Wasatch Fault
| Wasatch Fault | |
|---|---|
| Country | USA |
| State | Utah |
| Characteristics | |
| Segments | 10 |
| Length | 390km |
| Displacement | 0.8-1.2mm/yr |
| Tectonics | |
| Status | active |
| Earthquakes | 2020 Salt Lake City earthquake |
| Type | normal fault |

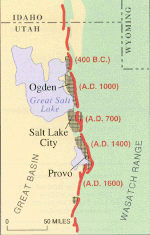

The Wasatch Fault is an active fault located primarily on the western edge of the Wasatch Mountains in the U.S. states of Utah and Idaho. The fault is about 240 miles (390 kilometres) long, stretching from southern Idaho, through northern Utah, before terminating in central Utah near the town of Fayette. The fault is made up of ten segments, five of which are considered active.[1] On average the segments are approximately 25 miles (40 kilometres) long, each of which can independently produce earthquakes as powerful as local magnitude 7.5.[2] The five active segments from north to south are called the Brigham City Fault Segment, the Weber Fault Segment, the Salt Lake City Fault Segment, the Provo Fault Segment and the Nephi Fault Segment.[citation needed]
The Wasatch Fault is a normal (vertical motion) fault which forms the eastern boundary of the Basin and Range geologic province which comprises the geographic Great Basin. The Wasatch Mountains have been uplifted and tilted to the east by movement of the fault.[3] The average vertical displacement rate of the fault over its history is approximately 0.8–1.2 mm/yr.[4]
Geological history
[edit]During the past 10,000 years, major earthquakes (magnitude 7.0 or greater) occur about every 900–1,300 years along any one of the five central segments of the Wasatch Fault. However, the average time-span between earthquakes along the entirety of the central segments is about 300 years.[5] The segment that underlies Salt Lake City produced a major earthquake approximately 1,200–1,300 years ago, the Weber, Provo, and Nephi segments each produced one about 200–700 years ago and the Brigham City fault segment has not produced a major earthquake in about 2,200–2,800 years.[3]
Earthquake assessment
[edit]Statistically, the Wasatch Fault is overdue for another major earthquake. Experts have given a 57% probability of an earthquake magnitude 6.0 or greater occurring within the next 50 years. However, statistical frequency does not necessarily imply periodic behavior, though it can serve as a good indicator.[6] Liquefaction due to a strong earthquake is of particular concern because many highly populated areas along the Wasatch Front lie on soft lake sediments, remnants of Lake Bonneville.[7][8]
A strong earthquake on the Wasatch Fault could trigger landslides, cause mass liquefaction, and flooding of low-lying areas forming near lakes due to subsidence and tilting. The quake may also rupture the surface causing displacement of up to 20 feet (6.1 m), and severely damage gas, electric, water, communication, and transportation lifelines.[9] A report released by Bob Carey of Utah's Office of Emergency Services and published by the Deseret News in April 2006 predicts that a strong earthquake occurring in Salt Lake City could kill up to 6,200 people, injure 90,000, and cause US$40 billion in economic losses. Due to the earthquake danger not being well known when many structures were built in the area, at least 42% of the buildings along the Wasatch Front are at risk of moderate to severe damage in the event of a strong earthquake. Many buildings, such as hospitals and schools, are located directly atop the Wasatch Fault. Approximately 50% of hospital beds in Salt Lake City are at risk.[10] Currently, about 80% of Utah's population live along the Wasatch Fault, representing the largest earthquake threat in the interior Western U.S.[11][1]
On the west end of Salt Lake Valley is another fault zone called the West Valley fault zone that spans 9 miles (16 km) north-northwest. Recent trench studies have shown that the West Valley fault tends to rupture simultaneously with the Wasatch Fault, compounding issues such as liquefaction, landslides and flooding. The two faults likely converge into a single fault deep underneath Salt Lake Valley.[11][12] On March 18, 2020, a 5.7 magnitude earthquake occurred just north of Magna, causing moderate damage.[13] In March 2021, a new study based on evaluations of the 2020 earthquake and aftershocks determined that the Wasatch Fault undercuts the Salt Lake Valley at a shallower depth than previously thought. This means that a large earthquake on the Salt Lake section of the Wasatch Fault would likely cause more ground shaking and greater damage than previously expected.[14]
Public awareness
[edit]As awareness has increased since the 1980s, many key structures in the region have been undergoing extensive seismic retrofitting, reservoirs on the fault have been drained, and development in at-risk areas curtailed.[15][16] The Utah Earthquake Program (a partnership between The Utah Geological Survey, University of Utah Seismograph Stations, and Utah Division of Emergency Management) has been actively working to educate communities in Utah, conduct research, and investigate technologies that can mitigate the damage caused by a strong earthquake along the Wasatch Fault.[17] Salt Lake City is currently utilizing federal grant funds to run a Fix the Bricks program targeting seismic safety upgrades in unreinforced masonry buildings.[18]
References
[edit]- ^ a b "wasatch fault zone: Topics by Science.gov". science.gov. Retrieved 2019-02-28.
- ^ "Surficial geologic map of the Wasatch fault zone, eastern part of Utah Valley, Utah County and parts of Salt Lake and Juab counties, Utah" (PDF).
- ^ a b "How Big and How Frequent Are Earthquakes on the Wasatch Fault?". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2020-03-19.
- ^ Jewell, Paul W.; Bruhn, Ronald L. (2013). "Evaluation of Wasatch fault segmentation and slip rates using Lake Bonneville shorelines". Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. 118 (5): 2528–2543. Bibcode:2013JGRB..118.2528J. doi:10.1002/jgrb.50174.
- ^ "Large Earthquakes on the Wasatch Fault". utahdnr.maps.arcgis.com. Retrieved 2019-02-27.
- ^ "Reports | U of U Seismograph Stations". Retrieved 2019-02-26.
- ^ Schuske, Kim. "Explore Utah Science – Earthquake Risk in the Salt Lake Valley". exploreutahscience.org. Retrieved 2019-02-26.
- ^ "Liquefaction – Utah Geological Survey". Retrieved 2019-02-26.
- ^ "Earthquake Hazard & Safety in Utah" (PDF).
- ^ Deseret News article
- ^ a b "Salt Lake City Could See Bigger Earthquakes".
- ^ "Salt Lake City Earthquake Risk May Be Higher Due To Connected Fault Zones, Geologists Find".
- ^ "5.7 magnitude earthquake in Utah knocks out power to thousands and diverts flights". Retrieved 2020-03-22.
- ^ "'Curved' Wasatch fault may be even more destructive and deadly than previously thought". Retrieved 2021-03-22.
- ^ Utah Geological Survey
- ^ "Utah Earthquake Program". DPS – Emergency Management. Retrieved 2019-02-26.
- ^ "Utah Seismic Safety Commission". ussc.utah.gov. Retrieved 2019-02-26.
- ^ "Salt Lake City Emergency Management". slc.gov. Retrieved 2020-01-16.
