11-inch gun M1877
| 11-inch gun M1877 | |
|---|---|
 An 11-inch M1877 at Suomenlinna. | |
| Type | Coastal artillery Fortress gun Siege gun |
| Place of origin | Russian Empire |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1880-? |
| Used by | |
| Wars | Russo-Japanese War World War I |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Obukhov State Plant |
| Designed | 1877 |
| Manufacturer | Obukhov State Plant Motovilikha Plants[1] |
| Produced | 1880 |
| Specifications | |
| Barrel length | 6.1 m (20 ft) L/21.8 calibers[2] |
| Shell | Separate-loading, bagged charges and projectiles. |
| Shell weight | 182–250 kg (401–551 lb) |
| Caliber | 280 mm (11 in) |
| Breech | Horizontal sliding-block |
| Recoil | Hydro-gravity |
| Carriage | Garrison mount[2] |
| Elevation | -6° to +20° |
| Traverse | 120° |
| Rate of fire | 1 round every 3 minutes |
| Muzzle velocity | 518 m/s (1,700 ft/s) |
| Maximum firing range | 12.5–14.4 km (7.8–8.9 mi)[2] |
The 11-inch gun M1877 was a Russian 280 mm (11 in) coastal, fortress and siege gun that was used in the Russo-Japanese War and World War I.
History
[edit]The M1877 was first designed and produced by the Obukhov State Plant in Saint Petersburg and was fairly conventional for its time and most nations had similar guns with similar roles such as the French Canon de 240 L Mle 1884 or British BL 10 inch gun Mk I – IV.
Design
[edit]The M1877 was a short barreled breech-loading gun. The barrel was a typical built-up gun of the period with reinforcing hoops which was built from cast iron and steel. The gun had an early form of Krupp horizontal sliding-block breech and it fired separate-loading, bagged charges and projectiles.[2]
Coastal Defense
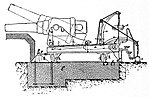
[edit]In the coastal defense role, the M1877 was mounted on a garrison mount which sat on a concrete slab behind a parapet. The mount consisted of a rectangular steel firing platform with a pivot at the front and two wheels at the front and rear to give 120° of traverse. The recoil system for the M1877 consisted of a U-shaped gun cradle which held the trunnioned barrel and a slightly inclined firing platform with a hydro-gravity recoil system. When the gun fired the hydraulic buffers under the rear slowed the recoil of the cradle which slid up a set of inclined rails on the firing platform and then returned the gun to position by the combined action of the buffers and gravity. Due to its limited angle of elevation 20°, the M1877 was a low-angle direct fire weapon instead of a high-angle indirect-fire coastal defense mortar like many of its contemporaries.[2]
Fortress & Siege Gun
[edit]In the fortress and siege gun roles, the M1877 used the same type of garrison mount as in the coastal defense role. Due to their weight, the guns were not designed to be mobile. After a string of Russian defeats in the first two years of the war, a number of M1877's were captured by the Germans. In 1916 the Germans transferred four M1877's to the Western Front where they were assigned to heavy artillery battalions of the army. Details of their employment are unknown and all are believed to have been withdrawn before 1918. However, since they didn't have very good range and they weren't capable of high angle fire they may have been used in their original coastal defense role instead of in a siege artillery role. In German service the guns had better range due to more efficient smokeless powder and more aerodynamic German projectiles.[2]
Photo Gallery
[edit]-
An 11-inch M1877 at Suomenlinna.
-
A M1877 captured during the Siege of Novogeorgievsk.
-
Details of the garrison mount.
-
The M1877's breech block.