Parkfield earthquake

35°48′54″N 120°22′26″W / 35.815°N 120.374°W Parkfield earthquake is a name given to various large earthquakes that occurred in the vicinity of the town of Parkfield, California, United States. The San Andreas fault runs through this town, and six successive magnitude 6 earthquakes occurred on the fault at unusually regular intervals, between 12 and 32 years apart (with an average of every 22 years), between 1857 and 1966.[1] The latest major earthquake in the region struck on September 28, 2004.
Earthquakes may occur regularly here because the location is about midway on a fault segment between a locked segment to the south (last major earthquake 1857) and a creeping segment to the north where two tectonic plates are continuously moving without major earthquakes.
Research
[edit]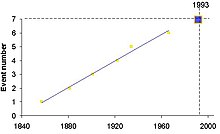
Geologists who hoped to study what happens before a quake, and in particular any signs that might enable them to predict future earthquakes, installed an elaborate array of seismometers, creepmeters, strainmeters, and other instruments in and around Parkfield starting in 1985. Scientists with the USGS and UC Berkeley had predicted, with a 90 to 95% confidence level, that an earthquake would strike the Parkfield area between 1985 and 1993.[2] This was known as the Parkfield Earthquake Prediction and the Parkfield Earthquake Experiment, conducted by the USGS. Attempts at predicting the quake continued until January 2001,[3] but an earthquake of 5.5 magnitude or greater did not occur from 1985 until the 2004 quake.
In June 2004, the USGS in partnership with the National Science Foundation began drilling a deep hole to house instruments to monitor the fault at depth. This action was a part of the San Andreas Fault Observatory at Depth (SAFOD) program.
Because of the regularity of large events (mb>5.5) at the Parkfield location (events in 1857, 1881, 1901, 1922, 1934, and 1966), and the fact that the waveforms from many of these events were almost identical, it was believed that the same segment of fault ruptured each time. This led to the prediction in 1984 of a similar event in 1993.[4]
2004 event
[edit]
The 6.0 magnitude primary shock in 2004 was the result of a fault movement of about 18 inches (.5 meter). There have been no indications found that could have been used to predict this earthquake. Although well overdue, the probability of this quake occurring in 2004 has been estimated at ten percent. The magnitude of the event was consistent with previous earthquakes in this region.
Substantial aftershocks continued for more than a week after the initial event, moving in a northwesterly progression. In early October, there was a cluster of small earthquakes near Paso Robles near a parallel fault to the west. These may be in response to the transfer of stress to these faults after the release of stress at Parkfield. Past earthquakes have also occurred to the east of Parkfield at about the same distance from the San Andreas fault near Coalinga and Avenal.
Recent developments
[edit]In December 2004, seismologists at the University of California, Berkeley announced the discovery of subtle tremors near Cholame, a hamlet near the San Andreas fault directly south of Coalinga. This is in a region of the locked fault below the Parkfield episodes, last creating an 8.0 magnitude quake at Fort Tejon in 1857. These tremors were discovered using deep borehole seismometers that avoid surface noise. The spectral signatures of these motions are more similar to those of magma movement near volcanoes than of typical earthquakes, but it is believed that the motions are not due to magma or fluid motion. It is hoped that this new discovery may sometime inform scientists as to the degree of danger presented by known locked faults. It is not currently expected that this knowledge will be refined into a precise predictive tool.
Fort Tejon earthquake
[edit]What is possibly the largest earthquake on the San Andreas fault in the last several hundred years is the 1857 Fort Tejon earthquake, with a fault rupture from the general vicinity of Parkfield to San Bernardino in Southern California, a distance of about 360 km (220 mi) and an offset of about 9 meters (30 feet).[5] The epicenter of this earthquake is (by various sources) believed to be somewhere in the region from Cholame to Parkfield, a location at the extreme northern end of the locked portion of the fault and at the southern end of the rapidly periodic segment. It is believed that this earthquake was preceded by a magnitude 6.0 foreshock that was centered at Parkfield.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Kanamori, Hiroo (2003). Earthquake Prediction: An Overview. International Association of Seismology and Physics of the Earth’s Interior. ISBN 978-0-12-440658-2.
- ^ "Research". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2020-04-03.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-02-22. Retrieved 2017-09-03.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Shearer, Peter M. (1999). Introduction to Seismology. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-66023-5.
- ^ Sieh, Kerry E. (1978a), "Slip along the San Andreas fault associated with the great 1857 earthquake" (PDF), Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 68 (5), Seismological Society of America : 1428
External links
[edit]- The Parkfield, California, Earthquake Experiment Archived 2008-07-06 at the Wayback Machine – United States Geological Survey
- San Andreas Fault Observatory at Depth – United States Geological Survey
- Interaction of the San Andreas fault creeping segment with adjacent great rupture zones and earthquake recurrence at Parkfield – Journal of Geophysical Research
- Essay and map concerning the Fort Tejon earthquake, showing epicenter near Cholame – Southern California Earthquake Data Center
