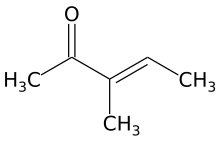
3-Methyl-3-penten-2-one
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Methylpent-3-en-2-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.440 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O | |
| Molar mass | 98.145 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear liquid |
| Density | 0.875 g/cm3 (at 20 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H226, H302, H312, H315, H319, H331, H332, H335 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P311, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 34 °C (93 °F) (closed cup) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
3-Methyl-3-penten-2-one is an unsaturated aliphatic ketone. It is an isomer of mesityl oxide and isomesityl oxide. It is a precursor of 3-methyl-2-pentanone (methyl sec-butyl ketone) and is obtained by acid-catalyzed dehydration of 4-hydroxy-3-methyl-2-pentanone. It is used as an intermediate in organic chemistry syntheses.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ Hardo Siegel, Manfred Eggersdorfer (2007), "Ketones", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry (7th ed.), Wiley, p. 5

