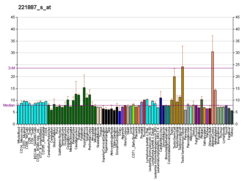
DFNB31
Appearance
(Redirected from WHRN)
Whirlin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DFNB31 gene.[5][6][7]
In rat brain, WHRN interacts with a calmodulin-dependent serine kinase, CASK, and may be involved in the formation of scaffolding protein complexes that facilitate synaptic transmission in the central nervous system (CNS).[8] Mutations in this gene, also known as WHRN, cause autosomal recessive deafness.[7]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000095397 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000039137 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Mburu P, Mustapha M, Varela A, Weil D, El-Amraoui A, Holme RH, Rump A, Hardisty RE, Blanchard S, Coimbra RS, Perfettini I, Parkinson N, Mallon AM, Glenister P, Rogers MJ, Paige AJ, Moir L, Clay J, Rosenthal A, Liu XZ, Blanco G, Steel KP, Petit C, Brown SD (Aug 2003). "Defects in whirlin, a PDZ domain molecule involved in stereocilia elongation, cause deafness in the whirler mouse and families with DFNB31". Nat Genet. 34 (4): 421–8. doi:10.1038/ng1208. PMID 12833159. S2CID 39603776.
- ^ Ebermann I, Scholl HP, Charbel Issa P, Becirovic E, Lamprecht J, Jurklies B, Millan JM, Aller E, Mitter D, Bolz H (Mar 2007). "A novel gene for Usher syndrome type 2: mutations in the long isoform of whirlin are associated with retinitis pigmentosa and sensorineural hearing loss". Hum Genet. 121 (2): 203–11. doi:10.1007/s00439-006-0304-0. PMID 17171570. S2CID 22632047.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: DFNB31 deafness, autosomal recessive 31".
- ^ Yap CC, Liang F, Yamazaki Y, et al. (2003). "CIP98, a novel PDZ domain protein, is expressed in the central nervous system and interacts with calmodulin-dependent serine kinase". J. Neurochem. 85 (1): 123–34. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01647.x. PMID 12641734. S2CID 46526881.
Further reading
[edit]- Holm G, Björkholm M, Mellstedt H, Johansson B (1976). "Cytotoxic activity of lymphocytes from patients with Hodgkin's disease". Clin. Exp. Immunol. 21 (3): 376–83. PMC 1538308. PMID 1081933.
- Nagase T, Kikuno R, Ishikawa K, et al. (2000). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XVII. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Res. 7 (2): 143–50. doi:10.1093/dnares/7.2.143. PMID 10819331.
- Mustapha M, Chouery E, Chardenoux S, et al. (2002). "DFNB31, a recessive form of sensorineural hearing loss, maps to chromosome 9q32-34". Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 10 (3): 210–2. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200780. PMID 11973626.
- Nakayama M, Kikuno R, Ohara O (2003). "Protein–Protein Interactions Between Large Proteins: Two-Hybrid Screening Using a Functionally Classified Library Composed of Long cDNAs". Genome Res. 12 (11): 1773–84. doi:10.1101/gr.406902. PMC 187542. PMID 12421765.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Kimura K, Wakamatsu A, Suzuki Y, et al. (2006). "Diversification of transcriptional modulation: Large-scale identification and characterization of putative alternative promoters of human genes". Genome Res. 16 (1): 55–65. doi:10.1101/gr.4039406. PMC 1356129. PMID 16344560.
- van Wijk E, van der Zwaag B, Peters T, et al. (2006). "The DFNB31 gene product whirlin connects to the Usher protein network in the cochlea and retina by direct association with USH2A and VLGR1". Hum. Mol. Genet. 15 (5): 751–65. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddi490. PMID 16434480.