ε-Viniferin
Appearance
(Redirected from Trans-ε-viniferin)
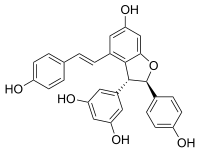 (−)-trans-ε-Viniferin
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
5-{(2R,3R)-6-Hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-[(E)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethen-1-yl]-2,3-dihydro-1-benzofuran-3-yl}benzene-1,3-diol | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C28H22O6 | |
| Molar mass | 454.478 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
ε-Viniferin is a naturally occurring phenol, belonging to the stilbenoids family. It is a resveratrol dimer.
It is found in Vitis vinifera[4] grapevines,[5] in wines,[6] in the Oriental medicinal plant Vitis coignetiae and in the stem bark of Dryobalanops aromatica.[7]
Cis-epsilon-viniferin can be found in Paeonia lactiflora.[3]
It shows a human cytochrome P450 enzymes inhibition activity.[8]
Glycosides
[edit]Diptoindonesin A is a C-glucoside of ε-viniferin.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Yáñez, M.; Fraiz, N.; Cano, E.; Orallo, F. (2006). "(−)-Trans-ε-viniferin, a polyphenol present in wines, is an inhibitor of noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake and of monoamine oxidase activity". European Journal of Pharmacology. 542 (1–3): 54–60. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.06.005. PMID 16828740.
- ^ Cornacchione, S.; Sadick, N. S.; Neveu, M.; Talbourdet, S.; Lazou, K.; Viron, C.; Renimel, I.; De Quéral, D.; Kurfurst, R.; Schnebert, S.; Heusèle, C.; André, P.; Perrier, E. (2007). "In vivo skin antioxidant effect of a new combination based on a specific Vitis vinifera shoot extract and a biotechnological extract". Journal of Drugs in Dermatology. 6 (6 Suppl): s8–13. PMID 17691204.
- ^ a b Kim, H. J.; Chang, E. J.; Cho, S. H.; Chung, S. K.; Park, H. D.; Choi, S. W. (2002). "Antioxidative Activity of Resveratrol and Its Derivatives Isolated from Seeds of Paeonia lactiflora". Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. 66 (9): 1990–3. doi:10.1271/bbb.66.1990. PMID 12400706. S2CID 24367582.
- ^ Privat, C.; Telo, J. O. P.; Bernardes-Genisson, V.; Vieira, A.; Souchard, J. P.; Nepveu, F. O. (2002). "Antioxidant Properties oftrans-ε-Viniferin As Compared to Stilbene Derivatives in Aqueous and Nonaqueous Media". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 50 (5): 1213–1217. doi:10.1021/jf010676t. PMID 11853506.
- ^ Langcake, P.; Pryce, R. J. (1977). "A new class of phytoalexins from grapevines". Experientia. 33 (2): 151–152. doi:10.1007/BF02124034. PMID 844529. S2CID 34370048.
- ^ Vitrac, X.; Bornet, A. L.; Vanderlinde, R.; Valls, J.; Richard, T.; Delaunay, J. C.; Mérillon, J. M.; Teissédre, P. L. (2005). "Determination of Stilbenes (δ-viniferin, trans-astringin, trans-piceid, cis- and trans-resveratrol, ε-viniferin) in Brazilian Wines". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 53 (14): 5664–5669. doi:10.1021/jf050122g. PMID 15998130.
- ^ Wibowo, A.; Ahmat, N.; Hamzah, A. S.; Sufian, A. S.; Ismail, N. H.; Ahmad, R.; Jaafar, F. M.; Takayama, H. (2011). "Malaysianol A, a new trimer resveratrol oligomer from the stem bark of Dryobalanops aromatica". Fitoterapia. 82 (4): 676–681. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2011.02.006. PMID 21338657.
- ^ Piver, B.; Berthou, F. O.; Dreano, Y.; Lucas, D. L. (2003). "Differential inhibition of human cytochrome P450 enzymes by ε-viniferin, the dimer of resveratrol: Comparison with resveratrol and polyphenols from alcoholized beverages". Life Sciences. 73 (9): 1199–1213. doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(03)00420-X. PMID 12818727.
External links
[edit] Media related to Epsilon-Viniferin at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Epsilon-Viniferin at Wikimedia Commons- e-viniferin on phenol-explorer.eu
