Vestibular aqueduct
| Vestibular aqueduct | |
|---|---|
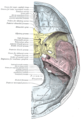
 Interior of right osseous labyrinth. | |
 The cochlea and vestibule, viewed from above. (Aquaeductus vestibuli labeled at bottom right.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | aquaeductus vestibuli |
| MeSH | D014723 |
| TA98 | A15.3.03.057 |
| TA2 | 6940 |
| FMA | 77821 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
At the posterior lateral wall of the temporal bone is the vestibular aqueduct, which extends to the posterior surface of the petrous portion of the temporal bone.[1] The vestibular aqueduct parallels the petrous apex, in contrast to the cochlear aqueduct, which lies perpendicular to the petrous apex.
It transmits a small vein, and contains a tubular prolongation of the membranous labyrinth, the ductus endolymphaticus, which ends in a cul-de-sac, the endolymphatic sac, between the layers of the dura mater within the cranial cavity.
Pathology
[edit]Enlargement of the vestibular aqueduct to greater than 2 mm is associated with enlarged vestibular aqueduct syndrome, a disease entity that is associated with one-sided hearing loss in children. The diagnosis can be made by high resolution CT or MRI, with comparison to the adjacent posterior semicircular canal. If the vestibular aqueduct is larger in size, and the clinical presentation is consistent, the diagnosis can be made. Treatment is with mechanical hearing implants. There is an association with Pendred syndrome and incomplete cochlear partition (so called "Mondini dysplasia").[2]
Additional images
[edit]-
Base of the skull. Upper surface.
-
Temporal bone
References
[edit]![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1048 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1048 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ "Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome".
- ^ Atkin, J. S.; Grimmer, J. F.; Hedlund, G; Park, A. H. (2009). "Cochlear abnormalities associated with enlarged vestibular aqueduct anomaly". International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology. 73 (12): 1682–5. doi:10.1016/j.ijporl.2009.08.028. PMID 19775757.