Żeligowski's Mutiny
| Żeligowski's Mutiny | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Polish–Lithuanian War | |||||||||
 Polish soldiers in Vilnius in 1920. | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
|
|
| ||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| 14,000 | 6,000–7,000 | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
| Unknown | 222 killed[1] | ||||||||
Żeligowski's Mutiny (Polish: bunt Żeligowskiego, also żeligiada, Lithuanian: Želigovskio maištas) was a Polish false flag operation led by General Lucjan Żeligowski in October 1920, which resulted in the creation of the Republic of Central Lithuania. Józef Piłsudski, the Chief of State of Poland, surreptitiously ordered Żeligowski to carry out the operation, and revealed the truth only several years afterwards.
The Second Polish Republic formally annexed Vilnius and its region on 4 March 1922 and the area was recognized by the Conference of Ambassadors as Polish territory on 15 March 1923, which was unrecognized by Lithuania, that claimed Vilnius and its region,[2] and by the Soviet Union.[3] The International Court of Justice in The Hague arbitrated in 1931 that Poland broke international law by occupying Vilnius.[4]
Background
[edit]
In the summer of 1920, the Polish–Soviet War was ending with the Soviet Russian Red Army defeated at the Battle of Warsaw and in full retreat. The disputed Vilnius region centered on the Lithuanian capital of Vilnius, founded by the Lithuanian Grand Duke Gediminas in 1323, and that had been the Lithuanian capital ever since. Vilnius had been occupied by the Soviets during their summer 1920 westwards offensive. The Soviets returned the region to the Lithuanians because the latter had allowed Soviet troops to move through Lithuanian territory as part of the Soviet–Lithuanian Peace Treaty. Lithuanians also clashed with Poles over territorial disputes as part of the Polish–Lithuanian War.
This move allowed the Soviets to retain tactical control of the region, deny it to the Poles, and increase the already high tensions between the Poles and Lithuanians, both of whom claimed the disputed territory as their own.[5][6]
The Poles rested their claim on then current ethnographic considerations, as approximately 65% of the inhabitants of the city at the time were Polish-speakers, while Lithuanians constituted approximately 1–2% of the city's population.[7] Lithuania pointed to Vilnius as its historical capital and denied Polish claims to it as baseless.[8] The Poles did not wish to continue the war as the Polish army was tired, and Polish Chief of State Józef Piłsudski was still hoping to create an Intermarium federation, to include a Lithuania friendly to Poland, but wanted to ensure that Vilnius would be part of a Polish sphere of influence. From the Lithuanian point of view, that was highly unlikely, as many Lithuanians saw Polish influence as pernicious and had wanted to be rid of Polish influence from as far back as the marriage of Grand Duke Jogaila to the then 11-year-old Queen Jadwiga of Poland in 1386. In particular, Lithuanian nationalists opposed any further connection to Poland, especially after the Polish occupation of Vilnius.
The negotiations on the future of the disputed area, held under the auspice of a Conference of Ambassadors in Brussels and Paris, reached a stalemate, and Piłsudski feared that the Entente might accept the fait accompli that had been created by the Soviets' transfer of territorial control to Lithuania.
On 10 July 1920, before the Battle of Warsaw, the Polish prime minister Władysław Grabski signed an agreement in the Spa Conference of 1920, whereby Poland would receive Allied help in exchange for giving up Vilnius to the Lithuanians and the Polish Army retreating to the Curzon demarcation line of 8 December 1919.[9] Then, under Allied pressure, the Poles and Lithuanians signed the Suwałki Agreement in early October 1920, but the Polish side was discontent with Vilnius remaining under Lithuanian control. Poland and Lithuania were to adhere to a mutually agreed upon ceasefire in Suwałki Region on October 10, but the Poles decided to circumvent the ceasefire by creating a "fait accompli" of their own. Piłsudski concluded that the best course of action would be one that supported the pro-Polish faction in Lithuania, but that could not be traced directly to Poland. However, his plans for a coup d'état in 1919 had been foiled by the premature and unplanned Sejny Uprising, which had led to the destruction of the Polish Military Organisation (P.O.W.) intelligence network in Lithuania by the Lithuanian Army and State Security Department.[10][11]
Prelude until 8 October 1920
[edit]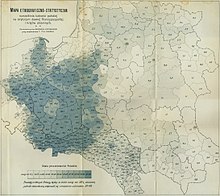

In October 1920, Polish General Lucjan Żeligowski, a native of the historic lands of Lithuania, was given command of the 1st Lithuanian–Belarusian Division (comprising mostly individuals from the Kresy).[12][13] Żeligowski had been contacted by Piłsudski as early as late September 1920 with suggestions to carry out a "mutiny." They prepared a plan by which Żeligowski and forces under his command were to pretend to desert from the Polish Army and then take control of the Vilnius and its region. The Polish government would officially deny its involvement, thereby preserving its reputation on the international scene.[13]
Żeligowski, like Piłsudski himself[14] was one of many who were torn between Lithuanian and Polish identities; possibly, in proclaiming a Central Lithuania, he honestly believed that he was creating a Lithuania even if it that was dominated by Polish culture rather than Lithuanian culture.[11]
In early October, there was intensive preparation for this operation.[15] On October 1, in the meeting of the Polish Council of National Defense, General Józef Haller said:
"It is necessary not only to occupy Vilnius, but also to maybe threaten Kaunas and change the Government of Lithuania."[15]
On October 6, 1920, Żeligowski informed his officers of the plans for mutiny; at that point, no one under his command knew that he was acting with Piłsudski's backing, and some refused to follow him. Support for Żeligowski wavered to such an extent that on October 7, he messaged Piłsudski that he could not carry out the operation due to lack of support among his troops. Eventually, however, most of the officers and men decided to follow him, and he proceeded with the operation.[16]
Żeligowski's operation: October 8–November 29
[edit]Żeligowski's forces set out on the morning of October 8 (two days before the Suwałki Agreement ceasefire was to take hold). That day, he declared that he would "liberate Wilno from Lithuanian occupation" and "form a parliament which will decide the fate of the disputed territories."[16]
To ensure a quick conclusion of the operation, Żeligowski was given 14,000 soldiers supported by the Polish 2nd and 3rd Armies.[17] His 1st Lithuanian–Belarusian Division and other units defeated the Lithuanian 4th Infantry Regiment near the Rūdninkai Forest and again in a skirmish near Jašiūnai.[13] The Polish forces reached the vicinity of Vilnius, but were slowed enough to delay their taking the city until the next day. The death toll, as reported by contemporary sources, was low: "a few casualties" on both sides.[18]

The Lithuanian forces in the region were heavily outnumbered: they not only faced Żeligowski's numerically superior regular forces, supported by Polish Army logistics, but also had to garrison Vilnius, whose Polish population was restless. On October 9, the Lithuanian forces were unable to defend Vilnius and evacuated the city, with only token attempts at defending it (the decision to evacuate was made in the afternoon of October 8, and the evacuation took place during the night of October 8–9). When Polish units assaulted the remaining Lithuanian defenses around Vilnius, the city's Polish population supported the Polish troops, with militia units staging an uprising and engaging Lithuanian units still in the city, and civilians welcoming the Polish troops as they entered Vilnius.[citation needed]
Lithuanian government representatives (led by Ignas Jonynas) passed control of the city to the resident Entente officials (led by French colonel Constantin Reboul). Żeligowski, however, refused to recognize their authority, and they were forced to leave the city.[18]

On October 12, Żeligowski proclaimed the independence of the area as the Republic of Central Lithuania, with Vilnius as its capital. Most historians agree that the state was dependent on Poland, but they disagree to what extent (Polish historian Jerzy Jan Lerski calls it a puppet state).[19]
Meanwhile, a uniformed Polish armed force of 20 airplanes and the 13th Wilno Uhlan Regiment under the command of Col. Butkiewicz joined the mutiny.[19] The Polish Army, however, was officially bound by the Suwałki Agreement ceasefire and did not engage the Lithuanian units by the line. On October 20–21 there were further battles between Central and Lithuanian forces near the village of Pikeliškiai.
November
[edit]On November 7, Żeligowski's army began to advance upon Giedraičiai, Širvintos and Kėdainiai. Żeligowski's proposals of a cease-fire were ignored by Lithuania.[20] Żeligowski ignored League of Nations's Military Control Commission proposals to withdraw to October 20–21 lines and begin negotiations. On November 17, Soviet Russia offered military aid, which the Lithuanians declined. Polish cavalry broke Lithuanian defense lines and on November 18 reached Kavarskas and continued toward Kaunas. However, on November 19–21, the Lithuanian main forces pushed Żeligowski's main forces back near Giedraičiai and Širvintos.[21] Łossowski described the battle as a local skirmish of minor importance[20][22] despite the Lithuanians dispersing the whole Polish Grodno Regiment.[citation needed]
Both sides were now exhausted. With the help of the League of Nations, on November 20 a ceasefire was negotiated, to take effect on November 21, 1920, at 9 o'clock in the morning; until then, both sides agreed to take no offensive actions. The Lithuanian 7th Infantry Regiment counterattacked at Giedraičiai on the night of November 20–21, just before the ceasefire was to go into effect, persisting even after the ceasefire (until 14:00); this offensive gained Giedraičiai for the Lithuanians. The Lithuanian forces stopped after a strong-worded request from the League of Nations, and a truce was finally signed on November 29.[23][24]
It was at this time that the close ally of Piłsudski, Michał Pius Römer, a leader of the Krajowcy movement, broke with Pilsudski and made the decision to side with the re-established Lithuanian Republic, even though Piłsudski offered to appoint him Prime Minister of the Republic of Central Lithuania.
Aftermath
[edit]
Żeligowski became the new state's de facto military dictator, but after elections he relinquished his powers to the newly elected Sejm of Central Lithuania. His military units became the Army of Central Lithuania.

In 1922, the Sejm voted for their state's incorporation into Poland.[25] In 1923, soon after the League of Nations had recognized the existing situation and accepted the Polish-Lithuanian border on March 15, Piłsudski on August 24, 1923 would publicly admit that Żeligowski's Mutiny had in fact been a pre-planned operation carried out with his knowledge and support.[11]
Despite Poland's claim to Vilnius, the League of Nations asked Poland to withdraw. Poland declined. In principle, British and French troops could have been asked to enforce the League's decision. France, however, did not wish to antagonize Poland, a possible ally in a future war against Germany, and Britain was not prepared to act alone. Thus, the Poles were able to keep Vilnius, where a provisional government (Komisja Rządząca Litwy Środkowej, the Central Lithuanian Governing Commission) was formed. Soon parliamentary elections were held and the Sejm of Central Lithuania voted on February 20, 1922, for incorporation into Poland as the capital of a Wilno Voivodeship. The elections were not recognized by the League of Nations.
The League of Nations Conference of Ambassadors accepted the status quo in 1923, but the Vilnius region remained in dispute between Poland and Lithuania (the latter still treated Vilnius as its constitutional capital and the capital of the Vilnius region).
In Poland, the Mutiny was supported by some groups, such as the Christian Democrats and the left, but criticized by the right-wing National Democrats.[why?]
The coup resulted in a serious rift between Pilsudski and Ignacy Jan Paderewski, who had played a major role in creating international support for the independence of Poland.[26] According to historian Timothy Snyder, the annexation of Vilnius by Poles pushed Lithuanian politicians from political towards ethnic understanding of the nation and gave arguments to radical politicians in Lithuania and also in Poland.[27]
Lithuania refused to recognize Central Lithuania. Polish-Lithuanian relations began to normalize after League of Nations negotiations in 1927, but it was not until the 1938 ultimatum issued by Poland that Lithuania was forced to establish diplomatic relations with Poland and thus de facto accept its neighbor's borders.
The Polish-Lithuanian conflict, however, left worsened relations between the two countries for decades to come.[11]
World War II
[edit]In September 1939, Poland's Eastern Borderlands, including Vilnius, was occupied by the Soviet Union. With the signing of the Soviet–Lithuanian Mutual Assistance Treaty, Vilnius was given to Lithuania, which it ruled from October 27, 1939 until June 15, 1940, when the whole country was occupied by the Soviet Union. In 1945, with the Polish–Soviet border agreement of August 1945, Vilnius was confirmed to be part of Lithuania, then under Soviet occupation.
See also
[edit]Sources
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Vitkus, Gediminas (2014). Lietuvos karai: Lietuvos XIX-XX a. nacionalinių karų sisteminė kiekybinė analizė (in Lithuanian). Generolo Jono Žemaičio Lietuvos karo akademija. pp. 197, 199. ISBN 978-609-437-250-6.
- ^ Allcock, John B. (1992). Border and territorial disputes. Gale Group. p. 146.
- ^ Snyder 2003, p. 78.
- ^ Miniotaitė, Gražina (1998). "7: Lithuania". In Mouritzen, Hans (ed.). Bordering Russia: Theory and Prospects for Europe's Baltic Rim. Ashgate Publishing. ISBN 9780429862885.
- ^ Łossowski 1995, pp. 112–116.
- ^ Łossowski 1995, pp. 112–128.
- ^ Eberhardt 2003, p. 39.
- ^ Michael MacQueen, The Context of Mass Destruction: Agents and Prerequisites of the Holocaust in Lithuania, Holocaust and Genocide Studies, Volume 12, Number 1, pp. 27–48, 1998, [1]
- ^ Balkelis, Tomas (2020). "A Dirty War: The Armed Polish-Lithuanian Conflict and its Impact on Nation-Making in Lithuania, 1919–23" (PDF). Acta Poloniae Historica (121): 238.
- ^ Łossowski 1995, p. 68.
- ^ a b c d Bojtár 1999, p. 202.
- ^ Łukowski & Stolarski 1994.
- ^ a b c Łossowski 1995, pp. 161–166.
- ^ Snyder 2003.
- ^ a b Butkus, Zenonas; Aleknavičė, Karolina. "Stebuklas prie Vyslos: kaip 1920 metais lenkai sutriuškino bolševikus". 15min.lt (in Lithuanian). Retrieved 2022-03-29.
- ^ a b Łossowski 1995, pp. 175–179.
- ^ Przemysław Hauser, "Walka o granice" [The fight over the borders], in "Polska XX wieku 1914–2003" [20th Century Poland: 1914–2003], pp. 27–29. Horyzont/Wydawnictwo Dolnośląskie, Warszawa-Wrocław 2004, ISBN 83-7311-797-0.
- ^ a b Łossowski 1995, pp. 179–185.
- ^ a b Jerzy J. Lerski, Historical Dictionary of Poland, 966–1945, 1996, Google Print, p. 309.
- ^ a b Łossowski 1991, p. 110.
- ^ Čepėnas 1986, p. 634.
- ^ Łossowski 1995, p. 217.
- ^ Text in League of Nations Treaty Series, vol. 9, pp. 64–67
- ^ Łossowski 1995, pp. 216–218.
- ^ Srebrakowski 1993.
- ^ "Paderewksi's Trip Off; Decides Not to Beard President Pilsudski Over Vilna Coup" (PDF). The New York Times. October 18, 1920. Retrieved May 5, 2009.
- ^ Snyder 2003, p. 69.
Bibliography
[edit]- Bojtár, Endre (1999). Foreword to the Past: A Cultural History of the Baltic People. Central European University Press. ISBN 963-9116-42-4.
- Čepėnas, Pranas (1986). Naujųjų laikų Lietuvos istorija (in Lithuanian). Chicago: Dr. Griniaus fondas.
- Snyder, Timothy (2003). The Reconstruction of Nations: Poland, Ukraine, Lithuania, Belarus, 1569–1999. New Haven: Yale University Press. ISBN 978-0-300-10586-5.
Polish sources
[edit]- Eberhardt, Piotr (2003). Ethnic Groups and Population Changes in Twentieth-Century Central-Eastern Europe: History, Data, Analysis. M.E. Sharpe.
- Łossowski, Piotr (1991). Polska-Litwa: Ostatnie sto lat [Poland and Lithuania: the Last Hundred Years] (in Polish). Warsaw: Wydawnictwo Oskar.
- Łossowski, Piotr (1995). Konflikt polsko-litewski 1918–1920 [The Polish-Lithuanian Conflict, 1918–1920] (in Polish). Warsaw: Książka i Wiedza. ISBN 83-05-12769-9.
- Łukowski, Grzegorz; Stolarski, Rafal E. (1994). Walka o Wilno: Z dziejów Samoobrony Litwy i Bialorusi, 1918–1919 [The Struggle for Vilnius: the History of the Self-Defense of Lithuania and Belarus, 1918–1919] (in Polish). Adiutor. ISBN 83-900085-0-5.
- Srebrakowski, Aleksander (1993). "Sejm Wileński 1922 roku: Idea i jej realizacja". Historia (in Polish). XCIX. Wrocław.
