple Express train on 24 December 2017, with locomotive NG15 NG119, the Apple Express began running a summer holiday special service between King's Beach halt and Valley Junction near the Chief Dawid Stuurman International Airport.
Since then, negotiations have been on going to recommence the Apple Express in the near future, but until such a time the Apple Express remains closed.
Motive power
[edit]Tender locomotives
[edit]The first locomotives entering service on the Langkloof line were the NG8 class from 1903 to 1931.
From 1915 to 1935 the NG6, from 1915 to 1939 the NG9 and from 1916 to 1948 the NG10.
The final and largest class to be employed on the Avontuur Railway were 21 NG15's from 1960 to the mid-1980s.
Tank locomotive
[edit]Class NG3 performed yard duties around Humewood Road Station in Port Elizabeth from 1939 to 1946
Garratt locomotives
[edit]The first Garratt locomotive to be introduced was the NGG11 class, soon to be followed with the NGG13 class in 1927, the latter setting the standard for motive power on the Avontuur railway for the next decades, to be followed with the NGG16 class, very similar to the NGG13.
The smaller Garratt classes NGG12 and NGG14 performed yard duties at Humewood Road railway station in Port Elizabeth until the 1950s.
Diesel locomotives
[edit]From 1973 the South African Class 91-000 General Electric diesels were introduced, the most powerful 2 foot gauge diesel in the world.
See also
[edit]- Alfred County Railway
- Sandstone Estates
- Welsh Highland Railway
- South African Class 91-000
- Langkloof
- Two-foot-gauge railways in South Africa
References
[edit]- ^ Lewis, Charles; Pivnic, Les. "Soul of A Railway". System 3: Cape Midland, based in Port Elizabeth.
- ^ Sellick, W.S.J. (1904). Uitenhage, past and present : souvenir of the Centenary, 1804–1904. p. 194.
- ^ "Report of the general manager of railways (1910)". 1906.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Mescht, J (July 2003). Proceedings of the 22nd Southern African Transport Conference (SATC2003). hdl:2263/6834. ISBN 0-9584609-6-5.
- ^ Payling, David; Paxton, Leith (January–February 2007). "Narrow Gauge World & Modeling" (49): 1.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "Avontuur Adventurer". geoffs-trains.com. Archived from the original on 21 December 2008. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- ^ Rollison, Richard (23 November 1973). "Saga of the Apple Express". Evening Post. Retrieved 26 December 2011. a-b.
- ^ "Full steam ahead for iconic train". HeraldLIVE.
- ^ "Delight as Apple Express hits the tracks once more". HeraldLIVE.
- ^ Green, Lawrence. "Chapter Seven - Bay of lost cargoes". Harbours of Memory.
- ^ a b "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 September 2011. Retrieved 6 November 2011.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
Further reading
[edit]- Hay, Richard (2023). The Avontuur Railway. South African Two Foot Railways No 1. Chippenham, Wilts, UK: Mainline & Maritime. ISBN 9781900340748.
External links
[edit] Media related to Avontuur Railway at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Avontuur Railway at Wikimedia Commons- Apple Express Official Site
- Map of Apple Express
- A 1976 Day trip to Loerie on the Avontuur Railway by Ted Polet, with photos, audio and video
- Apple Express History
- Soul of A Railway - System 3 Cape Midland, based in Port Elizabeth
- possible reopening of the line
