Alberta Clipper pipeline
| Alberta Clipper | |
|---|---|
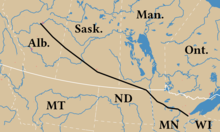 Map of Alberta Clipper | |
| Location | |
| Country | Canada United States |
| State | Wisconsin Minnesota |
| Province | Manitoba Saskatchewan Alberta |
| From | Hardisty, Alberta |
| Passes through | Metiskow, Alberta Kerrobert, Saskatchewan Milden, Saskatchewan Craik, Saskatchewan Regina, Saskatchewan White City Odessa, Saskatchewan Cromer, Manitoba Glenboro, Manitoba Gretna, Manitoba Viking, Minnesota Clearbrook, Minnesota Deer River, Minnesota |
| To | Superior, Wisconsin |
| General information | |
| Type | Crude oil |
| Owner | Enbridge Enbridge Energy Partners |
| Commissioned | 2010 |
| Technical information | |
| Length | 1,607 km (999 mi) |
| Maximum discharge | 0.88 million barrels per day (~4.4×107 t/a) |
| Diameter | 36 in (914 mm) |
| No. of pumping stations | 9 |
Alberta Clipper (also known as Enbridge's Line 67) is an oil pipeline in North America. It is owned and operated by Enbridge and is part of the extensive Enbridge Pipeline System. The pipeline runs from Hardisty, Alberta, in Canada, to Superior, Wisconsin, in the United States, integrating the company's Canadian oil sands pipeline system with the Lakehead system in the United States.[1]
Construction on the pipeline began in summer 2008.[1] Engineering for the Canadian portion was carried out by WorleyParsons. The majority of pipeline was built by the consortium of Michels Corporation, Precision Pipeline and US Pipeline, while Willbros Group built the portion between Sherwood Park and Hardisty, and the joint venture of Robert B Somerville and Techint Canada built three sections of the pipeline.
The pipeline was placed into service on April 1, 2010. The first shipment was moved in October 2010.[2]
The initial capacity of the 1,607-kilometre (999 mi) pipeline is 450,000 barrels per day (72,000 m3/d) which after expansion may be increased up to 800,000 barrels per day (130,000 m3/d).[3] It has pump stations at Hardisty, Alberta, Kerrobert, Milden, Cromer, Glenboro, Gretna, Viking, Minnesota, Clearbrook, and Deer River.[2] The diameter of the pipe is 36 inches (910 mm).[1] The pipeline cost US$3.3 billion.[2][4]
In 2013, Enbridge applied for the expansion project. At the first stage completion in 2014, the capacity increased up to 570,000 barrels per day (91,000 m3/d) and at the second stage completed in 2015, the capacity increased up to 880,000 barrels per day (140,000 m3/d).[5] According to Enbridge, Line 67 Upgrade Project Phase 2 was completed, and entered into service in July 2015.[6] As the United States presidential permit was still pending, oil was pumped before the Canada–US border into the Enbridge Line 3 pipeline and after the border crossing back to the Alberta Clipper.[7]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Anderson, Scott (2008-08-27). "Enbridge begins construction on Alberta Clipper". Reuters. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved 2014-03-15.
- ^ a b c "Alberta Clipper Pipeline Project, Canada". hydrocarbons-technology.com. Retrieved 2014-03-15.
- ^ Haggett, Scott (2008-02-22). "Canada regulator OKs C$3 bln Enbridge oil pipeline". Reuters. Archived from the original on December 13, 2019. Retrieved 2014-03-15.
- ^ Rascoe, Ayesha (2010-03-18). "U.S. mustn't discriminate against Canadian oil sands". Reuters. Archived from the original on March 5, 2016. Retrieved 2014-03-15.
- ^ Snyder, Jim; Penty, Rebecca (2013-05-02). "Enbridge Expansion Could Turn Into Keystone-Like Fight". Bloomberg. Retrieved 2014-03-15.
- ^ "Line 67 Upgrade Project (Phase 2)". Enbridge. Archived from the original on 2016-12-20. Retrieved 2016-12-05.
- ^ Mandel, Charles (2016-02-18). "Enbridge expansion of U.S. pipelines the new Keystone XL, report contends". National Observer. Retrieved 2016-12-05.
