18th century glassmaking in the United States

18th century glassmaking in the United States began before the country existed. During the previous century, several attempts were made to produce glass, but none were long-lived. By 1700, it is thought that little or no glass was being produced in the British colonies that would eventually become the United States. The first American glass factory operated with long–term success was started by Caspar Wistar in 1745—although two glass works in New Amsterdam that operated in the previous century deserve honorable mention. Wistar's glass works was located in the English colony known as the Province of New Jersey. In the southeastern portion of the Province of Pennsylvania, Henry Stiegel was the first American producer of high–quality glassware known as crystal. Stiegel's first glass works began in 1763, and his better quality glassmaking began in 1769. In the United States, the first use of coal as a fuel for glassmaking furnaces is believed to have started in 1794 at a short-lived factory on the Schuylkill River near Philadelphia. In 1797 Pittsburgh's O'Hara and Craig glass works was also powered by coal, and it contributed to the eventual establishment of Pittsburgh as a leading glassmaking center in the 19th century.
Many of the skilled glass workers in the United States during the 17th and 18th centuries came from the German-speaking region of Europe. German–born Johann Friedrich Amelung (later renamed John Frederick Amelung) employed 342 people in 1788 at his New Bremen glass works located in Frederick County, Maryland. His skilled workers were German. Other prominent glass makers such as Wistar, Stiegel, and the Stanger brothers were also German. In many cases, as a glass works failed, the skilled workers found work at another factory.
Other attempts to produce glass were made during the 1600s and 1700s, and a few had some success. Glass works in New Amsterdam and New York City, the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, Philadelphia, and the province of New Jersey's Glassboro are often mentioned by historians. Much of the evidence concerning the 17th century New Amsterdam glass factories has been lost, and a 17th-century Massachusetts glassworks did not last long. The works at Glassboro lasted into the 20th century. However, it is thought that there were no more than a dozen glass works of significant size producing in the United States in 1800.
Glassmaking
[edit]
Glassmakers use the term "batch" for the sum of all the raw ingredients needed to make a particular glass product.[1] To make glass, the glassmaker starts with the batch, melts it together, forms the glass product, and gradually cools it. The batch is dominated by sand, which contains silica. Smaller quantities of other ingredients, such as soda and limestone, are added to the batch.[2] Additional ingredients may be added to color the glass. For example, an oxide of cobalt is used to make glass blue.[3] Broken and scrap glass, known as cullet, is often used as an ingredient to make new glass. The cullet melts faster than the other ingredients, which results in some savings in fuel cost for the furnace. Cullet typically accounts for 25 to 50 percent of the batch.[4]
The batch is placed inside a pot that is heated by a furnace to roughly 3,090 °F (1,700 °C).[2][Note 1] Tank furnaces, which were created in England in 1870, did not began to supplant pot furnaces in the United States until the 1890s.[6] Glassmakers use the term "metal" to describe batch that has been melted together.[7] The metal is typically shaped into the glass product (other than plate and window glass) by either glassblowing or pressing it into a mold.[8] Although pressing glass by hand had long existed, mechanical pressing of glass did not exist until the 1820s—and it was an American invention.[9] All glass products must then be cooled gradually (annealed), or else they could easily break.[10] Annealing was originally conducted in the United States using a kiln that was sealed with the fresh glass inside, heated, and gradually cooled.[11] During the 1860s annealing kilns were replaced in the United States with a conveyor oven, called a lehr, that was less labor-intensive.[12]
Until the 1760s, most glass produced in what would become the United States was "green" or "bottle" glass, which has a greenish color because of impurities in the sand used in the batch—and a lack of additives used to remove the greenish tint or add a more pleasing color.[13] Crystal glass, a high quality clear glass that needs an additive known as red lead, began being produced by one works in the Province of Pennsylvania in the 1760s.[14] Window glass production during the 18th century involved blowing a cylinder and flattening it.[15] The crown method and the cylinder method (the latter of which was more advanced) were the two main methods used.[16]
One of the major expenses for the glass factories is fuel for the furnace, and this often determined the location of the glass works.[17] Wood was the original fuel used by glassmakers in the United States. Coal began being used in the 1790s.[18] Alternative fuels such as natural gas and oil did not become available in the United States until the second half of the 19th century.[19] Other important aspects of glassmaking are labor and transportation.[20] Glassmaking methods and recipes were kept secret, and most European countries forbade immigration to the United States by glassworkers.[21] Master glassmakers, including glassblowers and glass cutters, that had the secret glassmaking knowledge were smuggled from Europe to the United States to provide glassmaking expertise at American factories.[21]
Background
[edit]
The first attempt to produce glass in what became the United States happened in 1608 in the English (later British) Colony of Virginia near the settlement at Jamestown.[22] Glass was produced for a few years. A second attempt was made during the 1620s, but production ceased again after only a few years.[23] Glassmaking was conducted for a short time in the Colony of Massachusetts Bay near Salem in the 1640s, and in the province of Pennsylvania near Philadelphia in the 1680s.[24] At least two works produced glass in the Dutch colony of New Amsterdam during portions of the 1650s through 1670s.[25] Very little is known about the New Amsterdam glass factories, but it is possible that at least one of them continued producing into the 1760s.[26] Waterways provided transportation networks for the glass factories before the construction of highways and railroads.[27] The first railroad in the United States was not chartered until 1827, and construction began in 1828.[28]
Unless the glass works in New Amsterdam (now New York) was still operating, no glass works are known to have operated in what became the United States from 1700 until close to the 1740s.[24] Most glass was imported from London or Bristol. The English glass industry produced window glass using the crown method, and it produced good quality lead glass (crystal) tableware. The glass industry in German areas of Northern Europe was in a recession, and that situation may have led to Germans coming to the English colonies to produce glass.[29] Prior to 1800, about two dozen glass works operated in the English colonies that became the United States, and some of them continued production into the 19th century.[30]
18th century
[edit]Wistar - first long term success
[edit]
In 1738 Caspar Wistar, a German immigrant and manufacturer of brass buttons in Philadelphia, began plans for a glass works by purchasing land in Salem County, New Jersey.[Note 2] Production started in 1739.[32] Wistar, who was originally from the Palatine region of what is now Germany, hired German glassworkers to make bottles, tableware, and window glass.[33] The cylinder method was used for making the window glass, and bottles were made of a clear green glass.[34] His original partners in the glassmaking project were four glassblowers from German portions of Europe.[35][Note 3]
Wistar's glassmaking company was known by multiple names, including United Glass Company, Wistar Glass Works, Wistarberg Glass Works, and Wistarburg Glass Works.[37] Although the glass works was approximately 40 miles (64 km) from Philadelphia, Wistar maintained a Philadelphia residence and sold much of his glass there.[38] Benjamin Franklin used Wistar's glass for some of his electrical experiments.[35] After Caspar Wistar died in 1752, his son Richard led the glass works. The business continued to grow for about two more years before it began to have problems keeping workers, which led to problems with glass quality.[37] The glassworks operated sporadically beginning in the 1775–1776 winter, and was offered for sale in 1780. Richard Wistar died in 1781. The glass works was eventually closed and abandoned.[37]
Wistar began the German domination of American glassmaking that continued until the 19th century.[39] Many of Wistar's skilled German workers moved to rival glass companies or started their own glass works, and they taught their methods and styles to others.[40] Historians often consider Wistar's glass works to be the first commercially successful manufacturer of glass in the United States, although at least one has said the 17th century Smedes or Duijcking–Milyer glass works in New Amsterdam merit consideration.[41]
Stiegel - first lead crystal
[edit]
German immigrant Heinrich Wilhelm Stiegel, nicknamed "Baron Stiegel", was born in Cologne in 1729. He arrived in Philadelphia in 1750, and moved to Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, a few years later.[42] He married in 1752, and bought out his father–in–law's interest in a plantation that became known as Elizabeth Furnace, which included a blast furnace used to make iron stoves.[43] He became a citizen of the English colony of Pennsylvania in 1760, and changed his name to Henry William Stiegel.[44]
Stiegel was the second German to operate an American glass works on a large scale.[39] He built some "glass–ovens" at Elizabeth Furnace in 1762, and began making glass in 1763.[45] Products were bottles and window glass.[46] He hired European glassblowers, including some from Venice, and paid for their transportation to Pennsylvania.[47] One of his first hires was a glassblower who had worked at the Wistar works.[40]
Nearly two years later he started another glass factory in Manheim, Pennsylvania. During 1769, he started a third glass works in the same town that focused on quality tableware, and employed more men that had worked at the Wistar glass plant.[48] He called this works the American Flint Glass Manufactory.[49] Stiegel's works was the first to make lead glass in America.[50] The lead glass of this time period, commonly known as crystal because it was colorless and transparent, was typically used for fine tableware.[51] According to the American Philosophical Society, Stiegel's lead glass was "equal in beauty and quality to the generality of Flint Glass, imported from England."[52] Stiegel had retail outlets for his glass at various locations in the English colonies. However, he expanded too fast and ended production in 1774. He was briefly held in a debtors' prison.[53]
Stanger and Glassboro - nearly 150 years
[edit]
The Stanger family immigrated to Philadelphia in 1768.[54][Note 4] They were German glassmakers who came from Hesse, and the family had seven sons. At least one of the sons worked at the Wistar Glass Works.[54] The brothers started a glass works between 1779 and 1781 in what became known as Glassboro, New Jersey.[56] The works is believed to have begun producing in the fall of 1781.[57] The brothers were led by Solomon (the original land holder) and Daniel Stanger, and their glass works was the second (after Wistar) located in "South Jersey".[57] Their original products were bottles.[58]
By 1784 all of the Stanger brothers had sold their interests in the Glassboro glass works, although they remained working with glass.[54] At that time, Thomas Heston and Thomas Carpenter controlled the Glassboro works.[59] In addition to bottles, the company began making window glass and other products.[59] Heston died in 1802, but the factory operated under various owners for over 100 years—including the Whitney brothers who were descendants of Heston.[60] At one time the factory was known as the Olive Glass Works.[61] The Whitney brothers became sole owners of the plant in 1839.[62] The Whitney Glass Works was purchased by one of Michael Owens' companies in 1918.[63]
Amelung's big investment
[edit]
Another German, Johann Friedrich Amelung (later renamed John Frederick Amelung), arrived in Baltimore on August 31, 1784.[64] He brought 68 German–speaking glass workers, and at least 14 more joined him a few months later. He purchased land in Frederick County, Maryland along Bennett's Creek to the north and east of Sugarloaf Mountain.[65] He called the area "New Bremen", and built a glassmaking furnace and housing for his workers.[66][Note 5] On February 11, 1785, he announced that a group of "German manufacturers have arrived and will establish a factory", and that "window glass, table glass, optical glass, looking glass" would be their products.[66]
In 1788 Amelung employed 342 people at his glass works.[70] Window glass was made using the cylinder method and the crown method.[71] Archaeological evidence suggests his bottles were made with a transparent green glass that did not require molds.[67] During 1788 he applied for a loan from the State of Maryland, and received the loan plus tax exemption for five years. Over the next two years his glassmaking facilities had at least two fires that did an undetermined amount of damage.[70] Amelung had financial difficulties, and the glass works was offered for sale in 1795.[72] Amelung had invested more money in glassmaking than anyone ever had (at the time), and his factory produced impressive quality glass—but his business failed after 11 years.[73] Amelung died in 1798.[74]
18th century works still operating in the 19th century
[edit]In 1800 most of the nation's glass products came from Europe, and the United States was thought to have about ten glass factories.[75][Note 6] The domestic glass works were typically located near waterways that provided a transportation resource. Although some high–quality tableware may have been produced in Philadelphia or Baltimore, most glass factories produced bottles or window glass.[77]
Philadelphia–New Jersey
[edit]
- Kensington Glass Works: In 1771 Robert Towars and James Leacock started the Kensington Glass Works in Philadelphia's Kensington neighborhood.[78] Although glass factories had already been established near Philadelphia in Bucks and Lancaster counties, this was the first 18th century glass works in Philadelphia County.[38] The works may have used coal to power its furnace, possibly making it among the first American works to do so.[50] During November 1772, John Elliott, Samuel Elliott, and Isaac Gray gained control of the factory and they called it the Philadelphia Glass Works. Products were window glass, white glass, and green glass.[79] Glass was made sporadically (including periods of idleness that lasted for years) under various owners throughout the next century.[78]
- Stanger Brothers: The Stanger Brothers glass works in Glassboro, New Jersey, is believed to have begun production in 1781. In 1783 Thomas Heston and Thomas Carpenter gained control of the plant.[59] The factory operated under various owners (including descendants of Heston) until it was purchased in 1918.[80]
Maryland
[edit]
- Aetna Glass–House: Thomas Johnson, first governor of Maryland, owned the Aetna Glass House—which was sometimes referred to as the Johnson Glass Works. The plant was located southeast of Frederick, Maryland, on Bush Creek, and production began in 1792. Products were bottles, and window glass was also made later.[81] This works was offered for sale in November 1793, and it was operated only intermittently until 1807.[82] All glassmaking in Frederick County ended by the 1820s.[83]
- A. Kohlenberg's New Glassworks: In 1797 Adam Kohlenberg and John Christian Gabler purchased a portion of Amelung's land on Bennet's Creek in Frederick County, Maryland. The land included one of the glass ovens used by Amelung's failed glass works, and Kohlenberg employed some of the glassworkers from Amelung's New Bremen works. Kohlenberg's works produced glass intermittently for about 15 years.[82]
- Federal Hill Glass Works: In 1799 Frederick Amelung, son of John Frederick Amelung, built a glass works in Baltimore. The company name was Frederick M. Amelung and Company, and the glass works was located in Baltimore's Federal Hill neighborhood. The works is often called Federal Hill Glass Works or the Baltimore Glass Works, but was also called the Patapsco River Glass House and the Hughes Street Works because of its location.[84] The factory began producing in 1800, and its products were bottles and glassware.[83] Amelung lost financial control of the company in the early 1800s, but he remained as plant superintendent until 1806.[85] The works was still producing in the late 1820s, and it became known for "pictorial flasks".[86]
Pittsburgh
[edit]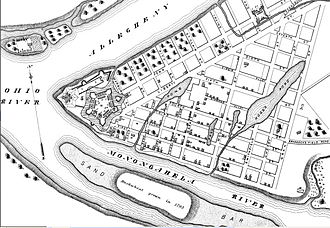
- Pittsburgh Glass Works (O'Hara and Craig): In 1796 Colonel James O'Hara and Major Isaac Craig began planning for the first glass works in Pittsburgh, which was also one of the first to use coal as a fuel for its furnaces.[87] Peter William Eichbaum, who had been involved with the Schuylkill glass works near Philadelphia that used coal for its furnaces, provided the glassmaking expertise and supervised the construction of the Pittsburgh works.[88] The plant was originally located at Coal Hill (now Mount Washington) on the south shore of the Monongahela River close to where it becomes the Ohio River.[89] Actual glass production started in June 1797, making it the first to produce glass in the United States west of the Allegheny Mountains.[90] The factory was called Pittsburgh Glass Works, and Eichbaum was its superintendent. In 1798, Eichbaum leased the factory, but control returned to O'Hara and Craig in 1800. Window glass, bottles, and other hollow ware were produced.[91] Craig left the business in 1804, and O'Hara was the only owner through 1818. The glassworks continued operations, under various owners and names, until 1883.[92]
- New Geneva Glass Works: In 1795 Albert Gallatin formed a partnership with James Nicholson (Gallatin's brother–in–law) and three others. They purchased land in western Pennsylvania's Fayette County for the purpose of commercial development, and they named their land New Geneva. Their location gave them access to the Monongahela River, which gave them access to the west using waterways. They also had access to the east coast using roads that connected to Philadelphia, Baltimore, and Washington, DC.[93] In September 1797 the partnership made an agreement with five German glassblowers to start a glass works.[94] Production began in 1798 shortly after production at the O'Hara and Craig works began in Pittsburgh.[95] The works was about 45 miles (72 km) south of O'Hara and Craig's Pittsburgh glass works.[96] Among his workers, mostly Germans, were former employees of the Amelung works.[97] Gallatin's glass company was originally called Gallatin & Company, but later it became the New Geneva Glass Works.[87] Gallatin sold his share of the company in 1803. The works was moved across the Monongahela River in 1807, making its new location at Greensboro in Greene County.[98] This site provided access to coal, and the works continued until 1847.[99]
- Ohio Glass Works: In May 1799 Hugh Scott bought land on the north side of the Ohio River close to the O'Hara and Craig glass works. He started the Ohio Glass Company, and it began producing window glass in 1800.[100] This works shut down by March 1801.[101]
New York–New England
[edit]
- Pitkin Glass Works: In 1783 William and Elisha Pitkin, and Samuel Bishop, established a glass works in East Hartford, Connecticut (which became part of Manchester in 1823).[102] This was the first works in Connecticut to actually be built and produce.[103] Products were bottles of various sizes and colors. J. P. Foster was one of the superintendents. Foster took over management in 1810, and the factory operated until 1830 when timber had become scarce.[104]
- Peterboro–Goff: David Goff and a group of Connecticut investors established a window glass house in Peterborough (now Peterboro), New York, around 1783.[98] The site was chosen because of the abundance of wood that was used as fuel for the furnaces. Good quality sand was within 20 miles of the factory.[105] The factory ceased operations in 1813.[106] Superior glass made by competitors, and the depletion of forests that provided wood for fuel contributed to the factory's demise.[105]
- Albany Glass Works: In 1785 Leonard de Neufville, with associates Jan Heefke and Ferdinand Walfahrt, built the Albany Glass Works at Dowesborough, New York, which was less than 15 miles (24 km) west of Albany.[107] The design of the works was very similar to the design used for Amelung's glass works in Maryland.[108] German workers were used, and production of window glass is believed to have begun in 1786.[108] De Neufville was a poor financial manager, and the glass works was abandoned by 1790.[109] James Caldwell and associates renovated the abandoned factory in 1792 and began producing window glass. He called his factory the Albany Glass House.[110] A fire severely damaged the factory during the summer of 1794, but by December the old glass works, and a new one, were operating.[111] More financial difficulties in 1795 caused the works to be taken over by Thomas and Samuel Mather.[112] Products were window glass and bottles.[113] The plant is thought to have closed in 1815 due to lack of fuel.[107]
- Boston Crown Glass Company: Robert Hewes, Samuel Walley, John Gore, and eight others organized the Boston Crown Glass Company on July 6, 1787. Production did not start until November 11, 1793. Original works was located on Essex Street in Boston, and produced high quality window glass.[114] Company was reorganized in 1809 with different owners, and a second works was completed during 1811 in South Boston. The company failed in 1827, and one of the glass factories was destroyed by fire in 1929.[114]
Other 18th century glass works
[edit]Some glass works existed during the 18th century but did not survive into the 19th century. The lists below for each region are in order of when the company started producing.[Note 7] The Schuylkill glass works, listed below, may have been the first glass factory to use coal to power its furnaces.[50][Note 8]
Philadelphia area
[edit]
- Barge glass works: Jacob Barge began producing glass in 1760 in the Province of Pennsylvania.[116] The works was located in Bucks County close to Philadelphia. Archeological evidence indicates that window glass was made using the cylinder method. Various types of bottles were also made. The glass works appears to have operated through 1784.[117]
- Schuylkill glass works: In 1794 John Nicholson built a glass works on the west side of Philadelphia at the falls of the Schuylkill River.[30][Note 9] Peter William Eichbaum supervised construction of the glass works and provided glassmaking expertise, and production began in 1795.[118] The factory's furnaces were coal powered, which means the works may have been the first American glass plant to use a furnace powered by coal.[50] Bottles were the main product, although a limited quantity of window glass may have been produced.[119] Financial difficulties and strikes caused by lack of pay caused the works' moveable property to be seized during 1797.[120]
Frederick Maryland
[edit]
- Foltz, Kramer & Eberhart: The first significant glass works in Maryland was built in Frederick County, Maryland, around 1780. The investors were Conrad Foltz, Martin Eberhart, and four Kramer brothers (Balthazer, Adam, Martin, and George), and some of these men had worked at the Stiegel glass works. When Foltz died in 1784, the works was sold to John Frederick Amelung.[121]
- Tuscarora Glass House: Thomas Johnson, owner of the Aetna Glass Works, built a small industrial complex that included a glass works. It was located along Tuscarora Creek on the north side of Frederick, Maryland.[81] The complex, which included a mill and tannery, was completed by 1793 or earlier. By 1798 the glass works was "out of repair".[81]
New York
[edit]
- Glasshouse Company of New York, New Found Land: In 1752 Matthew Earnest, Samuel Bayard, Loderwyck Bamper, Christian Hertell and Johan Martin Greiner agreed to establish a glass works in the city of New York. All of the partners were from New York except Greiner, who was from Saxe-Weimar in Europe. As part of the agreement, Greiner would travel from Europe to New York on February 1 (or when the New Yorkers were ready), and he would lead in the construction of the glass works as well as instruct in glass making.[122] The works was called "the Glass House Company of New York".[123] The Glass House Company of New York was located on the Hudson River on land that included the Glass House Farm and became known as New Found Land.[124] Newspaper advertising indicates that the works was producing by October 1754, and bottles were the main products. The glass works failed some time before 1762.[125] In 1767 the works and land was offered for sale.[126]
- Glasshouse Company of New York, New Windsor: During August 1752 Matthew Earnest, Samuel Bayard, Loderwyck Bamper, Christian Hertell purchased land in the Province of New York at New Windsor.[126] It is believed that this land was originally purchased as a source of wood for the Glass House Company of New York's works at Glass House Farm. However, a glass house was erected on the New Windsor property to make bottles and window glass. It is not known for certain if this works continued after the 1767 sale of the works at New Found Land, but some believe the New Windsor works operated until about 1785.[126]
- Brooklyn Glass Works: In 1754 Loderwyck Bamper started the Brooklyn Glass Works in New York City's Brooklyn borough in the Province of New York.[127] Products were bottles, but there is little evidence the works actually produced.[79]
New England
[edit]- Braintree: Peter Etter, Joseph Crellins, Norton Quincy, and John Franklin started a glass bottle works in the province of Massachusetts near Braintree (now part of Quincy).[128] The business failed before 1752, when it was leased to Joseph Palmer. Infrastructure improvements were made, but the works was destroyed by fire around 1756.[129]
- New England Glassworks: Boston businessman Robert Hewes started the New England Glassworks, not to be confused with the New England Glass Company, in 1780.[130] The plant was located in Temple, New Hampshire. German glassworkers were employed, but not Hessen deserters from the British army as local lore suggests.[131] The works was destroyed by fire almost immediately after construction. The facility was rebuilt and window glass (crown method) was produced during the summer. The works was shut down and abandoned during the winter of 1781–1782 because of financial difficulties.[132]
- India Point glass house: Politician John Brown started a glass works around 1796 at India Point in Providence, Rhode Island. The works made bottles for a nearby distillery, and may have been a small operation. Factory is thought to have been discontinued in 1799.[133]
New England – Did not operate
[edit]- Darling: In 1747 Thomas Darling was granted sole rights to produce glass in the Connecticut Colony for 20 years, but was unable to fulfill the conditions of the agreement.[134]
- Crellins: In 1752 Joseph Crellins was given permission by the Province of Massachusetts Bay colonial governor to begin a glass works provided he could secure German workmen. He could not meet the requirement before the agreement expired.[135]
- Windslow: In 1752 Isaac C. Winslow received sole rights to produce glass in the Colony of Rhode Island. It is not believed that glass was ever produced.[79]
Future glassmaking
[edit]
Glassmaking became difficult in the United States at the beginning of the 19th century. Red lead was a key additive for high–quality glassware and England controlled much of the supply.[136] The United States Embargo Act of 1807, and the War of 1812, made red lead extremely difficult for American companies to acquire.[137] After the War of 1812, English glass manufacturers began dumping low–priced glass products in the United States, which drove many American glass companies into bankruptcy.[136]
The United States Tariff of 1824, which was a protective tariff, helped the American glass industry. Between 1820 and 1840, nearly 70 glass factories were started. Most of these factories were small businesses employing 25 to 40 workers.[75] Higher quality glass became more available when American glass man Deming Jarves, sometimes called the "father of the American glass industry", developed a way to produce red lead from domestic sources of lead oxide.[138] The most important innovation for the 1820s was the development of machine pressed glass—pressing glass into a mold.[139] Bakewell and Company, New England Glass Company, and Jarves' Boston and Sandwich Glass Company were early users of machine pressed glass technology.[140]
Glassmaking on the East Coast of the United States peaked before 1850, as plants shifted to Pittsburgh because of the availability of coal for fuel.[141] By 1850, the United States had 3,237 free men above age 15 who listed their occupation as part of the glass manufacturing process.[142] Pennsylvania accounted for 40% of the glassmaking employees. Other states with more than 100 glass workers were New Jersey, New York, Massachusetts, and Virginia (including what is now West Virginia).[142][Note 10]
Notes
[edit]Footnotes
[edit]- ^ An older source quotes a glass works spokesman as saying the furnace is heated to between 2,800 °F (1,540 °C) and 3,600 °F (1,980 °C).[5]
- ^ Caspar Wistar's grandson, Dr. Caspar Wistar, became a famous physician.[31]
- ^ While at least three sources say the four glassblowers were German, at least one source says they were from Belgium.[36]
- ^ The family name has been spelled at least seven different ways: Stanger, Stenger, Stinger, Staenger, Steenger, Syanger, and Sanger.[55]
- ^ Sources conflict over Amelung building a glass works. An obscure glassworks known as the Foltz–Kramer–Eberhardt factory existed on the property.[67] Amelung never mentioned the previous works. It is not known if Amelung demolished the old works, or if he modified and added to it.[68] A Frederick newspaper article mentioned the Foltz–Kramer–Eberhardt glass factory, and notes that glassmaking in the area began around 1759.[69]
- ^ This count excludes at least two glass factories, one in Ohio and one in Baltimore, that began production during 1800.[76]
- ^ The "Name" in the list of other 18th cetury glass works is the name of the glass works if available. In cases where there was no name, either the main investor or some type of geographic identifier is used, and "glass works" or "glass house" is not capitalized. The major source for the list is the McKearin & McKearin book, although others have been reviewed.[115]
- ^ Many historians cite the O'Hara and Craig Pittsburgh glass works as the first glass plant using coal for fuel. The Pittsburgh works, which lasted much longer than the Schuylkill works, began in 1797 and was managed by Peter William Eichbaum—who also helped start the Schuylkill works.[50]
- ^ Some historians have said that Nicholson's sometime business partner, Robert Morris, was involved with the Schuylkill glass works, but that is not true.[30]
- ^ North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia were the southernmost states in the original Thirteen British American colonies, and they all had zero glassmaking employees in the 1850 Census.[142]
Citations
[edit]- ^ Shotwell 2002, pp. 32–33
- ^ a b "How Glass is Made – What is glass made of? The wonders of glass all come down to melting sand". Corning. Archived from the original on July 5, 2023. Retrieved July 5, 2023.
- ^ Shotwell 2002, p. 94
- ^ Shotwell 2002, pp. 114–115
- ^ Weeks & United States Census Office 1884, p. 35
- ^ Scoville 1944, p. 210
- ^ Shotwell 2002, p. 343
- ^ Weeks & United States Census Office 1884, p. 45
- ^ Madarasz, Historical Society of Western Pennsylvania & Senator John Heinz Pittsburgh Regional History Center 1998, p. 42
- ^ "Corning Museum of Glass – Annealing Glass". Corning Museum of Glass. Archived from the original on July 5, 2023. Retrieved July 5, 2023.
- ^ Madarasz, Historical Society of Western Pennsylvania & Senator John Heinz Pittsburgh Regional History Center 1998, p. 48
- ^
- Madarasz, Historical Society of Western Pennsylvania & Senator John Heinz Pittsburgh Regional History Center 1998, p. 48
- "Corning Museum of Glass – Lehr". Corning Museum of Glass. Archived from the original on July 5, 2023. Retrieved July 5, 2023.
- ^
- Purvis 1999, p. 107
- Shotwell 2002, p. 224
- Weeks & United States Census Office 1884, p. 21
- ^
- Weeks & United States Census Office 1884, p. 21
- Palmer 1979, p. 107
- ^ Weeks & United States Census Office 1884, p. 20
- ^ Louw 1991, p. 48
- ^ United States Department of Commerce, Bureau of Foreign and Domestic Commerce 1917, p. 12
- ^ United States Department of Commerce, Bureau of Foreign and Domestic Commerce 1917, p. 13
- ^
- ^ Skrabec 2007, p. 97
- ^ a b Skrabec 2011, p. 20
- ^ Scoville 1944, p. 194
- ^ Scoville 1944, pp. 194–195
- ^ a b Scoville 1944, p. 195
- ^ Knittle 1927, pp. 68–69, 73–74
- ^ Knittle 1927, p. 74
- ^ Poor 1868, p. 11
- ^ Poor 1868, p. 20
- ^ Palmer 1976, p. 77
- ^ a b c Palmer 1979, p. 102
- ^
- "Caspar Wistar 1761-1818". University of Pennsylvania, University Archives and Records Center. Archived from the original on November 13, 2023. Retrieved November 13, 2023.
- "The Wistar Institute - Our Story". The Wistar Institute of Anatomy and Biology. Archived from the original on November 13, 2023. Retrieved November 13, 2023.
- ^ Shotwell 2002, pp. 616–617
- ^
- Shotwell 2002, pp. 616–617
- Zerwick 1990, p. 71
- ^ Lanmon & Palmer 1976, p. 15
- ^ a b "1989 The Wistars and their Glass 1739 – 1777". Wheaton Arts and Cultural Center. Archived from the original on November 13, 2023. Retrieved November 13, 2023.
- ^
- "1989 The Wistars and their Glass 1739 – 1777". Wheaton Arts and Cultural Center. Archived from the original on November 13, 2023. Retrieved November 13, 2023.
- Shotwell 2002, p. 617
- Zerwick 1990, p. 71
- Knittle 1927, p. 86
- ^ a b c Shotwell 2002, p. 617
- ^ a b Palmer 1979, p. 104
- ^ a b Zerwick 1990, p. 71
- ^ a b Palmer 1976, p. 78
- ^
- "Find Rum Evidence from 18th Century". Midland Journal (from Chronicling America: Historic American Newspapers. Lib. of Congress). September 10, 1920. Archived from the original on 2023-11-13. Retrieved 2023-12-06.
- Zerwick 1990, p. 71
- "1989 The Wistars and their Glass 1739 – 1777". Wheaton Arts and Cultural Center. Archived from the original on November 13, 2023. Retrieved November 13, 2023.
- McKearin & McKearin 1966, p. 78
- Knittle 1927, pp. 94–95
- ^ Knittle 1927, pp. 118–119
- ^ "Elizabeth Furnace Plantation Site". Millersville University. Archived from the original on November 21, 2023. Retrieved November 21, 2023.
- ^ Knittle 1927, p. 119
- ^ Knittle 1927, p. 120
- ^ Lanmon & Palmer 1976, p. 16
- ^ Knittle 1927, pp. 121–122
- ^
- Lanmon & Palmer 1976, pp. 16–17
- Knittle 1927, p. 120
- ^ "Pocket Bottle". The Metropolitan Museum of Art. Archived from the original on December 20, 2023. Retrieved December 20, 2023.
- ^ a b c d e Palmer 1979, p. 107
- ^ Shotwell 2002, p. 112
- ^ Lanmon & Palmer 1976, p. 17
- ^ Lanmon & Palmer 1976, pp. 17–18
- ^ a b c "Stanger family". Corning Museum of Glass. Archived from the original on November 21, 2023. Retrieved November 21, 2023.
- ^ Knittle 1927, p. 152
- ^
- "Stanger family". Corning Museum of Glass. Archived from the original on November 21, 2023. Retrieved November 21, 2023.
- Knittle 1927, p. 153
- ^ a b Van Rensselaer 1926, p. 134
- ^ Knittle 1927, p. 153
- ^ a b c Knittle 1927, p. 154
- ^ Knittle 1927, pp. 154–155
- ^ Van Rensselaer 1926, p. 135
- ^ Knittle 1927, p. 155
- ^ Skrabec 2007, p. 43
- ^
- Quynn 1948, p. 158
- Zerwick 1990, p. 72
- ^ Quynn 1948, p. 158
- ^ a b Quynn 1948, p. 159
- ^ a b Lanmon & Palmer 1976a, p. 26
- ^ Lanmon & Palmer 1976a, pp. 26, 28
- ^ Martinkosky, Christina (August 1, 2020). "Preservation Matters: Glass–Making Located in Frederick". Frederick News–Post. Archived from the original on November 22, 2023. Retrieved November 22, 2023.
- ^ a b Quynn 1948, p. 167
- ^ Lanmon & Palmer 1976a, p. 27
- ^ Quynn 1948, p. 174
- ^ Zerwick 1990, p. 72
- ^ Lanmon & Palmer 1976a, p. 38
- ^ a b Dyer & Gross 2001, p. 23
- ^
- McKearin & McKearin 1966, p. 132
- Daniel 1949, p. 107
- Lanmon & Palmer 1976b, p. 41
- ^ McKearin & McKearin 1966, p. 132
- ^ a b Shotwell 2002, p. 277
- ^ a b c McKearin & McKearin 1966, p. 584
- ^
- Knittle 1927, pp. 154–155
- Skrabec 2007, p. 43
- ^ a b c Lanmon & Palmer 1976b, p. 39
- ^ a b Oland 1973, p. 272
- ^ a b Lanmon & Palmer 1976b, p. 41
- ^
- McKearin & McKearin 1966, p. 116
- Daniel 1949, pp. 103–104
- Knittle 1927, p. 297
- ^ Lanmon & Palmer 1976b, p. 42
- ^ Lanmon & Palmer 1976b, p. 43
- ^ a b Weeks & United States Census Office 1884, p. 83
- ^ McKearin & McKearin 1966, p. 129
- ^ Madarasz, Historical Society of Western Pennsylvania & Senator John Heinz Pittsburgh Regional History Center 1998, p. 20
- ^
- Weeks & United States Census Office 1884, p. 82
- Shotwell 2002, p. 430
- ^ McKearin & McKearin 1966, p. 587
- ^ Shotwell 2002, p. 430
- ^ Madarasz, Historical Society of Western Pennsylvania & Senator John Heinz Pittsburgh Regional History Center 1998, p. 18
- ^ Madarasz, Historical Society of Western Pennsylvania & Senator John Heinz Pittsburgh Regional History Center 1998, p. 19
- ^
- Weeks & United States Census Office 1884, p. 83
- "Albert Gallatin & Co.: 1795-1803". Carnegie Library of Pittsburgh. Archived from the original on June 7, 2014. Retrieved August 7, 2014.
- ^ Madarasz, Historical Society of Western Pennsylvania & Senator John Heinz Pittsburgh Regional History Center 1998, pp. 18–19
- ^ Weeks & United States Census Office 1884, p. 82
- ^ a b McKearin & McKearin 1966, p. 586
- ^ "Albert Gallatin & Co.: 1795-1803". Carnegie Library of Pittsburgh. Archived from the original on June 7, 2014. Retrieved August 7, 2014.
- ^ Daniel 1949, pp. 100–101
- ^ Daniel 1949, p. 107
- ^ "The Pitkin Glass Works 1783-1830". The Museum of Connecticut Glass. Archived from the original on December 15, 2023. Retrieved December 15, 2023.
- ^ Knittle 1927, pp. 192–193
- ^ Knittle 1927, pp. 193–194
- ^ a b "Bits of History From the Cottage Lawn Historical House". Cazenovia Republican (Newspaper Archive). July 16, 1964. p. 12.
In 1783 David Goff and a company of men....
- ^ Madison County Eagle (July 21, 2009). "Historical Glass Factories of Peterboro". Eagle News Online. Community Media Group, LLC. Archived from the original on December 15, 2023. Retrieved December 15, 2023.
- ^ a b McKearin & McKearin 1966, p. 585
- ^ a b Huey 1980, p. 37
- ^ Huey 1980, p. 38
- ^ Huey 1980, p. 39
- ^ Huey 1980, p. 42
- ^ Huey 1980, p. 43
- ^ Huey 1980, p. 44
- ^ a b McKearin & McKearin 1966, p. 131
- ^
- McKearin & McKearin 1966, pp. 584–587
- Purvis 1999, p. 107
- ^
- McKearin & McKearin 1966, p. 584
- Long, Liebeknecht & Tvaryanas 2008, pp. 320–321
- ^ Long, Liebeknecht & Tvaryanas 2008, pp. 320–321
- ^ Palmer 1979, pp. 104–105
- ^ Palmer 1979, p. 105
- ^ Palmer 1979, p. 113
- ^ Lanmon & Palmer 1976, pp. 18–19
- ^ Wall 1926, p. 95
- ^ McKearin & McKearin 1966, p. 96
- ^ McKearin & McKearin 1966, pp. 97–98
- ^ Wall 1926, pp. 98–99
- ^ a b c McKearin & McKearin 1966, p. 98
- ^ Hunter 1914, p. 152
- ^
- McKearin & McKearin 1966, p. 584
- "Founders Online - From Benjamin Franklin to John Franklin, 27 September 1750". National Historical Publications and Records Commission, National Archives. Archived from the original on 16 December 2023. Retrieved November 30, 2023.
- ^
- McKearin & McKearin 1966, p. 584
- Knittle 1927, pp. 103–106
- ^ Starbuck 1983, p. 46
- ^ "Robert Hewes, Glass Manufacturer". Corning Museum of Glass. Archived from the original on December 5, 2023. Retrieved December 5, 2023.
- ^ Starbuck 1983, p. 47
- ^ Frank 2003, pp. 61–62
- ^ Hunter 1914, p. 144
- ^ Knittle 1927, p. 102
- ^ a b Skrabec 2011, p. 19
- ^ Skrabec 2011, p. 18
- ^ Skrabec 2011, pp. 18, 20
- ^ Tillotson 1920, p. 354
- ^ Shotwell 2002, p. 444
- ^ Skrabec 2011, p. 24
- ^ a b c United States 1853, p. lxxi
References
[edit]- Daniel, Dorthy (December 1949). "The First Glasshouse West of the Alleghenies". The Western Pennsylvania Historical Magazine. 32 (4). Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania: Penn state Libraries Open Publishing: 97–113. OCLC 1769752. Archived from the original on December 16, 2023. Retrieved December 1, 2023.
- Dyer, Davis; Gross, Daniel (2001). The Generations of Corning: The Life and Times of a Global Corporation. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19514-095-8. OCLC 45437326.
- Frank, Caroline (Fall 2003). "John Brown's India Point" (PDF). Rhode Island History. 61: 51–69. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 15, 2023. Retrieved December 15, 2023.
- Huey, Paul R. (1980). "The Albany Glassworks from 1790 to 1800: A Study of American Industry During the Federal Period". Journal of Glass Studies. 22: 36–52. JSTOR 24190622. Archived from the original on December 15, 2023. Retrieved December 15, 2023.
- Hunter, Frederick William (1914). Steigel Glass. Boston, Massachusetts: Houghton Mifflin Co. OCLC 1383707. Archived from the original on December 4, 2023. Retrieved November 30, 2023.
- Knittle, Rhea Mansfield (1927). Early American Glass. New York, New York: The Century Co. ISBN 978-1-4047-5385-3. OCLC 1811743. Archived from the original on 2023-07-19. Retrieved 2023-08-03.
- Lanmon, Dwight P.; Palmer, Arlene M. (1976). "The Background of Glassmaking in America". Journal of Glass Studies. 18 (Special Bicentennial Issue): 14–19. JSTOR 24190008. Archived from the original on October 27, 2023. Retrieved October 27, 2023.
- Lanmon, Dwight P.; Palmer, Arlene M. (1976a). "The New Bremen Glassmanufactory". Journal of Glass Studies. 18 (Special Bicentennial Issue): 25–38. JSTOR 24190010. Archived from the original on November 22, 2023. Retrieved October 27, 2023.
- Lanmon, Dwight P.; Palmer, Arlene M. (1976b). "The Amelung Postscript". Journal of Glass Studies. 18 (Special Bicentennial Issue): 39–43. JSTOR 24190011. Archived from the original on December 10, 2023. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
- Long, David B.; Liebeknecht, William B.; Tvaryanas, Damon (2008). "Survey at Pennsylvania Glass Factory Site Yields Thousands of Fragments". Journal of Glass Studies. 50: 320–321. JSTOR 24191343. Archived from the original on December 14, 2023. Retrieved December 14, 2023.
- Louw, Hentie (1991). "Window-Glass Making in Britain c.1660-c.1860 and its Architectural Impact". Construction History. 7: 47–68. JSTOR 41613689. Archived from the original on April 18, 2021. Retrieved November 18, 2023.
- Madarasz, Anne; Historical Society of Western Pennsylvania; Senator John Heinz Pittsburgh Regional History Center (1998). Glass: Shattering Notions. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania: Historical Society of Western Pennsylvania. ISBN 978-0-93634-001-2. OCLC 39921461.
- McKearin, Georghe S.; McKearin, Helen (1966). American Glass. New York City: Crown Publishers. OCLC 1049801744.
- Oland, Dwight D. (Fall 1973). "The New Bremen Glass Manufactory". Maryland Historical Magazine. 68 (3): 255–272. Retrieved December 19, 2023.
- Palmer, Arlene (1976). "Glass Production in Eighteenth-Century America: The Wistarburgh Enterprise". Winterthur Portfolio. 11. Chicago, Illinois: University of Chicago Press on behalf of the Henry Francis du Pont Winterthur Museum Inc.: 75–101. doi:10.1086/495842. JSTOR 1180591. S2CID 161635810. Archived from the original on November 17, 2023. Retrieved November 17, 2023.
- Palmer, Arlene (1979). "A Philadelphia Glasshouse, 1794–1797". Journal of Glass Studies. 21. Corning, New York: Corning Museum of Glass: 102–114. JSTOR 24190039. Archived from the original on December 4, 2023. Retrieved November 29, 2023.
- Poor, Henry V. (1868). Poor's Manual of Railroads for 1868–69. New York City: H.V. & H.W. Poor. OCLC 5585553. Archived from the original on May 21, 2023. Retrieved May 21, 2023.
- Purvis, Thomas L. (1999). Colonial America to 1763. New York City: Facts on File. ISBN 978-1-43810-799-8. OCLC 234080971.
- Skrabec, Quentin R. (2007). Michael Owens and the Glass Industry. Gretna, Louisiana: Pelican Publishing. ISBN 978-1-45560-883-6. OCLC 1356375205.
- Skrabec, Quentin R. (2011). Edward Drummond Libbey, American Glassmaker. Jefferson, North Carolina: McFarland. ISBN 978-0-78648-548-2. OCLC 753968484.
- Shotwell, David J. (2002). Glass A to Z. Iola, Wisconsin: Krause Publications. pp. 638. ISBN 978-0-87349-385-7. OCLC 440702171.
- Scoville, Warren C. (September 1944). "Growth of the American Glass Industry to 1880". Journal of Political Economy. 52 (3): 193–216. doi:10.1086/256182. JSTOR 1826160. S2CID 154003064. Archived from the original on November 13, 2023. Retrieved November 2, 2023.
- Starbuck, David R. (1983). "The New England Glassworks in Temple, New Hampshire". The Journal of the Society for Industrial Archeology. 9 (1). Houghton, Michigan: Society for Industrial Archeology: 45–64. JSTOR 40968043. Archived from the original on December 29, 2023. Retrieved December 29, 2023.
- Tillotson, E. Ward (December 1920). "Modern Glass-Making – Putting the Glass Industry on a Scientific Basis". Scientific American Monthly. II (4). New York City: Scientific American Publishing Company: 351–354. Archived from the original on November 17, 2023. Retrieved August 25, 2023.
- United States (1853). The Seventh Census of the United States, 1850: Embracing a Statistical View of Each of the States and Territories, Arranged by Counties, Towns, Etc. ... Washington, District of Columbia: R. Armstrong. OCLC 1049765701. Archived from the original on July 7, 2023. Retrieved July 6, 2023.
- Quynn, Dorthy Mackay (September 1948). "Johann Friedrich Amelung at New Bremen" (PDF). Maryland Historical Magazine. XLIII (3). Baltimore, Maryland: Maryland Historical Society: 155–179. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 22, 2023. Retrieved November 22, 2023.
- United States Department of Commerce, Bureau of Foreign and Domestic Commerce (1917). The Glass Industry. Report on the Cost of Production of Glass in the United States. Washington: Government Printing Office. OCLC 5705310.
- Van Rensselaer, Stephen (1926). Early American Bottles and Flasks. Peterborough, New Hampshire: Transcript Print. Co. OCLC 1325741. Archived from the original on November 22, 2023. Retrieved November 22, 2023.
- Wall, A. J. (October 1926). "Proposals for Establishing a Glass Works in the City of New York in 1752". The New York Historical Society Quarterly Bulletin. X (3). New York City: New York Historical Society: 95–99. Archived from the original on December 12, 2023. Retrieved December 12, 2023.
- Weeks, Joseph D.; United States Census Office (1884). Report on the Manufacture of Glass. Washington, District of Columbia: U.S. Government Printing Office. OCLC 2123984. Archived from the original on July 16, 2023. Retrieved June 26, 2023.
- Zerwick, Chloe (1990). A Short History of Glass. New York: H.N. Abrams in association with the Corning Museum of Glass. ISBN 978-0-81093-801-4. OCLC 20220721.
External links
[edit]- Jamestown and New Jersey - University of Central Florida History Department
- Glass of H.W. Stiegel - Corning Museum of Glass
- Stanger-Whitney-Glassboro - Rowan University
