Antonio María Esquivel

Antonio María Esquivel y Suárez de Urbina (8 March 1806 – 9 April 1857) was a Spanish painter in the Romantic style who specialized in portraits.[1]
Biography
[edit]Esquivel was born in Seville. His father was a cavalry officer who was killed at the Battle of Bailén in 1808.[2] He began his studies at the Real Academia de Bellas Artes de Santa Isabel de Hungría in Seville. There, he became familiar with the pictorial techniques practiced by Murillo.
In 1831, already married and in need of work, he moved to Madrid and enrolled at the Real Academia de Bellas Artes de San Fernando, becoming a merit scholar. He was also involved in the intellectual life of Madrid and, in 1837, was an active participant in founding the local "Artistic and Literary Lyceum", where he gave classes in anatomy, a subject that he would later teach at the San Fernando Academy.[2]
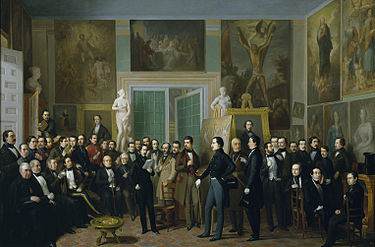
He returned to Seville in 1839, suffering from an illness that left him nearly blind. Deeply depressed, he tried to commit suicide by jumping into the Guadalquivir. Afterwards, his friends and colleagues at the Lyceum took up a collection[2] that would enable him to receive treatment from a famous ophthalmologist[who?] in France. Thanks to their support, by the end of 1840 he had recovered his vision.
His official recognitions include the "Commander's Cross" of the Order of Isabella the Catholic. In 1843, he was named Court painter and, in 1847, a Professor at the San Fernando Academy.[2] He was a founding member of the "Society for the Protection of the Fine Arts" and wrote a book on art theory: Tratado de Anatomía Pictórica. He died in Madrid, aged 51.
His sons, Carlos and Vicente, also became painters.
Gallery
[edit]-
Saint Mary Magdalene
-
Saints Justa and Rufina
-
The Saviour
References
[edit]Further reading
[edit]- Enrique Arias Anglés: Del Neoclasicismo al Impresionismo. Madrid: Ediciones Akal, 1999, ISBN 84-460-0854-8
External links
[edit]- ArtNet: More works by Esquivel
- Biography and appreciation @ Museo del Prado website
- Works on Antonio María Esquivel in the Biblioteca Digital Hispánica of the Biblioteca Nacional de España




