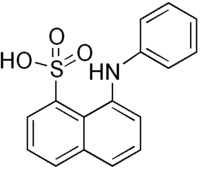
8-Anilinonaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
8-Anilinonaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid | |
| Other names
8-(Phenylamino)naphthalene-1-sulfonic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.308 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H13NO3S | |
| Molar mass | 299.34 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
8-Anilinonaphthalene-1-sulfonic acid (ANS), also called 1-anilino-8-naphthalenesulfonate, is an organic compound containing both a sulfonic acid and an amine group. This compound is used as a fluorescent molecular probe.[1] For example, ANS can be used to study conformational changes induced by ligand binding in proteins, as ANS's fluorescent properties will change as it binds to hydrophobic regions on the protein surface. Comparison of the fluorescence in the presence and absence of a particular ligand can thus give information about how the binding of the ligand changes the surface of the protein. Its permeability to mitochondrial membranes makes it particularly useful.[2]
References
[edit]- ^ Andras Malnasi-Csizmadia; György Hegyi; Ferenc Tölgyesi; Andrew G. Szent-Györgyi & László Nyitray (1999). "Fluorescence measurements detect changes in scallop myosin regulatory domain". European Journal of Biochemistry. 261 (2): 452–8. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00290.x. PMID 10215856.
- ^ Gains N; Dawson AP (April 1975). "8-Anilinonaphthalene-1-sulphonate interaction with whole and disrupted mitochondria: a re-evaluation of the use of double-reciprocal plots in the derivation of binding parameters for fluorescent probes binding to mitochondrial membranes". Biochem. J. 148 (1): 157–60. doi:10.1042/bj1480157. PMC 1165518. PMID 1156395.
