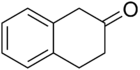
2-Tetralone
Appearance
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-2(1H)-one | |
| Other names
β-Tetralone; 2-Tetralone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.727 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H10O | |
| Molar mass | 146.189 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Density | 1.106 g/mL |
| Melting point | 18 °C (64 °F; 291 K) |
| Boiling point | 70–71 °C (158–160 °F; 343–344 K) /0.25 mm |
| in basic water | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
2-Tetralone is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C10H10O. This colourless oil is an intermediate in organic synthesis. It is a ketone derivative of tetralin, a hydrogenated derivative of naphthalene. A related compound is 1-tetralone.
2-Tetralone is prepared by reductive cleavage of 2-naphthyl ethers.[1]
Applications
[edit]2-Tetralone is an intermediate in the synthesis of a variety of pharmaceutical drugs including L-687,384, nepinalone, napamezole,[2] spirodone, and trioxifene.
References
[edit]- ^ M. D. Soffer, M. P. Bellis, Hilda E. Gellerson, and Roberta A. Stewart "β-Tetralone" Org. Synth. 1952, 32, 97 doi:10.15227/orgsyn.032.0097
- ^ Wentland, Mark P.; Bailey, Denis M.; Alexander, E. John; Castaldi, Michael J.; Ferrari, Richard A.; Haubrich, Dean R.; Luttinger, Daniel A.; Perrone, Mark H. (1987). "Synthesis and antidepressant properties of novel 2-substituted 4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole derivatives". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 30 (8): 1482–1489. doi:10.1021/jm00391a034. PMID 3039138.
