Volsci
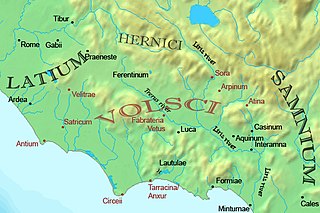
The Volsci (UK: /ˈvɒlskiː/, US: /ˈvɔːl-, ˈvɒlsaɪ, -siː/,[1][2][3] Latin: [ˈwɔɫskiː]) were an Italic tribe, well known in the history of the first century of the Roman Republic. At the time they inhabited the partly hilly, partly marshy district of the south of Latium, bounded by the Aurunci and Samnites on the south, the Hernici on the east, and stretching roughly from Norba and Cora in the north to Antium in the south.[4] Rivals of Rome for several hundred years, their territories were taken over by and assimilated into the growing republic by 304 BC.[5][6] Rome's first emperor Augustus was of Volscian descent.
Description by the ancient geographers
[edit]Strabo says that the Volsci formed a sovereign state near the site of Rome.[7] It was placed in the Pomentine plain, between the Latins and the Pontine marshes, which took their name from the plain.
The Volsci were divided in Antiates Volsci (capital Antium) on the Tyrrhenian coast,[8] and Ecetran Volsci (Ecetra) in the hinterland.[9]
Language
[edit]The Volsci spoke Volscian, a Sabellic Italic language, which was closely related to Oscan and Umbrian, and more distantly to Latin.[10]
In the Volscian territory lay the little town of Velitrae (modern Velletri), home of the ancestors of Caesar Augustus. From this town comes an inscription dating probably from early in the 3rd century BC; it is cut upon a small bronze plate (now in the Naples Museum), which must have once been fixed to some votive object, and dedicated to the god Declunus (or the goddess Decluna).[4]
Conflict with ancient Rome
[edit]The Volsci were among the most dangerous enemies of ancient Rome, and frequently allied with the Aequi, whereas their neighbors, the Hernici, were allied with Rome after 486 BC.[11][4]
According to the semi-legendary history of early Rome, its seventh and last king, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was the first to go to war against the Volsci, commencing two centuries of conflict between the two states.[8]
Gaius Marcius Coriolanus, the legendary Roman warrior, earned his cognomen after capturing the Volscian town of Corioli in 493 BC. The reputed rise and fall of this Roman hero is chronicled in Plutarch's Parallel Lives, which served as the basis for the Shakespeare play, Coriolanus.[12]
However, if Livy's account of the war between Rome and Clusium is accurate, it would seem that the relationship between Rome and the Volsci was not always hostile. Livy writes that at the approach of the Clusian army in 508 BC, with the prospect of a siege, the Roman senate arranged for the purchase of grain from the Volsci to feed the lower classes of Rome.[13]
Prominent Volsci
[edit]- Camilla in Virgil's Aeneid, a Volscian Warrior Maiden (like the legendary Amazons).
- Attius Tullus Aufidius, leader of the Volsci during the Roman–Volscian wars.
Prominent Romans of Volscian ancestry
[edit]Roman Gentes of Volscian origin
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Volsci". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (5th ed.). HarperCollins. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ^ "Volsci". Collins English Dictionary. HarperCollins. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ^ "Volsci". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 31 May 2019.
- ^ a b c One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Conway, Robert Seymour (1911). "Volsci". In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 28 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 197–198.
- ^ Smith, William. "VOLSCI". perseus.tufts.edu.
- ^ "Volsci". britannica.
- ^ Strabo. "Book 5 Chapter 3". Geography. Tufts University, Perseus Digital Library.
- ^ a b Livy Ab urbe condita 6.6; 6.9; 8.1
- ^ Devoto, Giacomo (1937). "Volsci". Istituto della Enciclopedia Italiana (in Italian).
- ^ James Clackson; Geoffrey Horrocks (23 May 2011). The Blackwell History of the Latin Language. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 59–. ISBN 978-1-4443-9358-3.
- ^ Nathan Rosenstein; Robert Morstein-Marx (7 September 2011). A Companion to the Roman Republic. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 279–. ISBN 978-1-4443-5720-2.
- ^ William Shakespeare (1969). Coriolanus. CUP Archive. ISBN 978-0-521-07529-9.
- ^ Livy Ab urbe condita 2. 9
Further reading
[edit]- Coarelli, Filippo. "Roma, i Volsci e il Lazio antico". In: Crise et transformation des sociétés archaïques de l'Italie antique au Ve siècle av. JC. In: Actes de la table ronde de Rome (19-21 novembre 1987). Rome: École Française de Rome, 1990. pp. 135–154. (Publications de l'École française de Rome, 137) [www.persee.fr/doc/efr_0000-0000_1990_act_137_1_3901]
